Preparation method of proanthocyanidin polymer and proanthocyanidin polymer
A technology of proanthocyanidins and polymers, applied in chemical instruments and methods, azo dyes, organic dyes, etc., can solve the problems of lack of preparation methods for proanthocyanidins polymers, achieve high degree of polymerization and mild process conditions , The effect of simple preparation process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] Step S1, prepare bayberry leaf (water chestnut) raw material;
[0030] Step S2, drying the bayberry leaf in an oven at 25-40°C for 12 hours, taking it out, crushing it with a pulverizer to pass through a 60-80 mesh sieve, and then freezing the bayberry leaf powder in a -20°C refrigerator.
[0031] Step S3, weighing 10g red bayberry leaf powder and adding it into a brown silk bottle with 400mL 70% acetone aqueous solution to obtain a mixed solution, adding 0.4g ascorbic acid to the obtained mixed solution to prevent oxidation during the extraction process, and shaking the obtained material solution Mix well and seal, then shake the brown silk bottle intermittently in the dark at room temperature to extract proanthocyanidin polymers, and the shaking extraction time is 12 hours.
[0032] Step S4, suction-filter the obtained mixed material liquid to obtain a filtrate, extract the filtrate with 400 mL of analytically pure chloroform at a ratio of 1:1, shake well and let stan...
Embodiment 2
[0040] Change the 10g bayberry leaf powder in embodiment 1 into 20g bayberry leaf powder; change the 70% acetone of 400mL in embodiment 1 step 3 into the 70% acetone of 800mL; the ascorbic acid that adds is 0.8g (0.1%w / v) ; The filtrate extraction in step 4 is changed into 1:1 equivolume extraction with the analytical pure chloroform of 800mL; All the other steps are with embodiment 1.
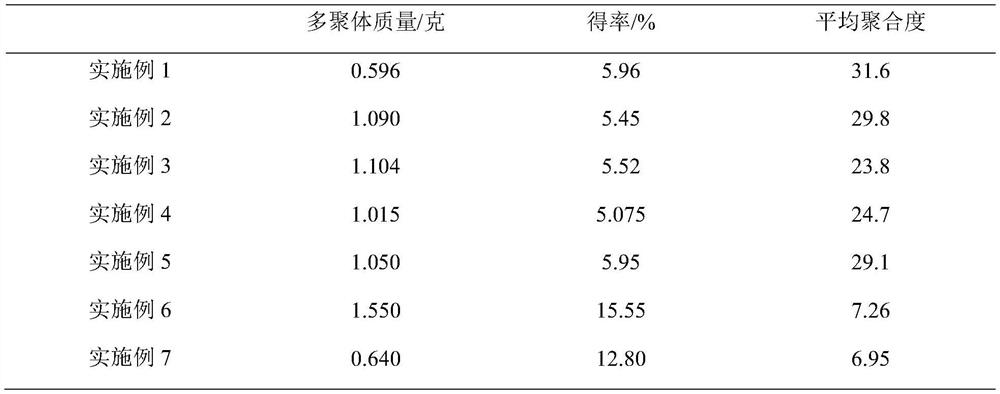
[0041] Finally, 1.090 g of myrica rubra leaf proanthocyanidin multimer was obtained, and the yield was 5.45%.
