Synthesis and characterization of well defined poly(propylene fumarate) and poly(ethylene glycol) block copolymers
A technology of polytrimethylene fumarate and diblock copolymer, which is applied in prosthesis, medical science, etc., and can solve problems that have not yet been discovered or developed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0150] Synthetic Mg(BHT) 2 (THF) 2 catalyst
[0151] In a nitrogen-filled, oven-dried anti-bump Schlenk flask, 13.22 g (0.06 mol) of 2,6-di-tert-butyl-4-methylphenol (BHT) was dried under high vacuum for 40 min. The flask was backfilled with nitrogen and then injected with 20 mL of anhydrous THF (0.31 mol). After the BHT was dissolved, 30 mL of 1.0 M dibutylmagnesium in heptane (0.03 mol) was added dropwise within 1 hour, and the flask was cooled on ice. The reaction was stirred on ice for another 2 hours before a white precipitate formed. The solvent was removed by vacuum transfer, and the catalyst was dried overnight before being stored in a glove box. (17.5 g, 96% yield)
Embodiment 2
[0153] Dried polyethylene glycol raw material
[0154]Polyethylene glycol diol and methyl ether polyethylene glycol starting materials were purchased from Sigma (2 kDa and 4 kDa PEG-diol and methyl ether PEG) and TCI (1 kDa PEG-diol and methyl ether PEG) and dried according to previous literature. (See, Kinard, L.; Kasper, K.; Mikos, A. Drying Poly(Ethylene Glycol). Protoc. Exch. 2012, the disclosure of which is incorporated herein by reference in its entirety.) Briefly, 10.00 g Each PEG derivative was dissolved in anhydrous toluene and refluxed overnight using a Dean-Stark apparatus. The solution is then transferred through the cannula to a Molecular sieves in a dry round bottom flask overnight and then transferred to another dry round bottom flask with vacuum dried molecular sieves overnight. The toluene was then removed under vacuum and the PEG was transferred to a glove box. For scale-up polymerizations, the sieve drying step was omitted as the reaction was found to be...
Embodiment 3
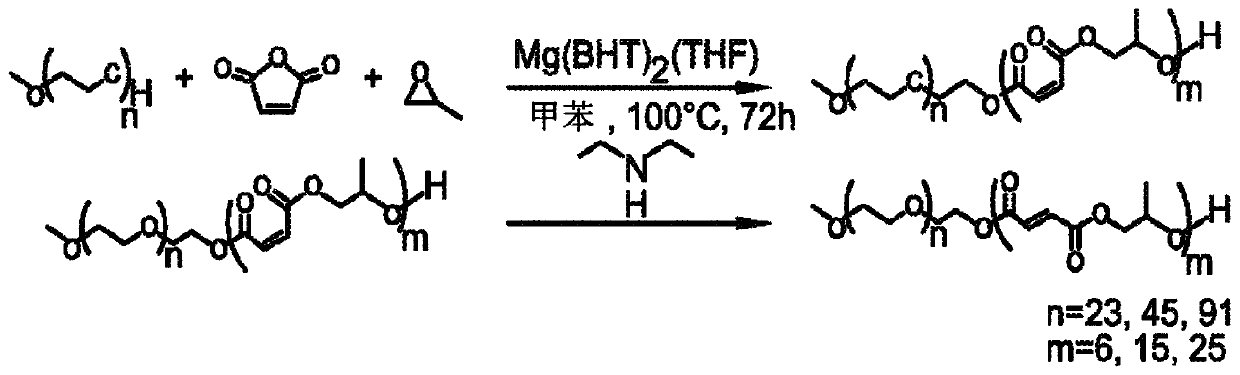
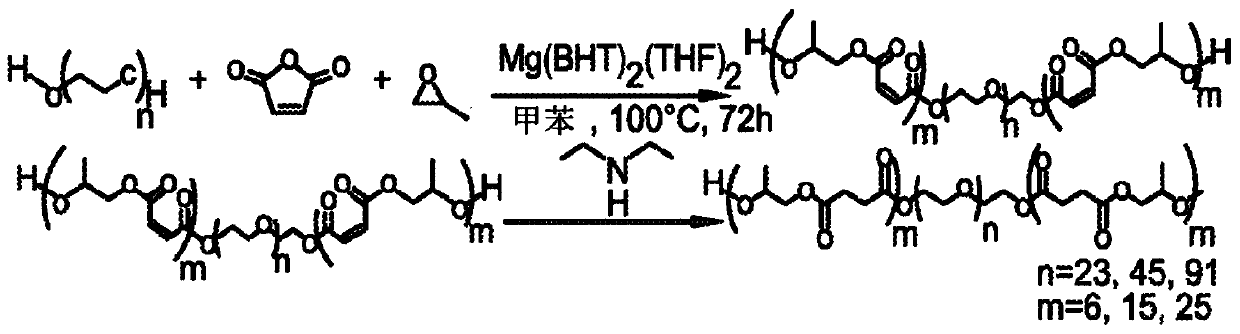
[0156] Synthesis of Poly(Ethylene Glycol-Chemo-Trimethylene Maleate), DP 20 Using Methyl Ether PEG (MW 750)
[0157] Initiated by methyl ether PEG (MW 750) and induced by Mg(BHT) 2 (THF) 2 Catalyzed, poly(ethylene glycol-block-trimethylene maleate) was synthesized by the copolymerization of maleic anhydride and propylene oxide to a degree of polymerization (DP) of 20. As shown in Scheme 3 below.
