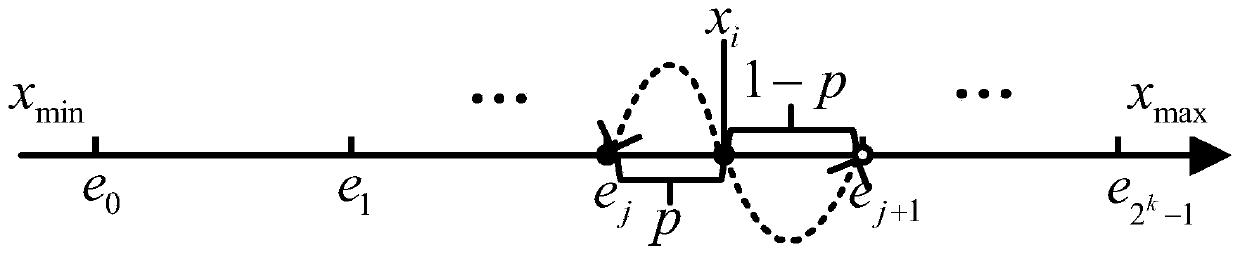
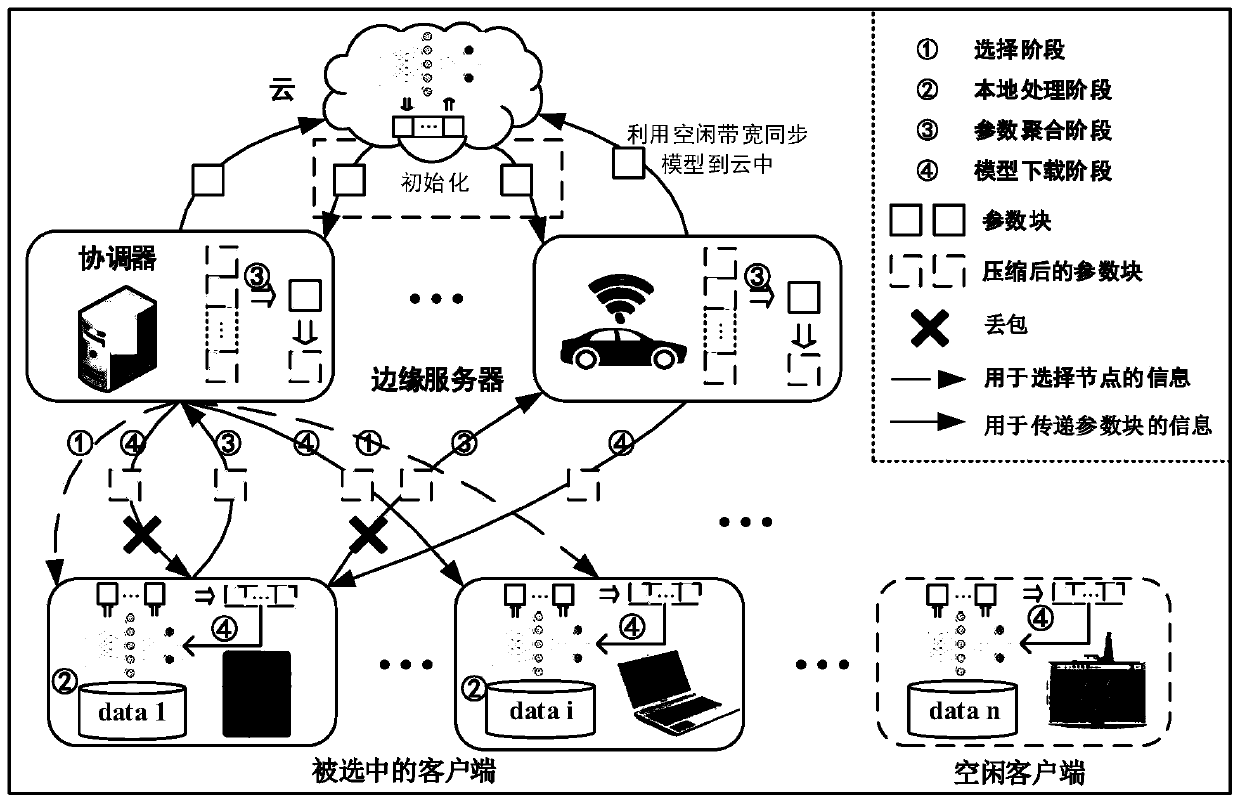
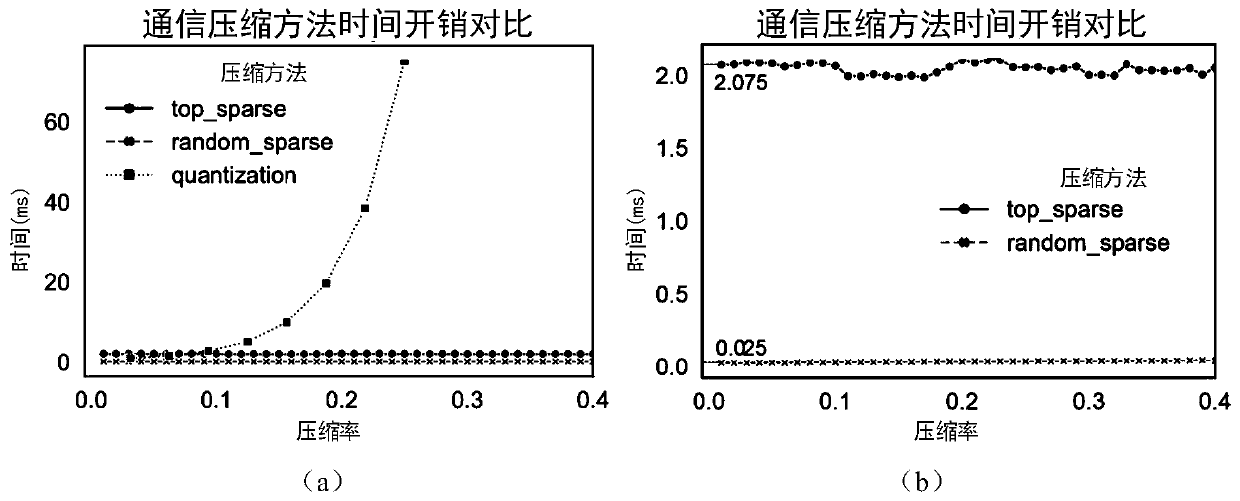
Federated learning architecture under dynamic bandwidth and unreliable network and compression algorithm of architecture
A dynamic bandwidth and compression algorithm technology, applied in machine learning, data exchange network, computing, etc., can solve problems such as limiting client scale, increasing communication interruption, bandwidth peak occupation, etc., to reduce redundant data exchange and communication delay , the effect of using bandwidth resources
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0047] Federated learning is a special form of federated optimization for machine learning. Therefore, this embodiment first defines federated optimization as a type of distributed optimization with a data-parallel setting, where data is distributed across different computing devices, as follows:
[0048]
[0049] where f is the global optimization objective, f i :R d → R is the target defined by the local data available on each node, w i ∈ R d means f i solution.
[0050] When solving a federated optimization problem, each computing device searches f from its local data i the solution w i , then the server uses the aggregation algorithm f agg will w i Aggregated to obtain the global solution w * :
[0051] w * = f agg (w 1 ,...w n ) (2)
[0052] The server then takes the global solution w * as its new w i distributed to each client. Each customer starts with this new w i Search for a better solution for a starting point. The client and server repeat the...
Embodiment 2
[0143] This embodiment uses image classification, sentiment analysis and next character prediction tasks as experimental examples to evaluate the effectiveness of ACFL. All of these tasks correspond to typical machine learning models including Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN), Bag-of-Words Logistic Regression (Bag-Log-Reg), and Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM). The datasets for these tasks conform to federated settings characterized by non-IDD, imbalance, and large-scale distribution. For the image classification task, this example uses Federated Extended MNIST (FEMNIST), which is constructed from the author's partitioning of data in Extended MNIST. There are 62 different categories (10 digits, 26 lowercase letters, 26 uppercase letters) images in FEMNIST, 28 x 28 pixels with 3500 users. For the sentiment analysis task, this example uses Sentiment140, which is constructed by annotating tweets according to the emoji present in them and partitioning them according to 660120 Twi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com