Quadruple vaccine for poultry and preparation method and application thereof
A technology for poultry and vaccines, which is applied in the field of quadruple vaccines for poultry and its preparation, can solve the problems of aggravating stress and disease susceptibility, increasing manpower and material resources, and reducing the production performance of chicken flocks, and achieves good antigenicity and safety. The effect of high sex and long duration of immune protection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
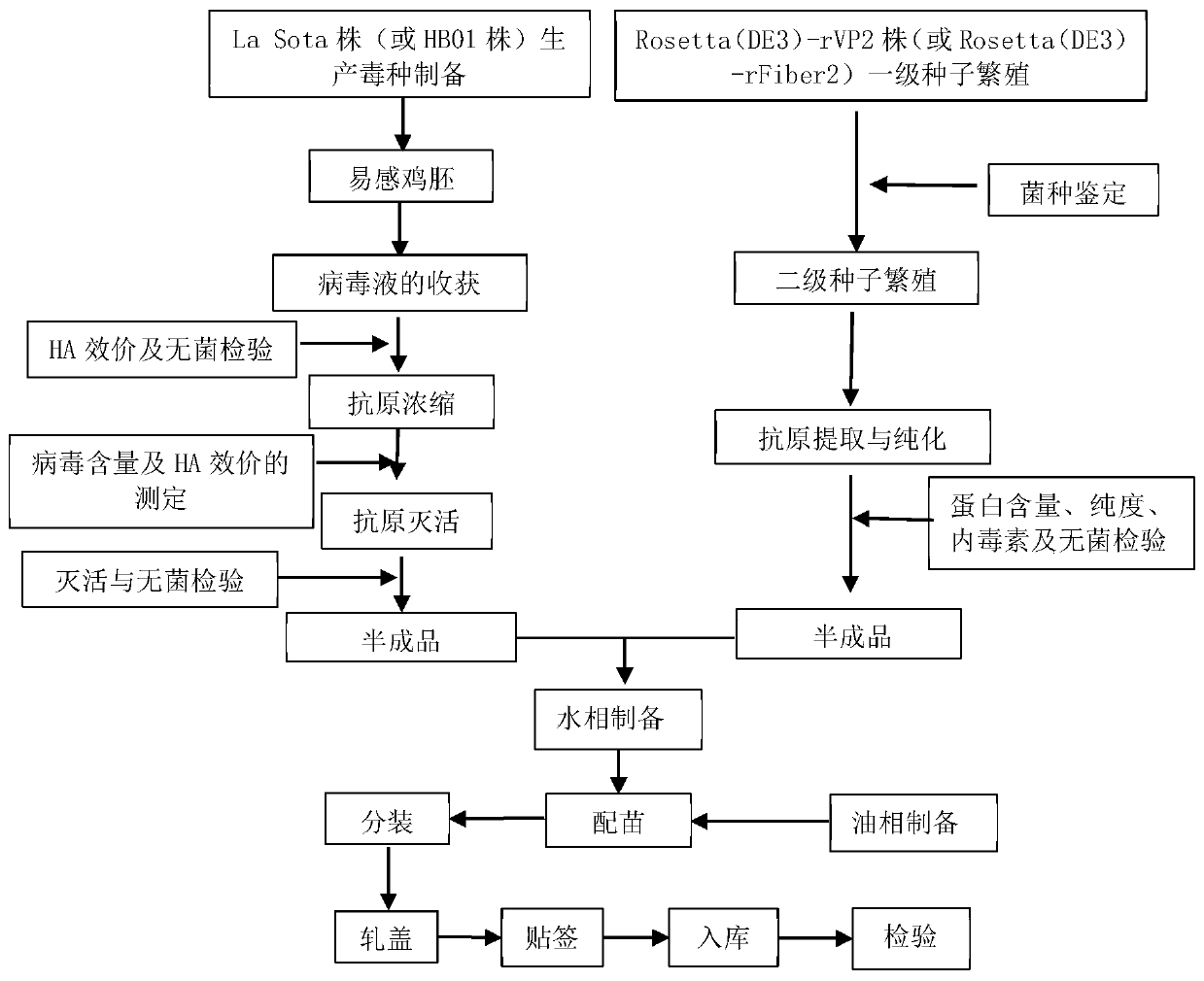
[0037] This embodiment provides the preparation method of chicken Newcastle disease, avian influenza, infectious bursal disease and avian adenovirus disease quadruple vaccine, figure 1 Be the flowchart of this preparation method, concrete steps comprise:
[0038] (1) Sources of poisonous (bacteria) species used in production
[0039] This product is produced with chicken Newcastle disease virus La Sota strain, H9 subtype avian influenza virus HB01 strain, recombinant Escherichia coli Rosetta (DE3)-rVP2 strain expressing infectious bursal disease virus VP2 protein, expressing avian adenovirus (group I, 4 Type) Fiber2 protein recombinant Escherichia coli Rosetta (DE3)-rFiber2 strains were identified, kept and supplied by Wuhan Keqian Biotechnology Co., Ltd.
