Method for recovering selenium from Cu-In-Ga-Se waste
A copper indium gallium selenium and selenium recovery technology, applied in the direction of element selenium/tellurium, etc., can solve the problems of high cost, difficult control of electrode results, and high anti-corrosion requirements
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
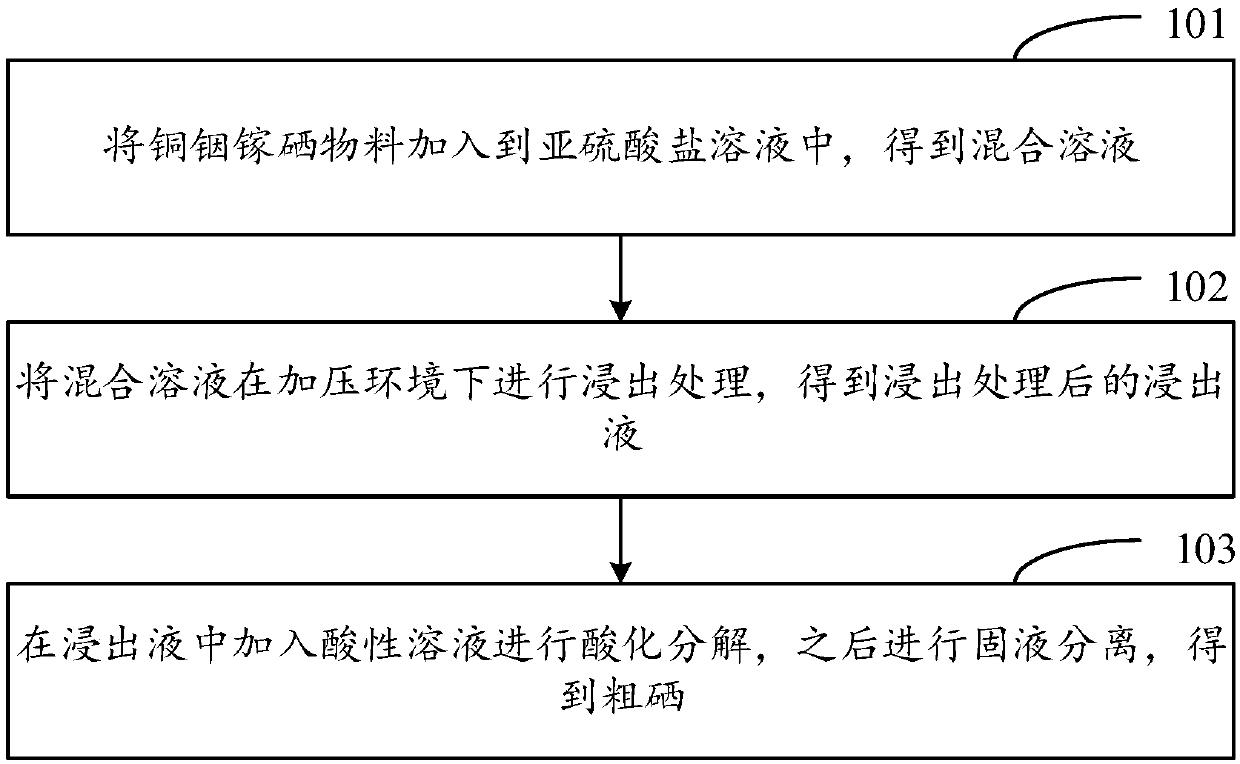
[0049] The method for recovering selenium from copper indium gallium selenide waste provided by the embodiment of the present invention comprises the following steps:
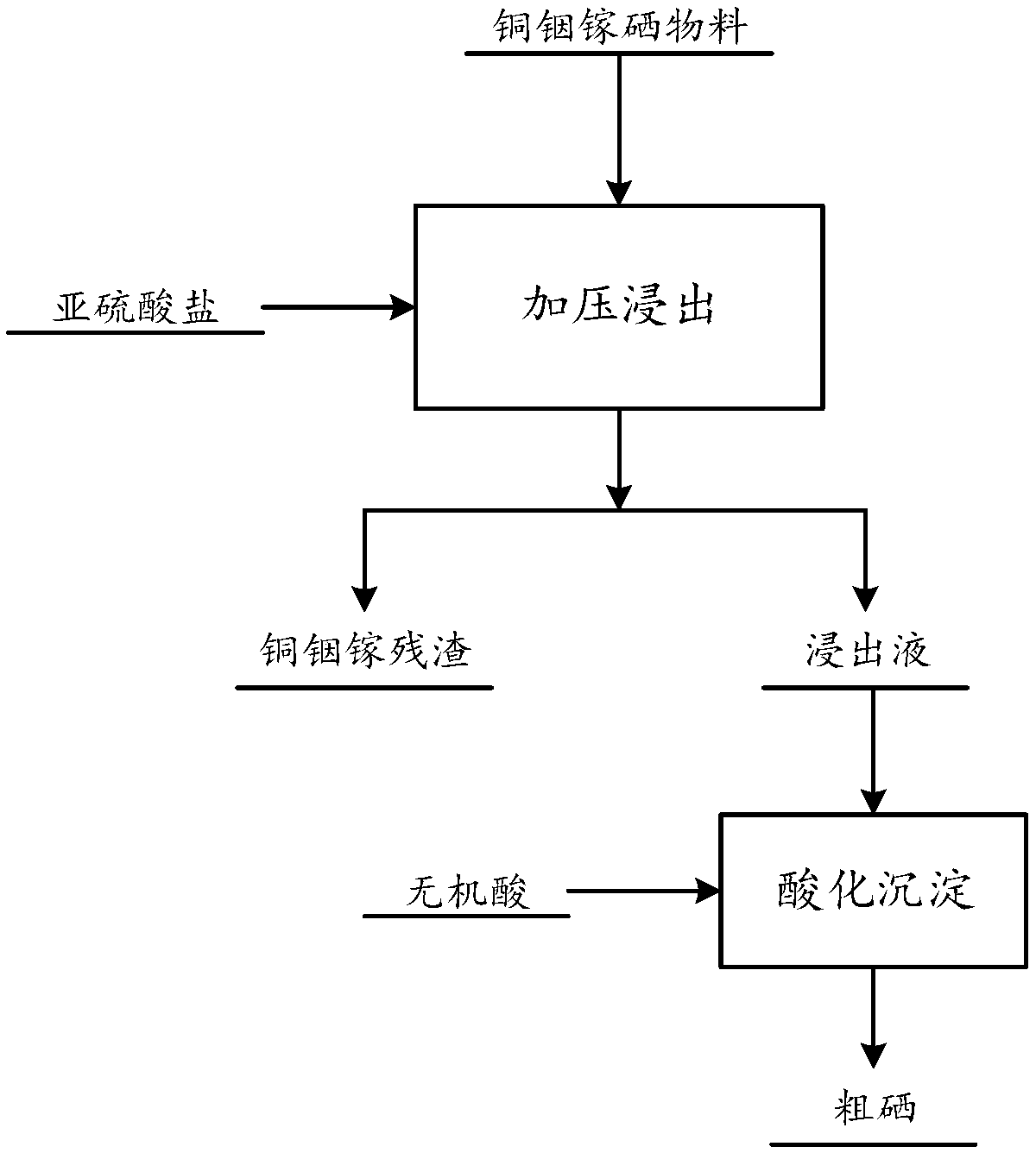
[0050] Step A1: Add 1 kg of CIGS material to 6 L of 100 g / L sulfite solution to obtain a mixed solution of CIGS material and sulfite solution.
[0051] Step A2: Put the mixed solution into a pressure leaching kettle, close the leaching kettle, keep the pressure in the leaching kettle at 0.6 MPa, and keep the temperature at 180° C., and leaching for 5 hours.
[0052] Step A3: Use a solid-liquid separation device to filter out the copper indium gallium residue in the leaching tank to obtain a sodium selenosulfate leaching solution.
[0053] Among them, after the copper indium gallium residue is obtained, other methods can be used to recycle the copper indium gallium residue, and the copper, indium, and gallium in it can be recovered.
[0054] Step A4: adding an appropriate amount of hydrochloric acid to the leac...
Embodiment 2
[0058] The method for recovering selenium from copper indium gallium selenide waste provided by the embodiment of the present invention comprises the following steps:
[0059] Step B1: using a ball mill to crush the CIGS waste to obtain granular CIGS materials.
