Ecological ditch system and method for intercepting agricultural non-point source pollution by utilizing waste aquaculture pond
A technology for agricultural non-point source pollution and ecological ditches, applied in the field of environmental protection, can solve the problems of lack of nitrogen and phosphorus interception and purification functions, increased nitrogen and phosphorus loss load in farmland systems, and poor water flow.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
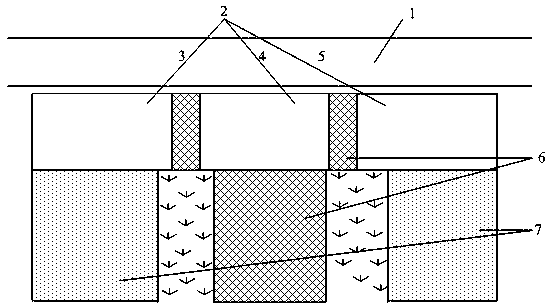
[0043] An ecological ditch system utilizing abandoned aquaculture ponds to intercept agricultural non-point source pollution, which includes multi-level ecological ponds, intercepting layer interception structures are set between the multi-level ecological ponds and in the retention ditch; wherein the multi-level ecological ponds 2 include: An anaerobic pond 3, an aerobic pond 4, and an aerobic pond 5 are connected in sequence. The interception layer interception structure 6 is set between the multi-level ecological ponds and in the interception ditch. Emerging water, floating leaves and submerged water are planted in the multi-level ecological pond 2. Add plants and benthic animals to the water body;
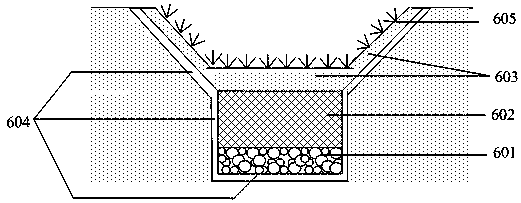
[0044] The interception structure of the intercepting layer comprises: gravel layer 601, biological filler matrix layer 602, planting layer 603; waterproof layer 604, plant 605; wherein the gravel layer is arranged at the bottom, and the planting layer is set on the upper part o...
Embodiment 2
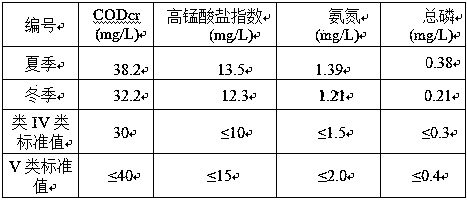
[0047] The first-class river channel 1 in a district of Tianjin, the aquaculture pond around 30 meters of the river channel was abandoned, and the surrounding area was farmland, and the abandoned aquaculture pond was changed into an ecological pond. The multi-level ecological pond 2 was transformed from an abandoned aquaculture pond. Through transformation, Ecological ponds are arranged alternately along the direction of water flow as shallow water / deep water areas to form aerobic ponds, facultative oxygen ponds, and anaerobic ponds. Abandoned aquaculture ponds have a water depth of 0-3 meters during normal operation. After transformation, 20% of the areas are set as anaerobic ponds with a water depth of less than 2.0 meters, and 30% of the ecological ponds are set as facultative ponds with a water depth of 1-1.5 meters. 50 % Ecological ponds with a water depth of 0.5-1.0 meters are set as aerobic ponds.
Embodiment 3
[0049] A farmland interception channel in Tianjin has been transformed, and its bottom is longitudinally provided with a gravel layer and a biofiller matrix layer; the upper part of the biofiller matrix layer is provided with a planting layer, and plants are planted on the side slope of the ecological ditch and the planting layer at the bottom of the ecological ditch. The thickness ratio is 1:2:1. The gravel layer is gravel with a particle size of 5-25mm. The ecological ditch is set in the base soil, and a bentonite waterproof layer is set between the ecological ditch and the base soil. The waterproof layer is arranged vertically through the bottom of the ecological ditch and on the side slope, and the gravel layer and the biological filler matrix layer are arranged on the upper part of the waterproof layer. The planting layer is local soil, and its laying thickness is 30-50cm. The gravel and biological filler matrix layer in the closure layer of the ecological ditch natural...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com