[0040] Among them, the preservation number of the H9 subtype avian influenza virus HB01 strain is CCTCC NO: V202017, and it was preserved in the Chinese Type Culture Collection Center of Wuhan University on January 07, 202...
Embodiment 2
[0074] In this embodiment, the quadruple vaccine prepared in Example 1 is tested, and the specific steps are as follows:
[0075] 1 character
[0076] 1.1 Appearance Milky white homogeneous emulsion.
[0077] 1.2 Dosage form It is water-in-oil type. Take a clean straw, suck a small amount of vaccine and drop it in cold water. Except for the first drop that diffuses in the form of cloud, each subsequent drop should not spread.
[0078] 1.3 Stability Take 10ml of the vaccine and put it into a centrifuge tube, centrifuge at 3000r / min for 15min, the water precipitated at the bottom of the tube should not be more than 0.5ml.
[0079] 1.4 Viscosity is measured according to the appendix of the current "Chinese Veterinary Pharmacopoeia", and it should meet the regulations.
[0080] 2 Loading volume inspection: Measure according to the appendix of the current "Chinese Veterinary Pharmacopoeia", and it should meet the regulations.
[0081] 3 Sterility test According to the current "...
Embodiment 3
[0091] 1. Sequencing and sequence analysis of H9 subtype avian influenza virus HB01 strain
[0092] According to the genome sequence of the avian influenza virus in the GeneBank database, primers were designed to amplify the HA and NA gene fragments of the HB01 strain. The primer sequences are as follows:
[0093] HA-F: 5'-GGGAGCAAAAGCAGGGG-3' (SEQ ID NO.1);
[0094] HA-R: 5'-GGAGTAGAAACAAGGGTGTTTT-3' (SEQ ID NO.2);
[0095] NA-F: 5'-GGGAGCAAAAGCAGGAGT-3' (SEQ ID NO.3);
[0096] NA-R: 5'-GGAGTAGAAACAAGGAGTTTTTT-3' (SEQ ID NO. 4).
[0097] After sequencing the HA and NA gene fragments, the genetic evolution information of the HA and NA genes were analyzed by MEGA6 software.
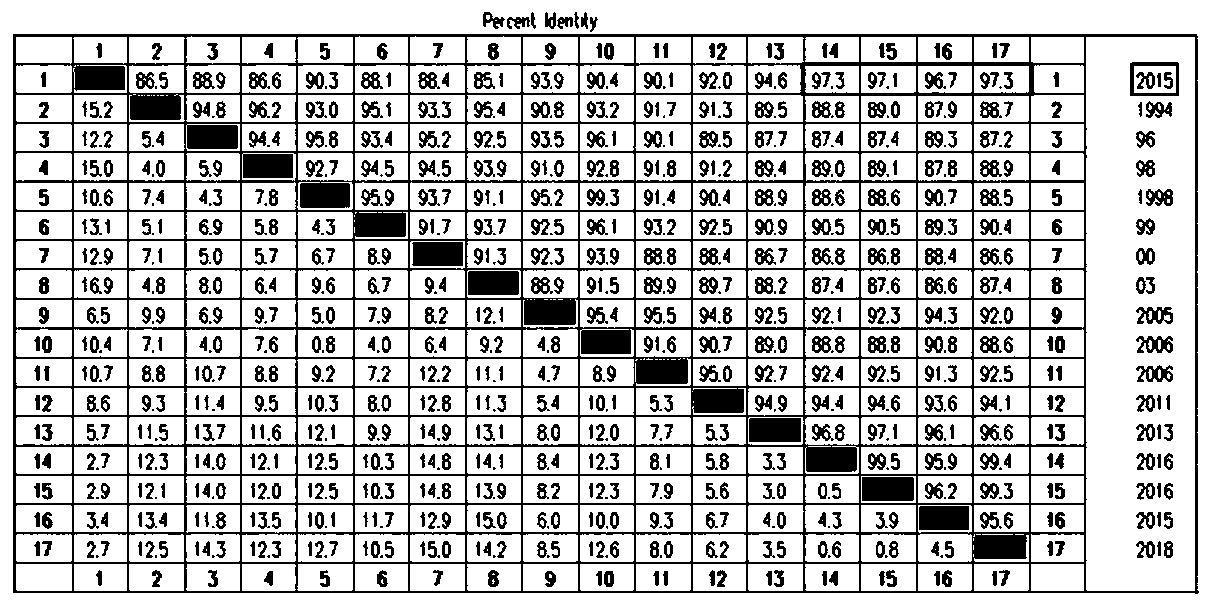
[0098] Comparing the HA gene sequence of the HB01 strain with the nucleotide sequences of 16 representative H9 subtype avian influenza virus reference strains registered on GenBank, it can be seen that the homology between the HB01 strain and the early epidemic strains is low, and it is similar to The ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com