Amidase mutant and application thereof in catalytic synthesis of 2-chloronicotinic acid
A mutant, amidase technology, applied in the field of enzyme engineering, can solve the problems of low yield, heavy production process pollution, lengthy synthesis steps and the like, and achieve the effect of improving the activity of the parent
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] Example 1. Induction and expression purification of amidase
[0030] Step 1: Cultivation of Recombinant Bacteria
[0031] Inoculate 10 μL of the preserved bacterial solution in glycerol tubes into 10 mL of liquid LB medium (containing Kan 50 μg / mL), incubate at 37°C and 200 r / min for 12 hours, then transfer to 100 mL of fresh LB medium containing Kan at 2% inoculum size to continue Grow to OD 600 When it reaches 0.6, add IPTG with a final concentration of 0.1 mM, and induce culture at 28° C. overnight (12 h). After the cultivation, the cells were collected by centrifugation and washed twice with 0.85% saline.
[0032] Step 2: Purification of amidase
[0033] (1) Take 5 g of wet bacteria and suspend them in 50 mL of Tris-HCl buffer (20 mM, pH 8.0), oscillate and shake well, and use an ultrasonic cell disruptor to break the cells (crushing power 40 W, each ultrasonic work 5 s, interval 5 s, total 99 loops);
[0034] (2) After the crushing is completed, take the crush...
Embodiment 2
[0042] Example 2. Site-directed saturation mutation and screening of amidase
[0043] Description of site-directed saturation mutation technology reference (Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2014,98(6):2473-2483), reference of high-throughput screening model for positive mutants (CN100370034; Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2007,74:256-262) description of. The specific process is as follows:
