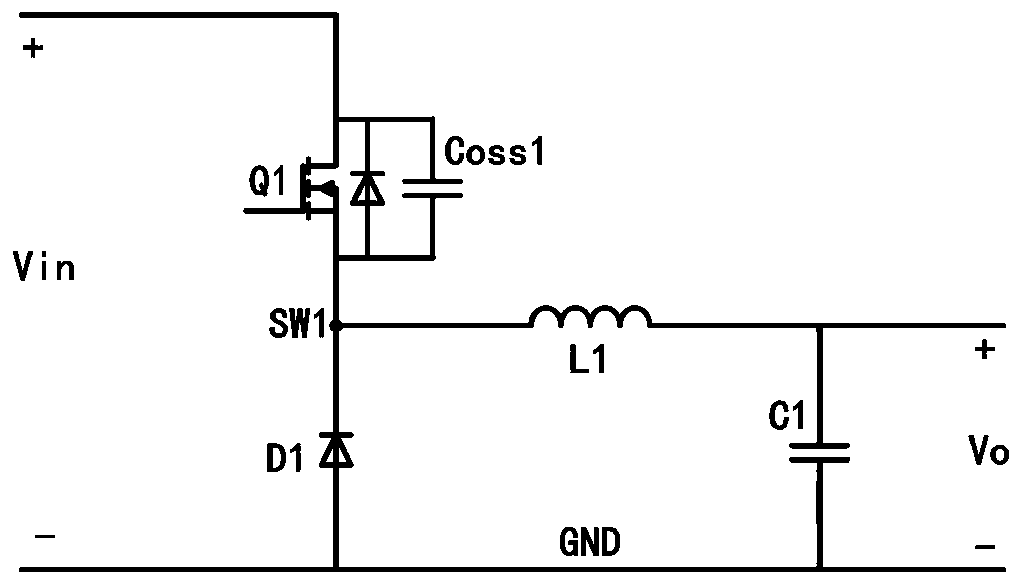
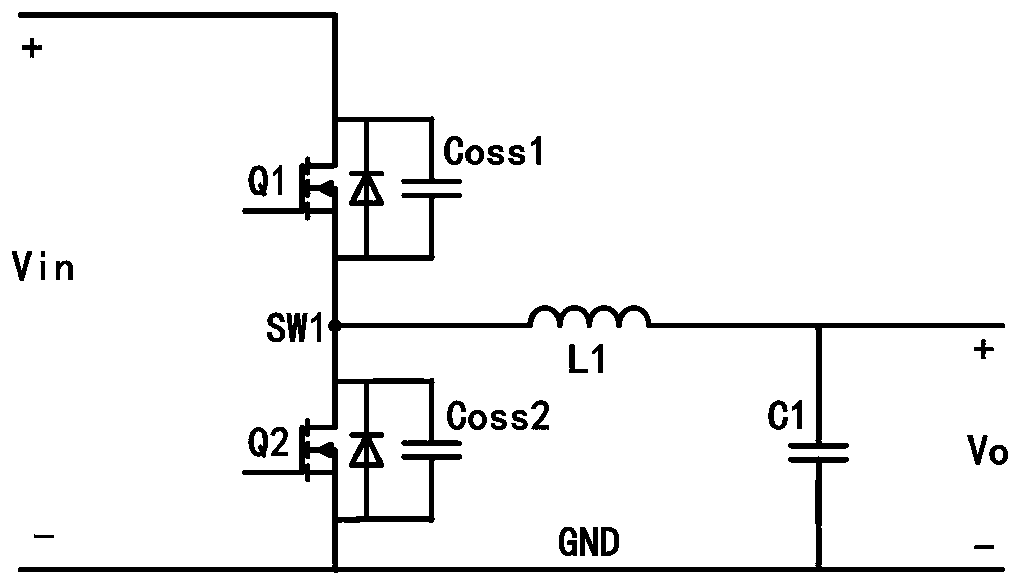
Soft switching Buck converter and control method thereof
A soft switch and converter technology, applied in control/regulation systems, DC power input conversion to DC power output, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of high switching loss, EMI noise, etc., to improve power density, reduce EMI noise, conduction The effect of reducing the pass loss
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
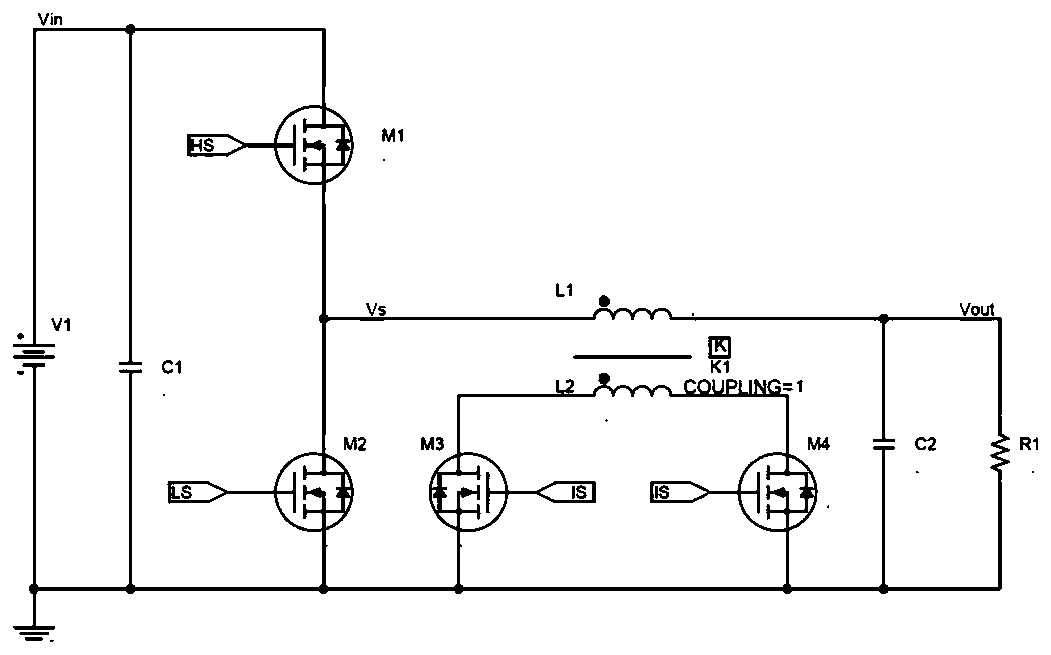
[0051] Figure 4 It is the circuit schematic diagram of the first embodiment of the present invention, including input power supply positive Vin, output voltage positive Vo, power supply common ground GND, switch tube Q1, switch tube Q2, switch tube Q4, diode D3, inductor L1, inductor L2 and capacitor C1; the drain of the switching tube Q1 is connected to the positive Vin of the input power supply, the source of the switching tube Q1 and the drain of the switching tube Q2 are connected to one end of the inductor L1, and one end of the inductor L1 is also connected to one end of the inductor L2, and the diode D3 The cathode is connected to the other end of the inductor L2, the source of the switching tube Q4 is connected to the cathode of the diode D3, the drain of the switching tube Q4 and the other end of the inductor L1 are connected to one end of the capacitor C1, the source of the switching tube Q2 is connected to the capacitor C1 Connect the other end to the power supply ...
no. 2 example
[0065] Figure 6 It is the schematic circuit diagram of the second embodiment of the present invention. In this embodiment, on the basis of the first embodiment, the diode D3 is replaced by a switch tube Q3, which has a synchronous rectification function. The drain of the switch tube Q3 is connected to the other end of the inductor L2, and the source of the switch tube Q3 is connected to the switch tube Q4. source.
