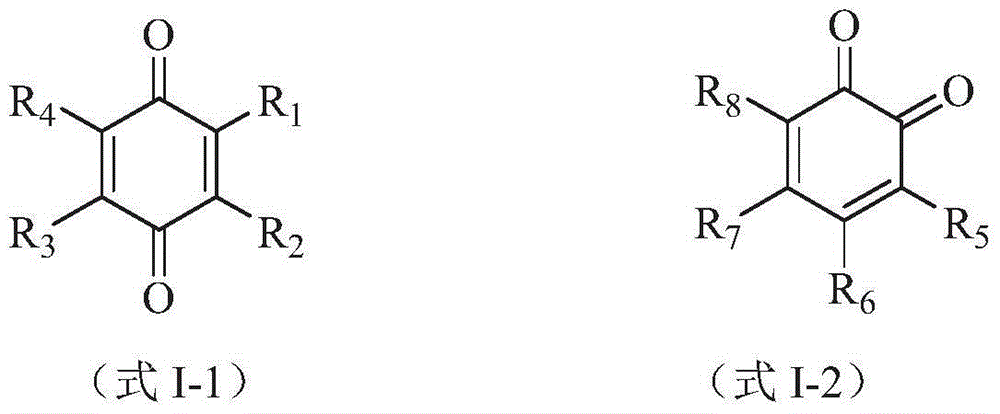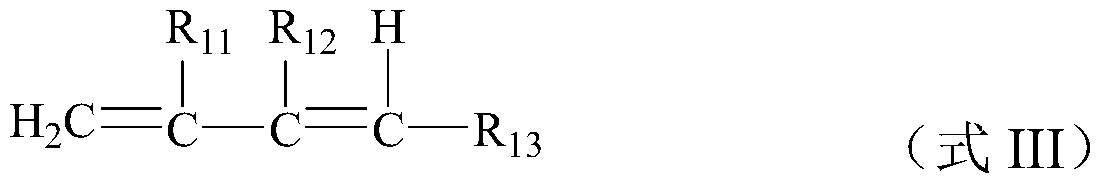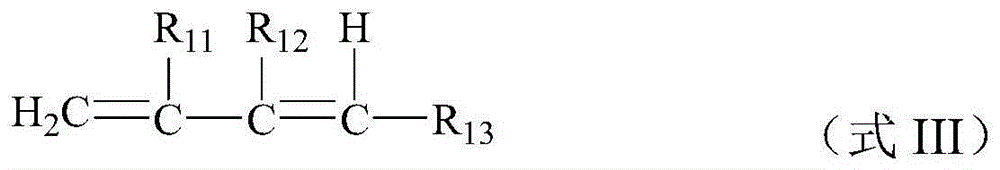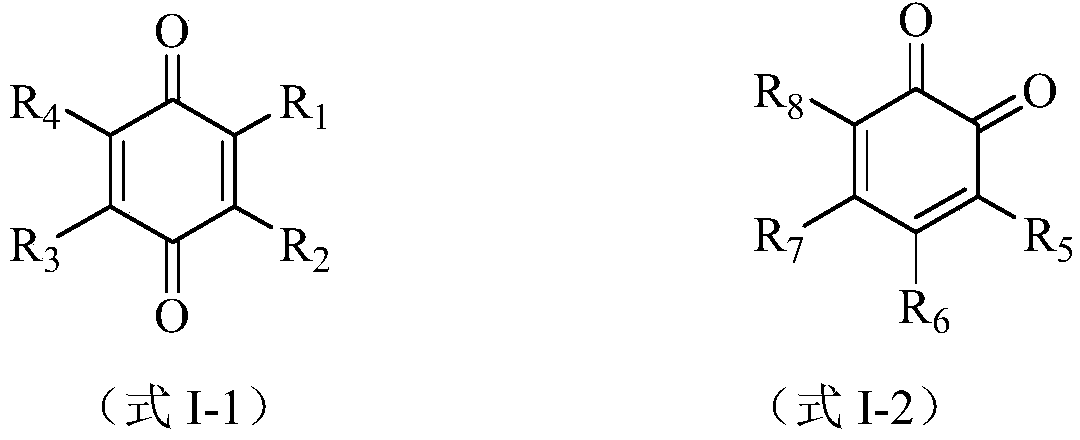Patents
Literature
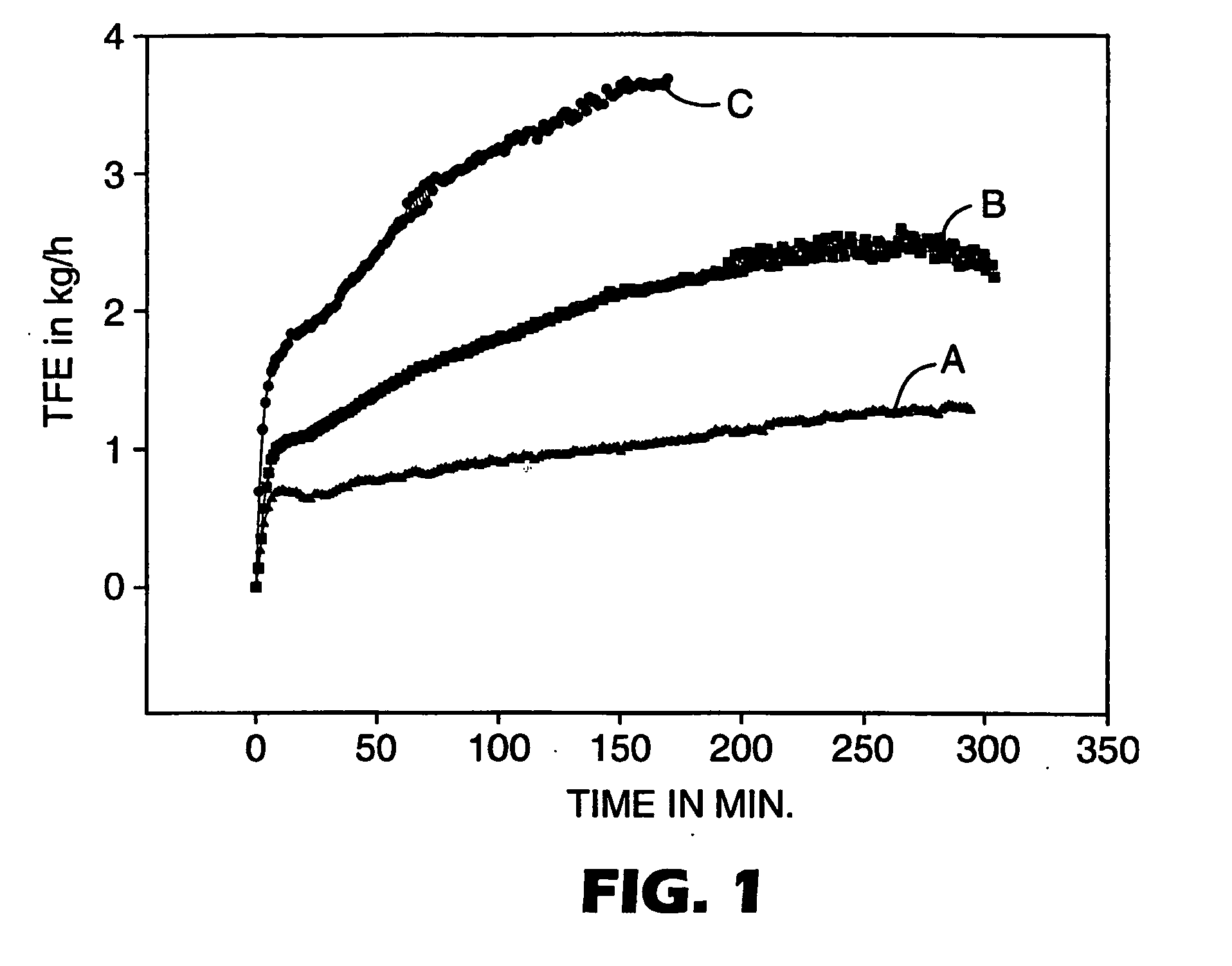
53 results about "Polymer yield" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Defining yield in polymers involves complexities not normally encountered with metals. Polymers are viscoelasti,: and therefore the measured yield stress is sensitive to the