[0158] Option 3
[0159]
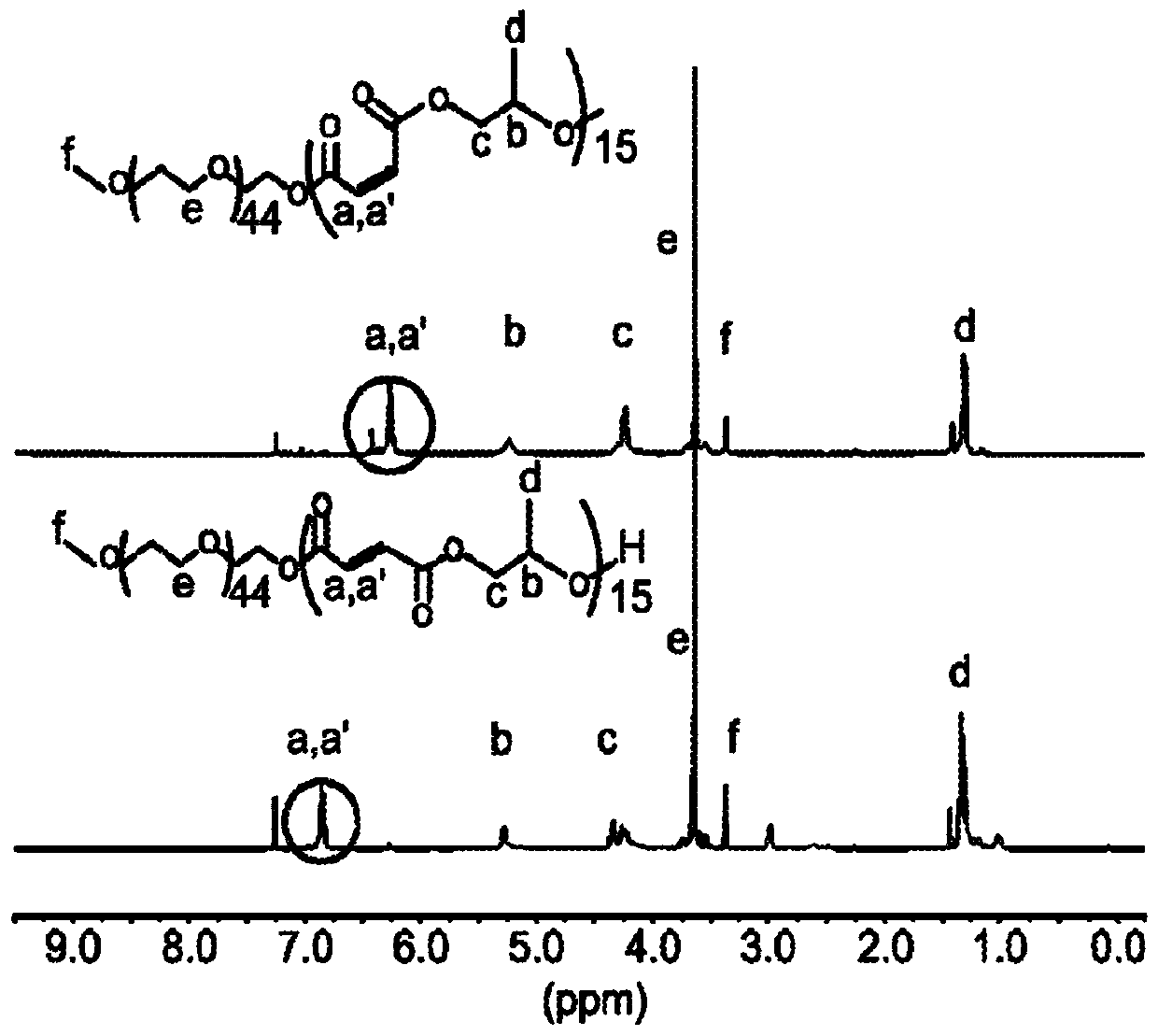
[0160] Fill ampoules with Mg(BHT) using standard Schlenk line technology 2 (THF) 2 (57.8 mg, 0.095 mmol), methyl ether polyethylene glycol MW 750 (0.3573 g, 0.4764 mmol), propylene oxide (0.683 mL, 9.76 mmol) and maleic anhydride (0.9571 g, 9.76 mmol). The solution was dissolved in toluene so that the total monomer concentration was 2M. The ampoule was sealed and heated at 100°C for 72 hours. The resulting polymer was recovered by precipitation in excess diethyl ether and characterized by: 1 H NMR ((300MHz,303K,CDCl 3 ): δ=6.28-6.24(t,OC(=O)CH...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| degree of polymerization | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com