[0066] The switch tube Q3 can be turned on at any time during the time period from the switch tube Q2 to the switch tube Q4, which is a zero-current switch-on; the switch tube Q1 is turned on at the moment when the switch tube Q1 is turned on or through the detection signal to realize the switch-off tube Q3, which is zero voltage Turn off; when the current of the inductor L2 drops to zero or the voltage at the other end of the inductor L2 is greater than the output voltage Vo, a detection signal is output.
[0067] Compared with the first embodiment, the synchro...
no. 3 example
[0070] Figure 8 It is the circuit schematic diagram of the third embodiment of the present invention. This embodiment adds clamping diodes D1 and D2 on the basis of the second embodiment. The cathode of diode D1 is connected to the input power supply positive Vin, and the cathode of diode D2 is connected to inductor L2. The other end of the diode D1 is connected to the anode of the diode D1, and the anode of the diode D2 is connected to the power supply common ground GND.
[0071] Figure 9 Shown is the working sequence of the third embodiment, the working process is similar to the working sequence of the second embodiment, the only difference is that after the clamping diodes D1 and D2 are added, the output capacitor Coss3 of the switching tube Q3 and the inductor L2 are resonantly clamped Position, the voltage stress between the drain and source of the switching tube Q3 and the switching tube Q4 is greatly reduced, which increases the advantage of device selection and redu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com