stress- or strain-rate imposed. Researchers have attempted to def'me the yield stress of polymers in a variety of ways.
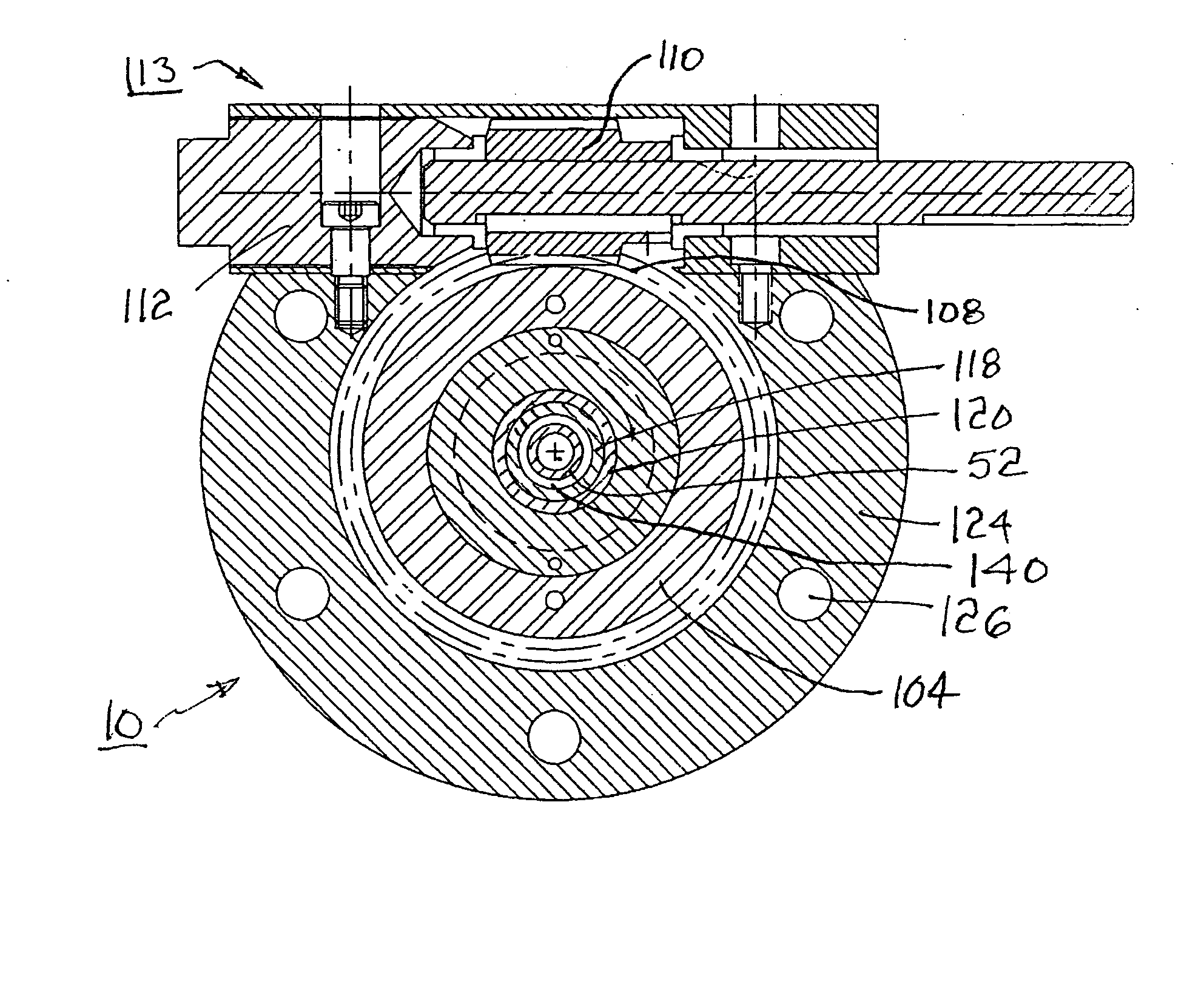
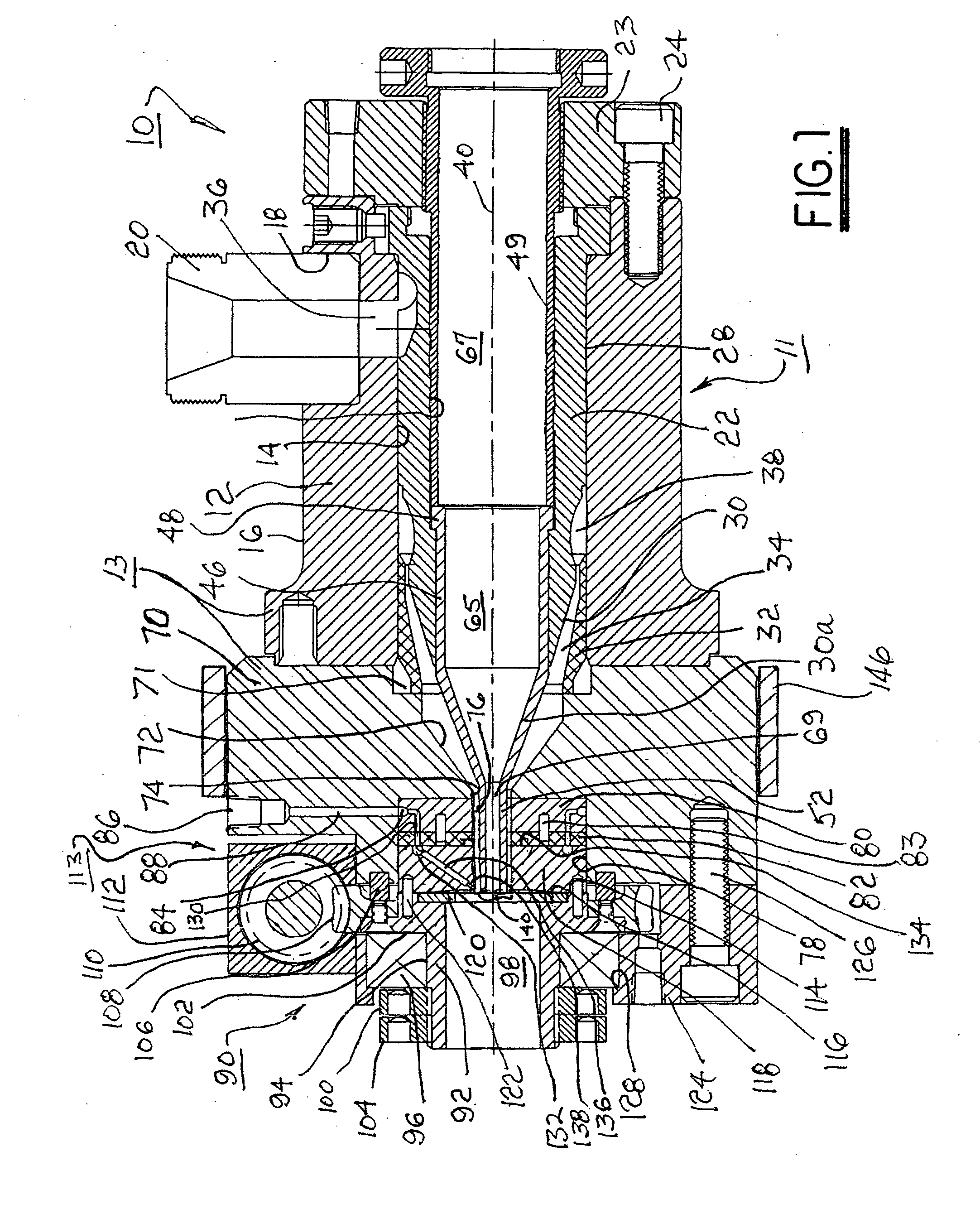
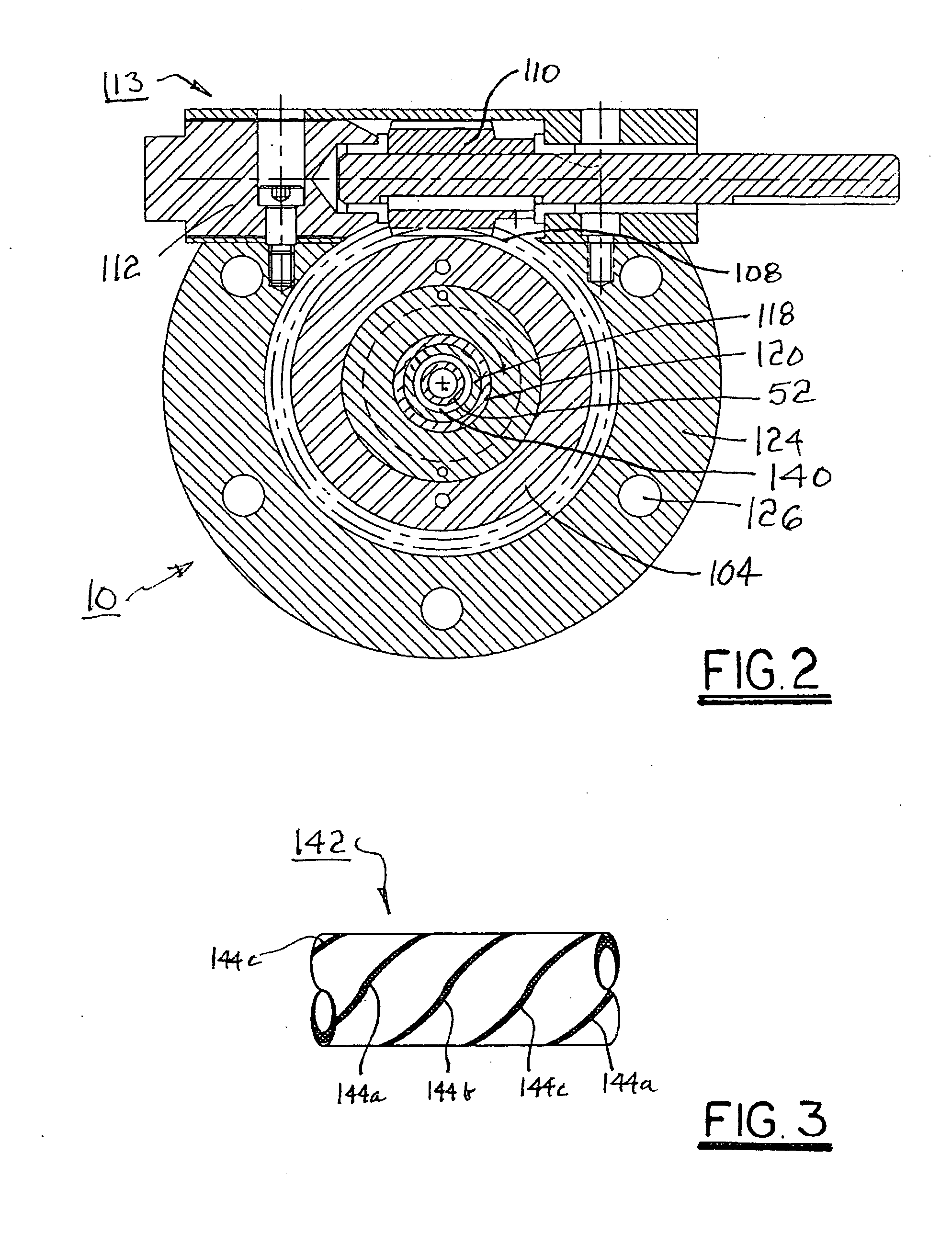
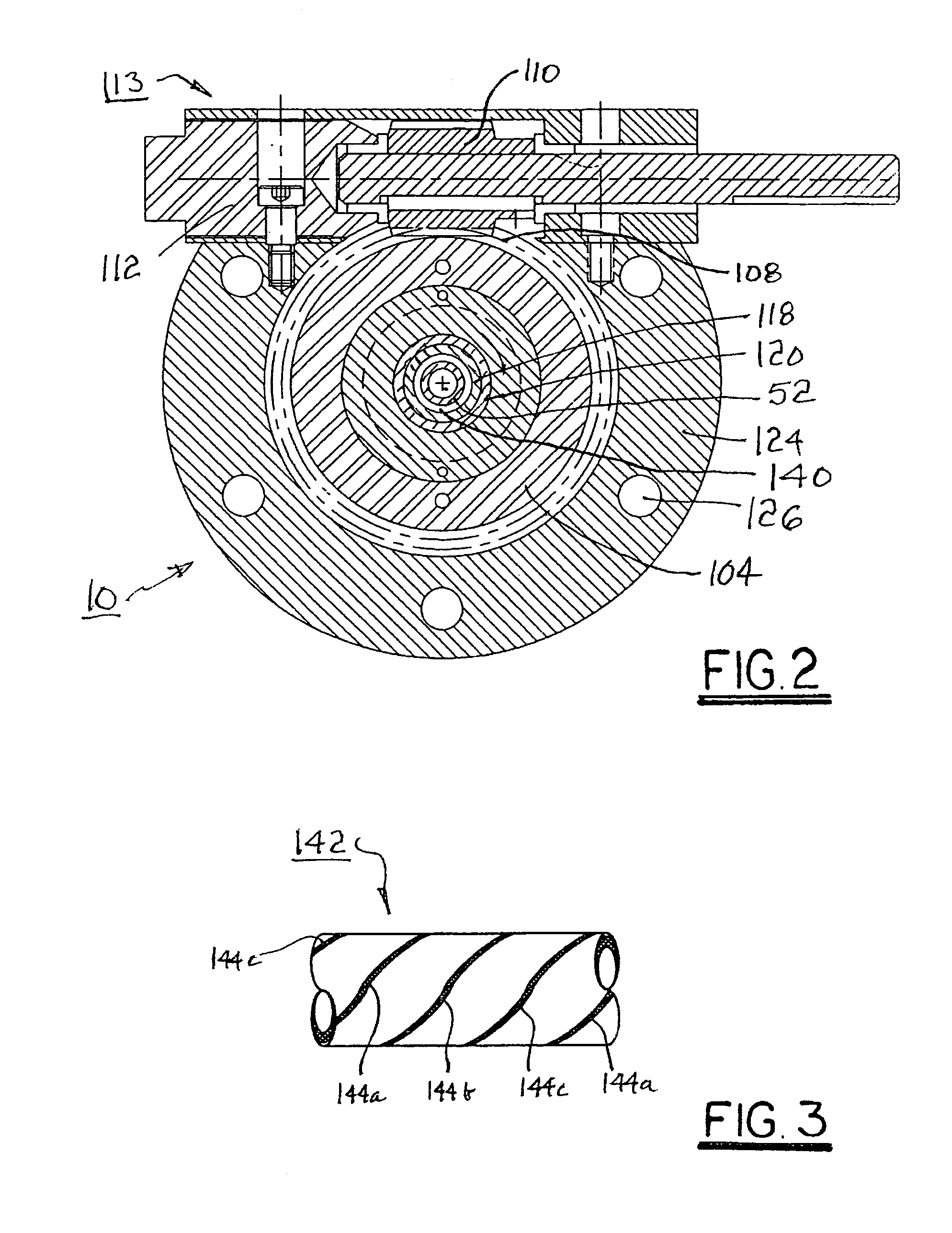
Rotatable head for forming spiral extrusions
InactiveUS20050260408A1Increase sealing forceAvoid pollutionConfectioneryFilament/thread formingEngineeringCounterbore
A polymer extrusion crosshead assembly for forming a spirally-striped extrusion. The assembly includes conventional components for admitting, turning, and accelerating primary molten polymer toward a novel rotating die sub-assembly. A body element includes an axial counterbore for receiving a manifold supply block in communication with a source of secondary striping polymer. A wear plate is attached to the manifold block. The die sub-assembly includes a striping die having an annular passage for conveying the primary polymer to form an extruded tube or a core material coating. The die is loaded against the wear plate by a Belleville washer. The die includes one or more striping nozzles in communication with the manifold block for injecting secondary striping polymer into the annular stream of primary polymer flowing through the die, creating a longitudinal stripe of striping polymer. Rotating the die while extruding both polymers yields a helically striped (spiral) extrusion.
