Brown lactic acid bacteria beverage and preparation method thereof
A lactic acid bacteria beverage, brown technology, applied in the direction of Lactobacillus, dairy products, bacteria used in food preparation, etc., can solve the problems of health concept that does not conform to sugar reduction and high sugar content, and achieves benefits that are beneficial to human health and fat content. The effect of falling and not easy to deteriorate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1-4
[0065] A kind of brown lactobacillus drink, comprises following component:
[0066] Milk powder, lactase, stabilizer, functional sweetener, Lactobacillus paracasei, water;
[0067] In embodiments 1-4, skim milk powder is used as the milk powder, and whole milk powder, half-fat milk powder, etc. can also be used in other embodiments;
[0068] In Examples 1-4, pectin is used as the stabilizer, and modified starch E1442, modified starch E1414, etc. can also be used in other embodiments.
[0069] In Examples 1-4, the functional sweetener is combined with crystalline fructose and sucralose. In other implementations, crystalline fructose or sucralose can also be used alone, or high fructose syrup, aspartame, licorice Combination of sweetener, Luo Han Guo extract, etc.
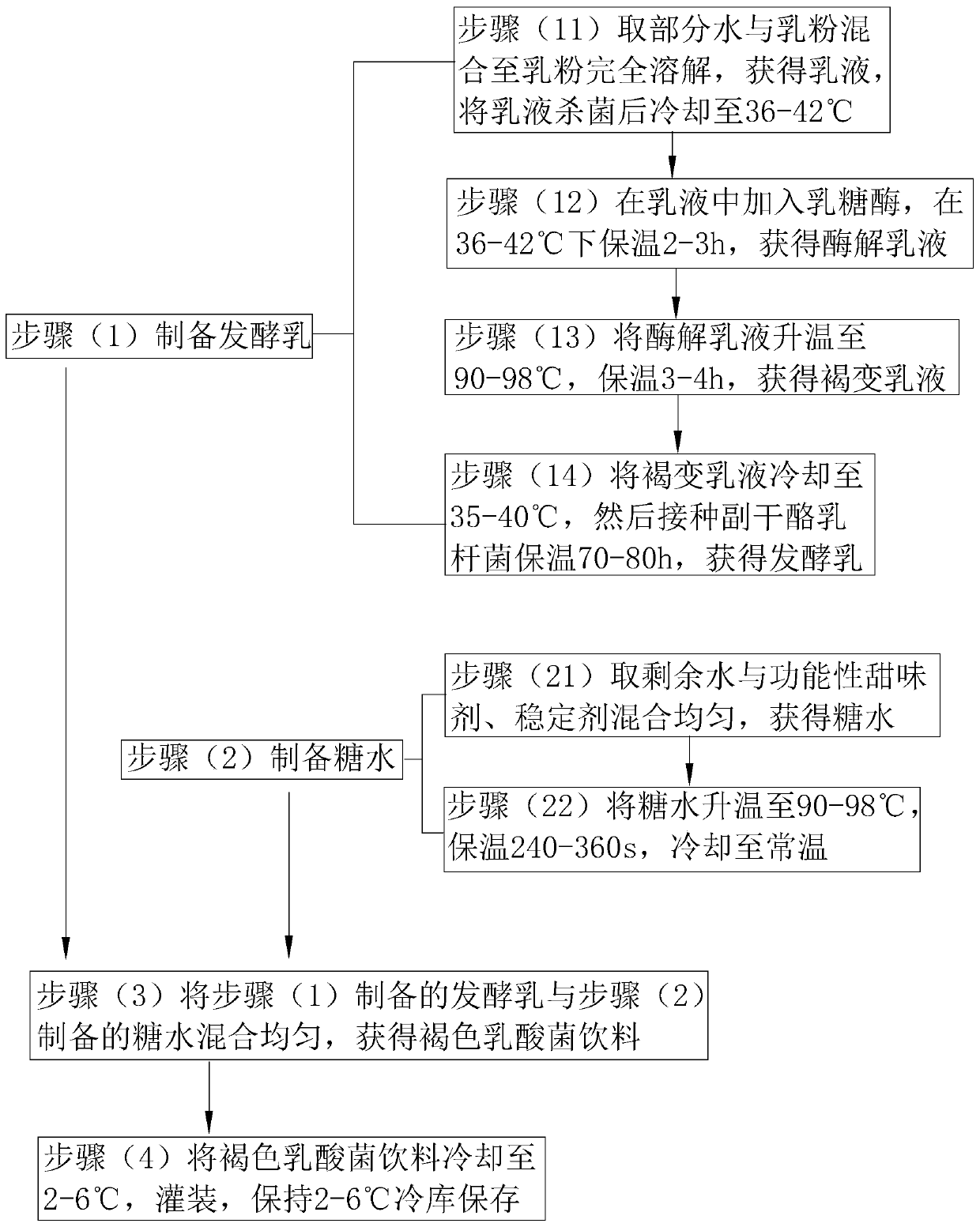
[0070] refer to figure 1 , is the preparation method of the brown lactic acid bacteria beverage of embodiment 1-4, specifically comprises the following steps:
[0071] Step (1) prepares fermented milk, specifical...
Embodiment 5
[0086] Compared with embodiment 4, the difference only lies in:
[0087] Step (11): cooling the emulsion to 36°C;
[0088] Step (12): After stopping the stirring, keep the temperature at 36°C and keep it warm for 3 hours to obtain the enzymolysis emulsion;
[0089] Step (13): raising the temperature of the enzymolysis emulsion to 90°C and keeping it warm for 4 hours to obtain the browning emulsion;
[0090] Step (14): cooling the browning emulsion to 35° C., then inoculating Lactobacillus paracasei for 80 hours to obtain fermented milk;
[0091] Step (22): heat up the sugar water to 90°C and keep it warm for 360s;
[0092] Step (4): Cool the brown lactic acid bacteria beverage to 2°C, fill it, and keep it in a cold storage at 2°C;
Embodiment 6
[0094] Compared with embodiment 4, the difference only lies in:
[0095] Step (11): cooling the emulsion to 42°C;
[0096] Step (12): After stopping stirring, keep at 42°C and keep warm for 2 hours to obtain the enzymatic emulsion;
[0097] Step (13): raising the temperature of the enzymatic emulsion to 98°C and keeping it warm for 3 hours to obtain a browned emulsion;
[0098] Step (14): cooling the browning emulsion to 40° C., then inoculating Lactobacillus paracasei for 70 hours to obtain fermented milk;
[0099] Step (22): heat up the sugar water to 98°C and keep it warm for 240s;
[0100] Step (4): Cool the brown lactic acid bacteria beverage to 6°C, fill it, and keep it in a cold storage at 6°C;
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com