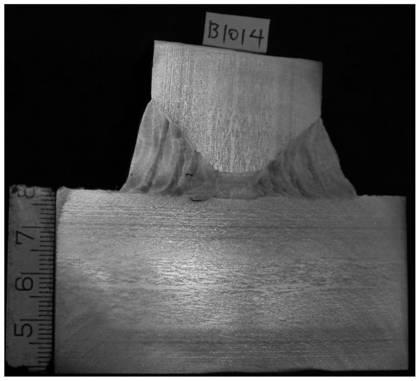
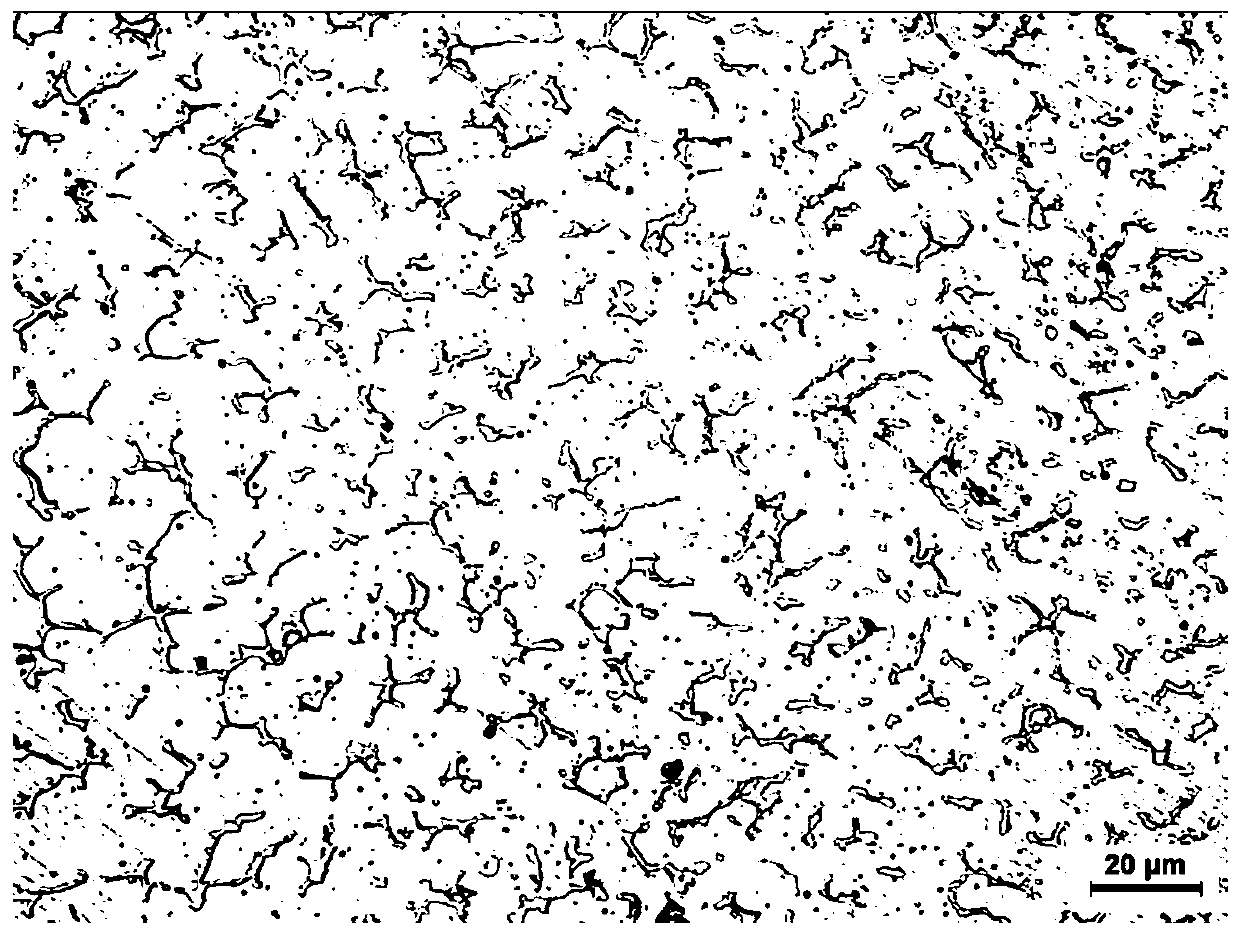
304L austenitic stainless steel MIG welding method
A technology of austenitic stainless steel and welding method, applied in the direction of welding medium, welding equipment, welding equipment, etc., can solve problems such as not meeting the requirements of use, achieve the effect of eliminating small unfused, improving low temperature toughness, and realizing engineering application
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0070] The specific steps of this welding method are as follows:
[0071] (1) Preparation before welding
[0072] A 500×150×40mm (2 pieces) 304L austenitic stainless steel test plate was prepared with a beveling machine for a symmetrical X-shaped bevel, with a single-side bevel angle of 35°, and a grinder (stainless steel grinding wheel) was used to align the bevel Grind and clean the 20mm range on both sides to remove oil and impurities; use oxyacetylene neutral flame to quickly heat the 20mm range on both sides of the 304L base metal groove to remove moisture; combine the two test plates to be welded Assembling, the blunt edge is 0mm, the gap is 3mm, and the spot welding is carried out by argon tungsten arc welding. The welding material and welding process of the spot welding are the same as that of argon tungsten arc welding bottom welding (front groove). After the spot welding is finished, use a grinder to grind the weld seam on the back of the spot welding until the silv...
Embodiment 2
[0082] The shielding gas in this welding method is 98%Ar+2%CO 2 , the unilateral bevel angle is 30°, and the rest of the welding process is consistent with Example 1.
[0083] After testing, the tensile strength of the welded joint is 581MPa, the two side bending samples have no cracks, and the two side bending samples have some cracks of 0.6~2.1mm. The impact energy of welded joints at -196°C is: argon arc welding seam 73J, argon arc welding heat affected zone 128J, MIG welding seam 52J, MIG welding heat affected zone 103J, greater than 50J, in line with military products such as large low temperature wind tunnel for Welded joints -196 ℃ impact energy requirements, but there is no allowance. Compared with the -196°C impact energy of the MIG welded joint in Example 1, both the weld seam and the heat-affected zone have decreased in value, indicating that there are subtle The lack of fusion reduces the low temperature toughness at -196°C.
Embodiment 3
[0085] In this welding method, the groove form is a symmetrical K-shaped groove, the single-side groove angle is 45°, and the shielding gas is 98%Ar+2%O 2 , the rest of the welding process is consistent with embodiment 2.
[0086] After testing, the tensile strength of the welded joint was 559MPa, and several cracks of 0.4~2.6mm appeared in three side bending samples, and one side bending sample was intact. The impact energy of welded joints at -196°C is: argon arc welding seam 68J, argon arc welding heat affected zone 133J, MIG welding seam 48J, MIG welding heat affected zone 94J, among which the impact energy of MIG welding seam <50J, does not meet the requirements Military products such as large-scale low-temperature wind tunnels require -196°C impact energy for welded joints. It shows that in the welded joints using the above-mentioned shielding gas and groove angle, there is a slight lack of fusion, which reduces the low-temperature toughness at -196°C.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| yield strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com