Owner:CANGEN HLDG
Aqueous emulsion polymerization process for producing fluoropolymers
InactiveUS20040072977A1Reduced coagulumThe polymerization process is simpleFibre treatmentPolymer scienceEmulsion polymerization
The present invention provides a method of making a fluoropolymer through emulsion polymerization of one or more fluorinated monomers in an aqueous phase in the presence of a fluorinated surfactant. At least part of the fluorinated surfactant is added to the aqueous phase as an aqueous mixture with at least one organic liquid that is not miscible with water and that is selected from halogenated and non-halogenated organic liquids, the mixture having droplets having an average droplet diameter of not more than 1000 nm and the mixture being added to the aqueous phase in such an amount that the total amount of the fluorinated surfactant is not more than 1% by weight based on the weight of the aqueous phase and the total amount of said organic liquid is not more than 1% by weight based on the weight of said aqueous phase. The invention allows for an improvement of the efficiency of an aqueous emulsion polymerization process. In particular, the polymerization time can be reduced and the polymer yield may be improved.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
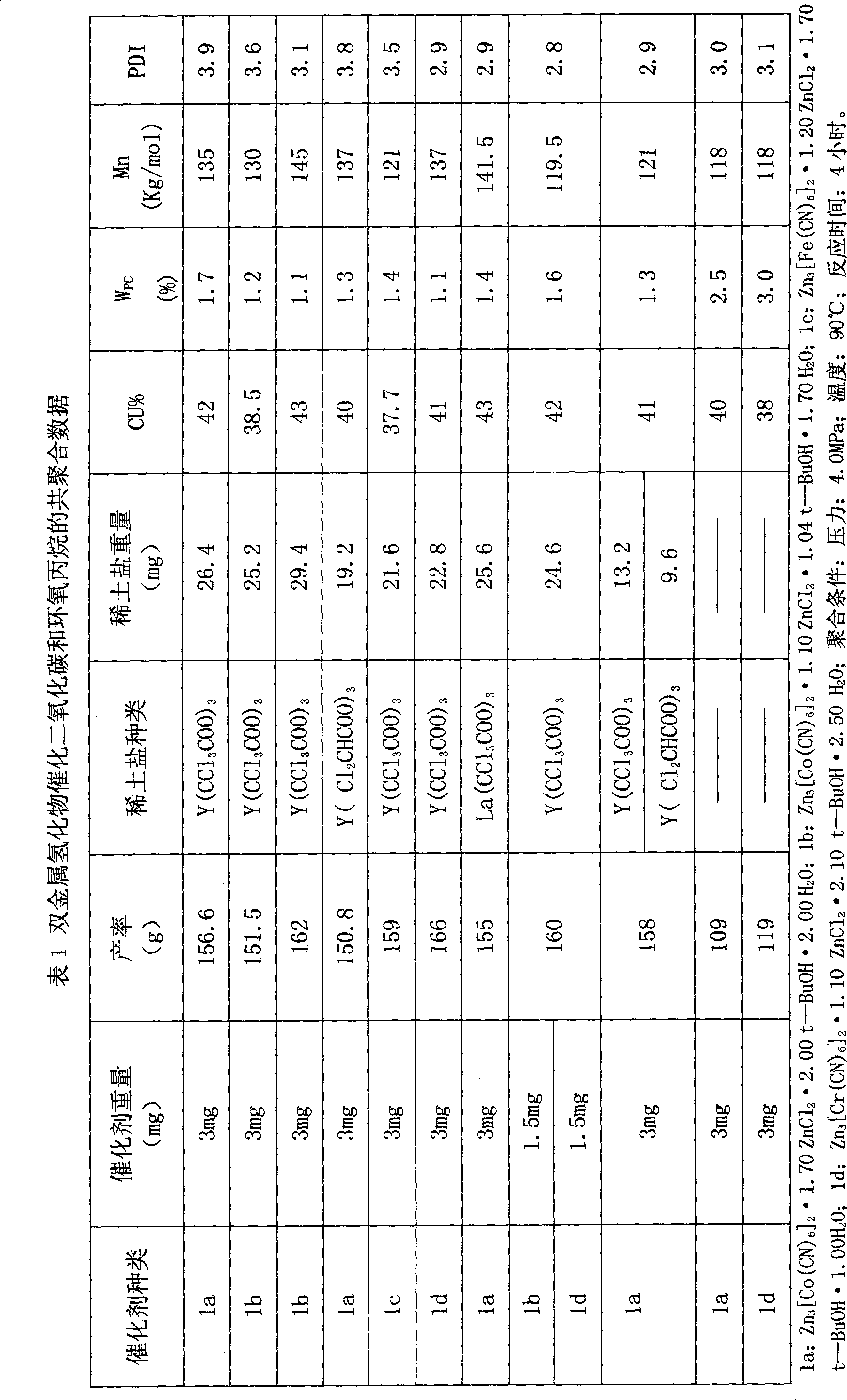
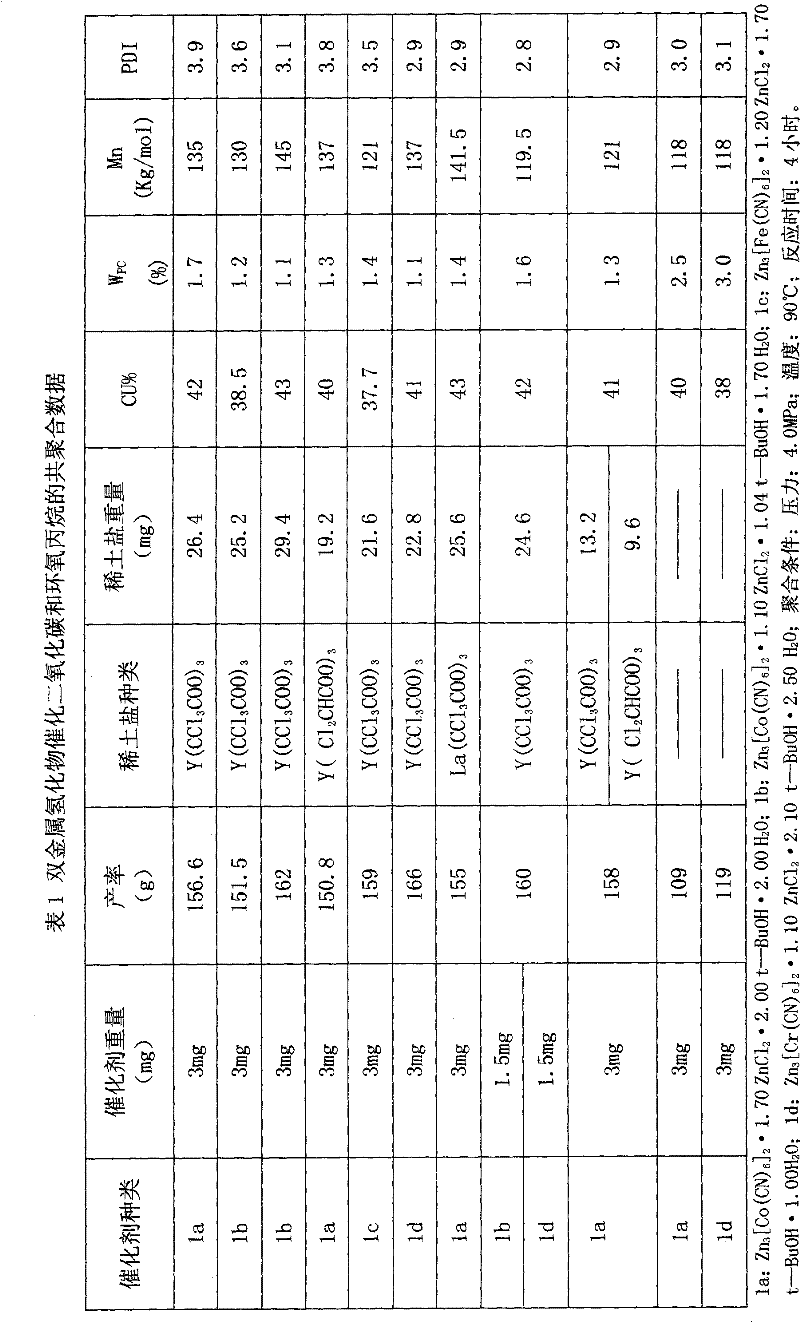
Double metal cyanide-rare earth compound composite catalyst for CO2-epoxypropane copolymerization
The invention provides a double metal cyanide-rare earth compound composite catalyst for CO2-epoxypropane copolymerization. In the catalyst, the mol ratio of the metal Co, Fe, Ni or Cr to La, Pr, Nd, Yb, Lu or Y of rare earth is 1:1-1:16. When the catalyst is used for the CO2-epoxypropane copolymerization, the weight content of cyclic carbonate ester in a reaction mixture is less than 2 percent, the polymer yield in a crude product is improved by more than 30 percent compared with the condition that only the double metal cyanide is used as the catalyst, and the maximum catalysis efficiency can reach 52kg of polymer in 1g of compound DMC (Dimethyl Carbonate). In the copolymer, the content of carbonic ester is more than 35 percent, and the content of Mn is more than 100,000g / mol.