[0060] Step B2: adding an appropriate amount of copper indium gallium selenide material to 8L of 160g / L sulfite solution, the liquid-solid ratio of the sulfite solution to the copper indium gallium selenide material is 15:1, and the copper indium gallium selenide material is obtained and a mixed solution of sulfurous acid.
[0061] Step B3: Put the mixed solution into a pressure leaching kettle, close the leaching kettle, keep the pressure in the leaching kettle at 0.8 MPa, and keep the temperature at 170° C., and leaching for 4 hours.
[0062] Step B4: Use a solid-liquid separation device to filter out the copper indium gallium residue in the leaching tank to obtain a sodium selenosulfate leaching solution.
[0063...
Embodiment 3
[0068] The method for recovering selenium from copper indium gallium selenide waste provided by the embodiment of the present invention comprises the following steps:
[0069] Step C1: using a ball mill to crush the CIGS waste to obtain 2 kg of granular CIGS material.
[0070] Step C2: adding 2 kg of copper indium gallium selenide material into 10 L of 150 g / L sulfite solution to obtain a mixed solution of copper indium gallium selenide material and sulfite solution.
[0071] Step C3: Put the mixed solution into a pressure leaching kettle, close the leaching kettle, keep the pressure in the leaching kettle at 1 MPa, and keep the temperature at 190° C., and leaching for 2 hours.
[0072] Step C4: Use a solid-liquid separation device to filter out the copper indium gallium residue in the leaching tank to obtain a sodium selenosulfate leaching solution.
[0073] Among them, after the copper indium gallium residue is obtained, other methods can be used to recycle the copper indiu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com