[0044] Step 1: Site-directed mutagenesis
[0045] Carry out saturation mutation at the 378th, 402 and 403 amino acids in the amino acid sequence of the parent pantoea amidase mutant G175A, and design primers A378, V402 and L403 (see Table 1) to clone the pantoea amidase mutation The plasmid pET28-G175A encoding gene of body G175A was used as a template for full plasmid amplification.
[0046] Table 1 Design table of primers for site-directed saturation mutagenesis
[0047]
[0048] Note: N=A / G / C / T, K=G / T, M=A / C.
[0049] The PCR system is: 2×phanta Max buffer 25 μL,...
Embodiment 3
[0055] Example 3. Re-screening of amidase positive mutants
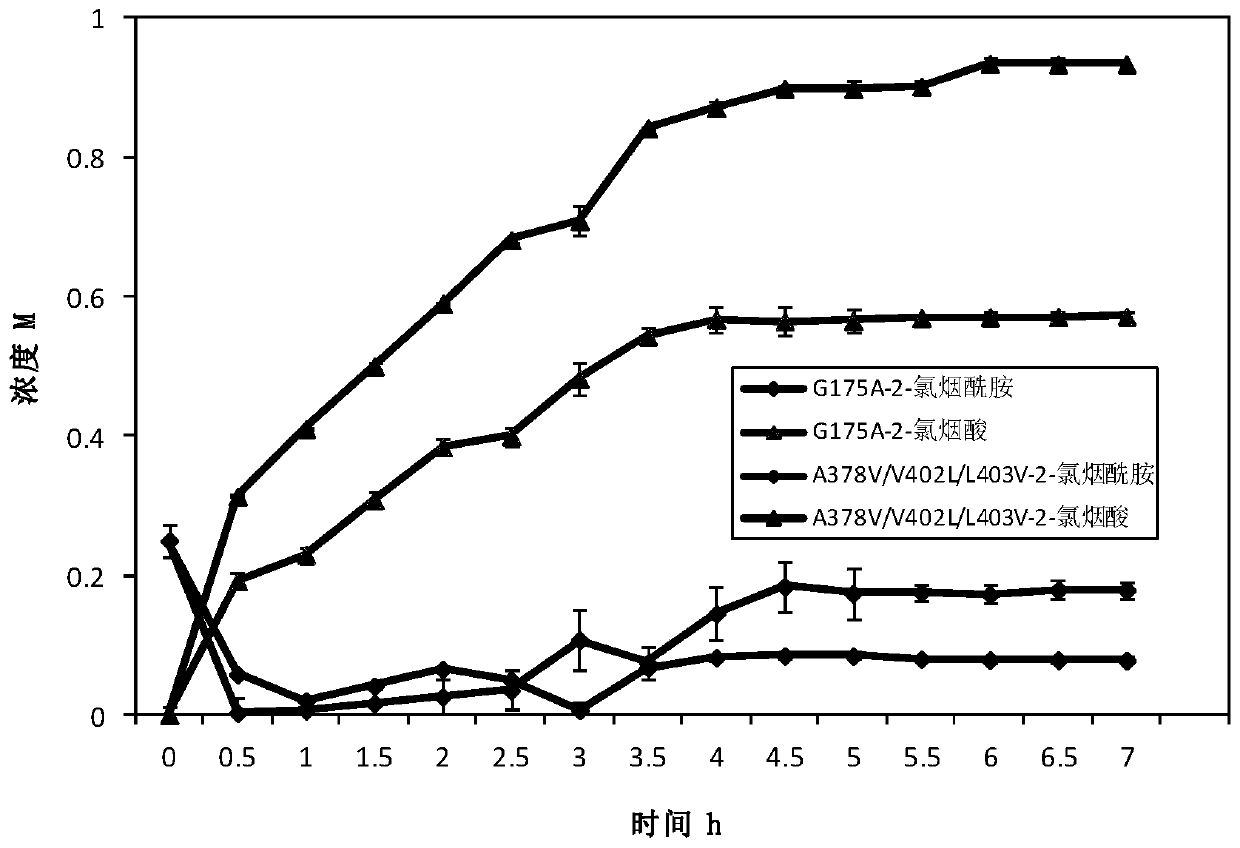
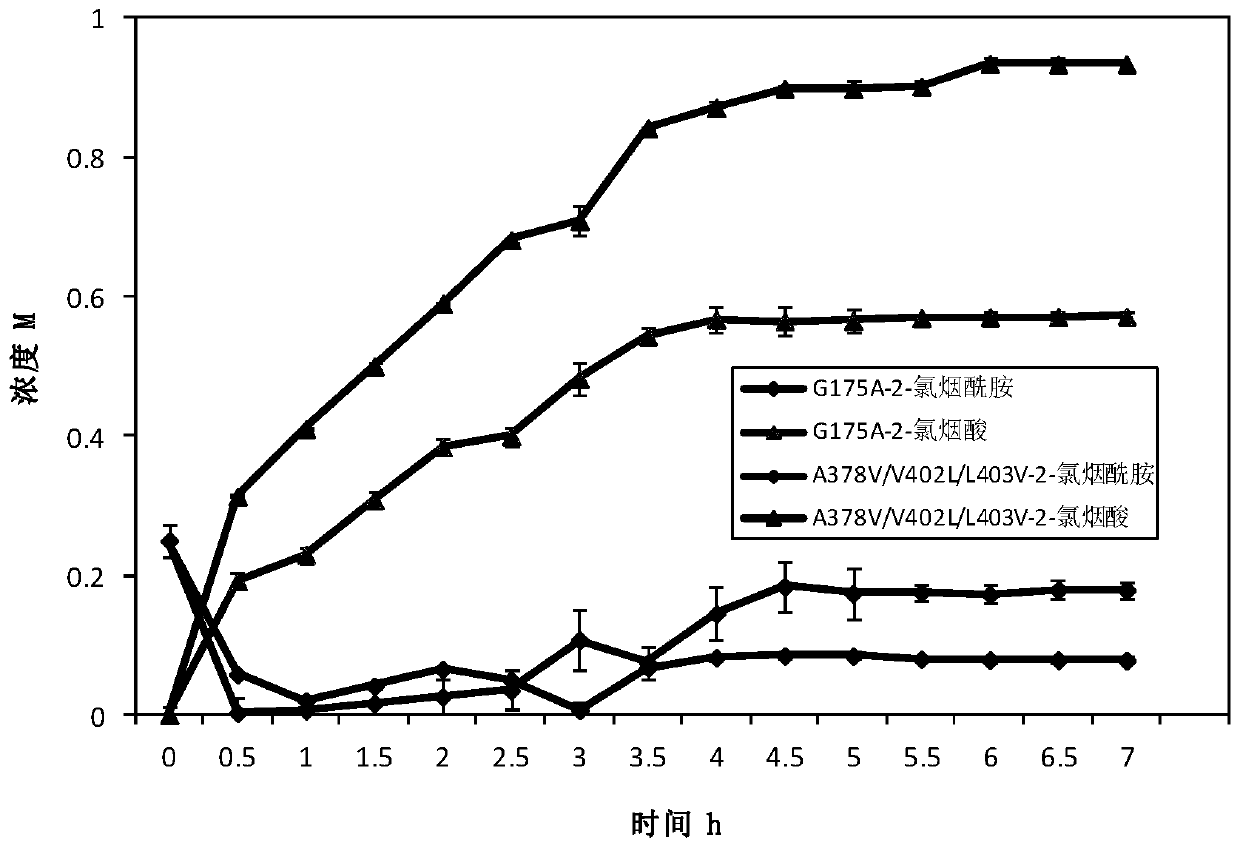
[0056] The positive bacteria obtained in Example 2 were cultured according to the culture conditions of Example 1 to obtain mutant whole cells. Weigh the wet cells and add buffer to mix well to make a bacterial suspension with a wet cell concentration of 40g / L. The reaction system for the determination of mutant viability was: total system 10mL, cell final concentration 0.25g / L, 50mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0), 50mM 2-chloronicotinamide. Shake at 55°C, 150r / min, react for 10min, take 1mL and add 100μL 2M hydrochloric acid to terminate the reaction, dilute 10 times and use liquid chromatography for detection. Liquid chromatography detection conditions: mobile phase: acetonitrile: water: phosphoric acid = 250:750:1, flow rate 1mL / min, 2-chloronicotinic acid detection wavelength 270nm.
[0057] Enzyme activity unit (U) definition: Under the conditions of 55°C and pH 8.0, the cells required to catalyze 2-chloronicotinamide to p...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com