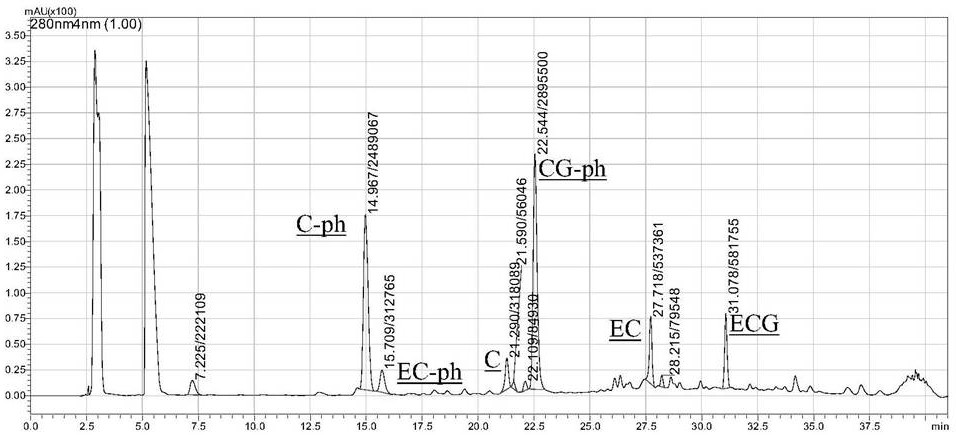
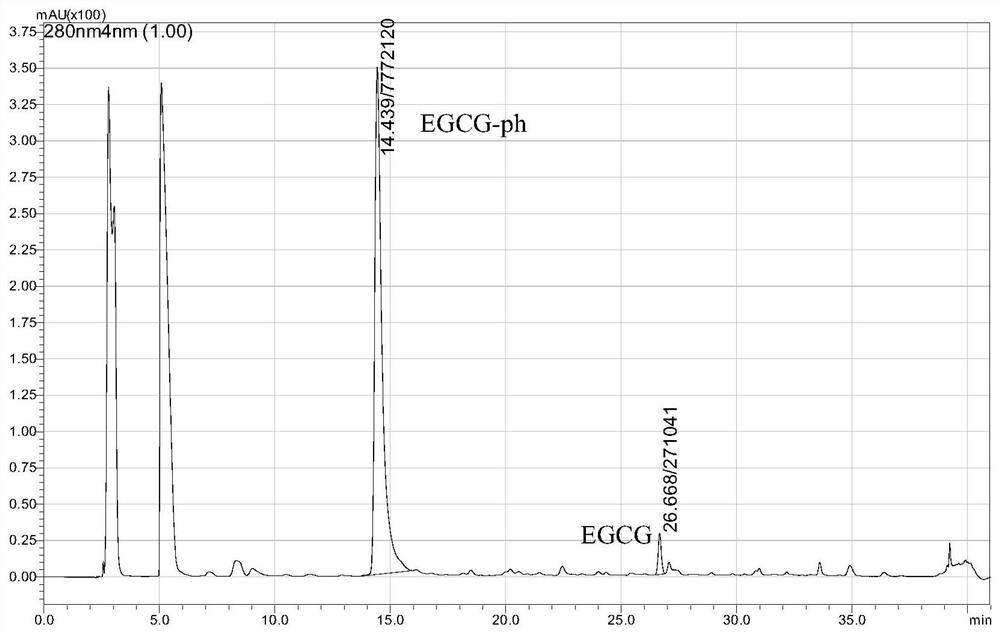
[0042] After being degraded by phloroglucinol-sulfuric acid method, it is detected by RP-HPLC-DAD, and the detection results are as follows: figure 2 As shown, the average degree of polymerization of bayberry leaf proanthocyanidin multimer is 29.8.
Embodiment 3
[0044] Change the 10g bayberry leaf powder in embodiment 1 into 20g bayberry leaf powder; change the 70% acetone of 400mL in embodiment 1 step 3 into the 70% acetone of 800mL; the ascorbic acid that adds is 0.8g (0.1%w / v) ; The filtrate extraction in step 4 was changed to 1:1 equal-volume extraction with 800mL of analytically pure chloroform; extracted twice during the shaking extraction time of 12h; the remaining steps were the same as in Example 1.
[0045] The final proanthocyanidin multimer of bayberry leaf was 1.104g, and the yield was 5.52%.
[0046] After being degraded by the phloroglucinol-sulfuric acid method, the average degree of polymerization of the above-mentioned bayberry leaf proanthocyanidin multimer was 23.8 as detected by RP-HPLC-DAD.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com