Owner:中科应化(长春)科技有限公司
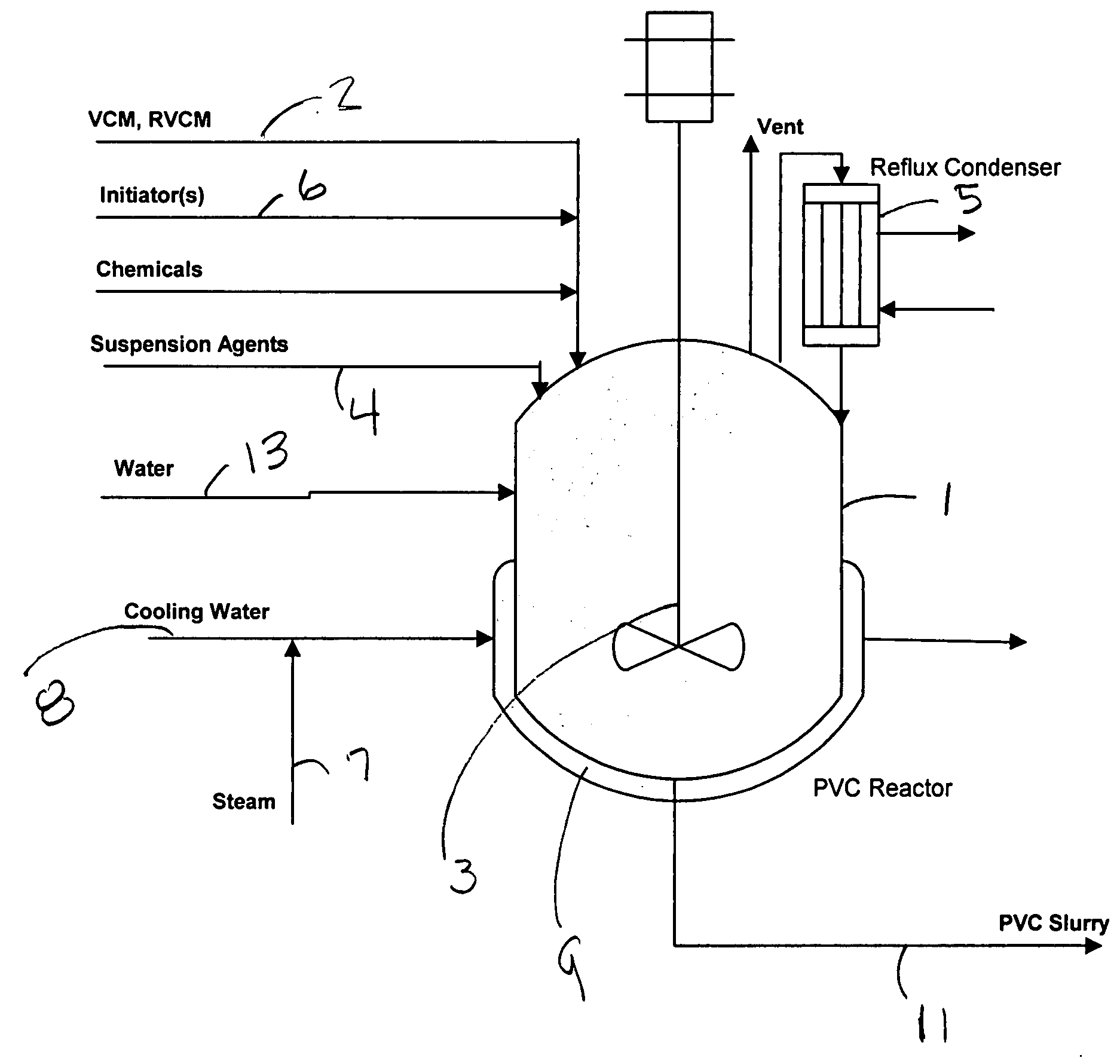
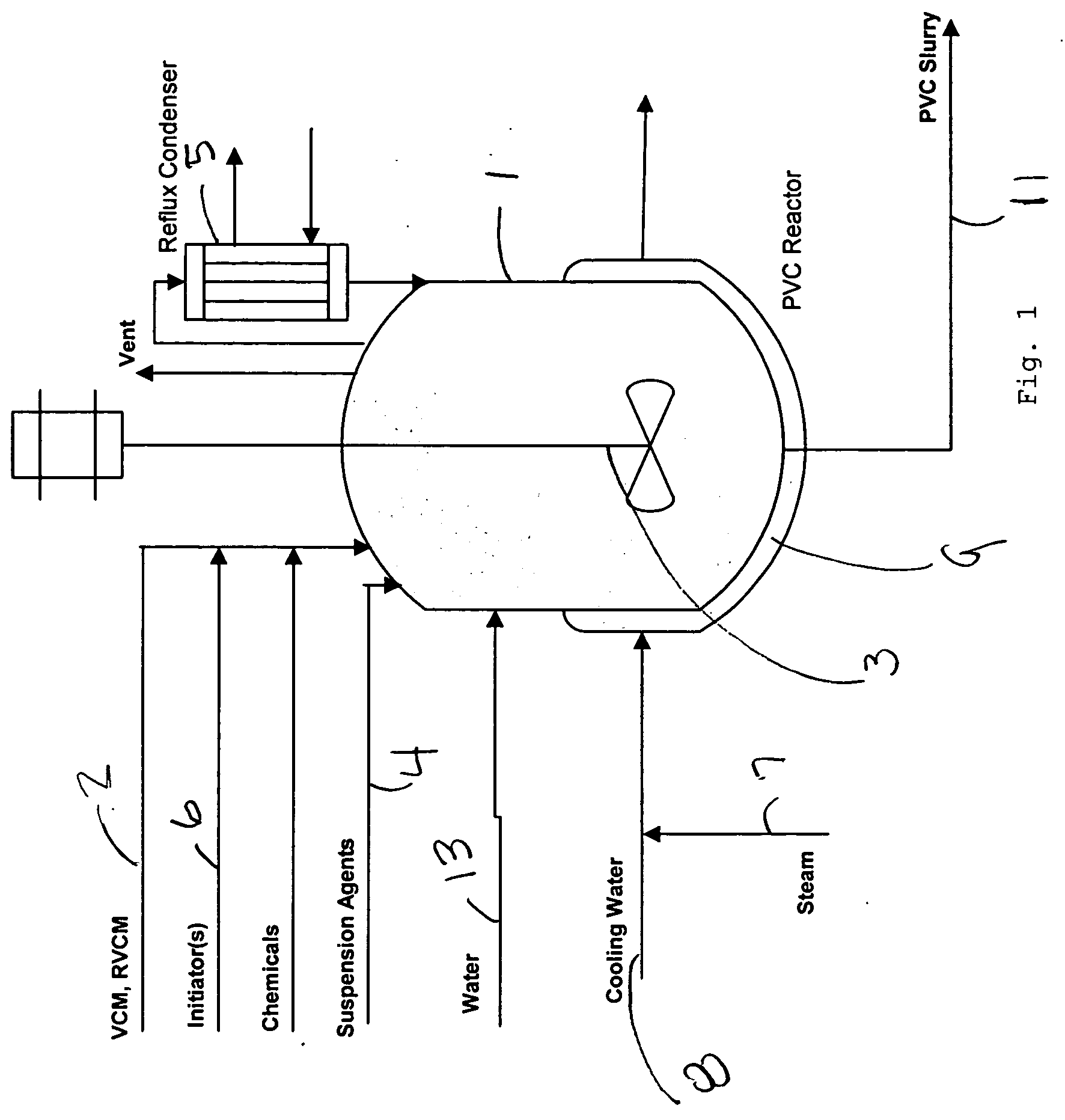
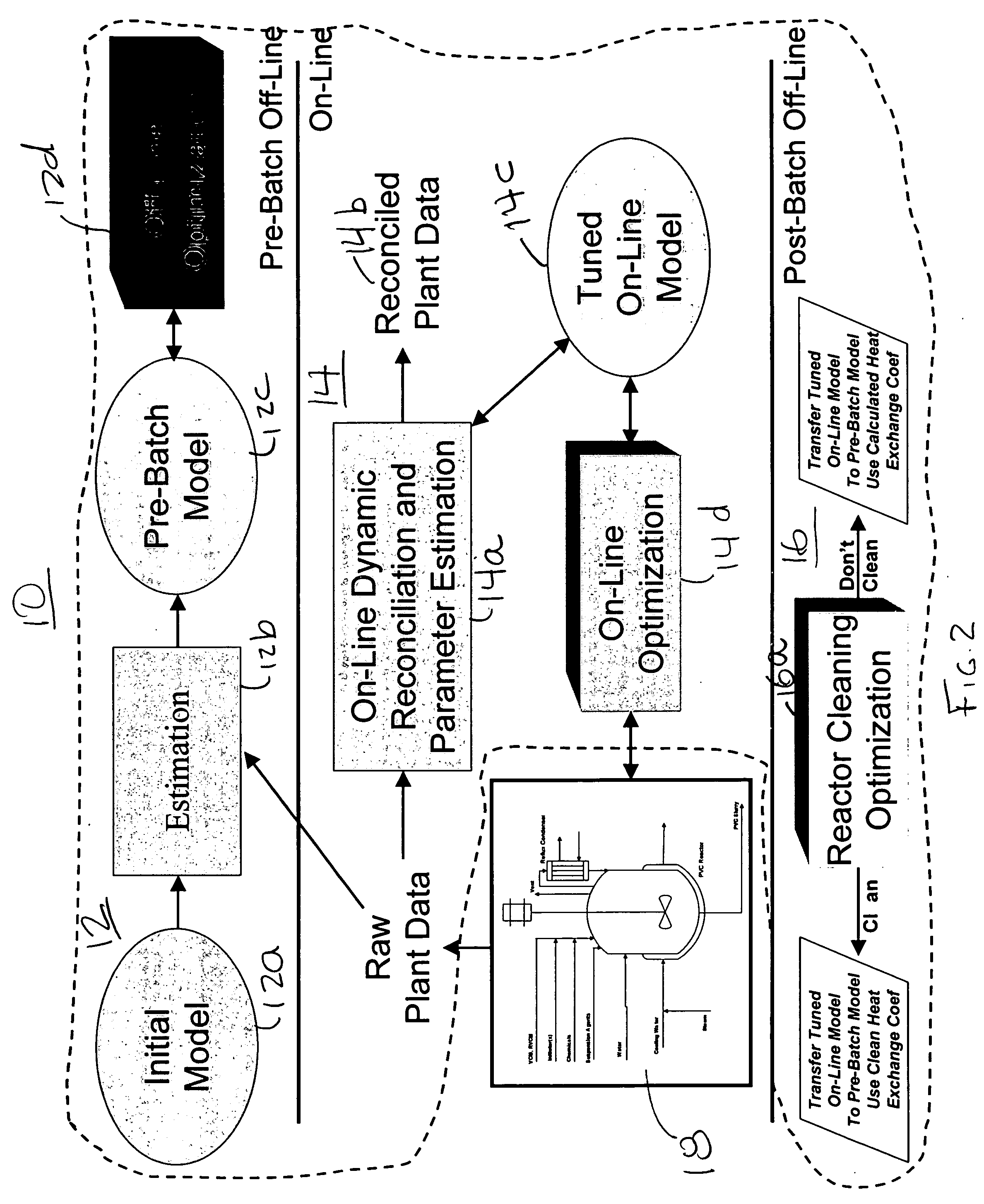
Polymer reaction and quality optimizer
A polymer reaction and quality optimizer that optimally determines all factors affecting the finished polymer prior to initiating the batch, uses the optimized parameters in setting up and starting the batch, in an on-line procedure for correcting assumptions made in the optimal determination based upon measurement responses from batch startup, and in an on-line procedure that periodically executes to determine and adapt reactor temperature control profiles across the remaining life of the batch to achieve the desired polymer properties and optimal polymer yield. The reaction and quality optimizer also determines at the end of a batch using several criteria if any of the equipment used within the process such as the reactor should be cleaned.
Owner:ABB INC
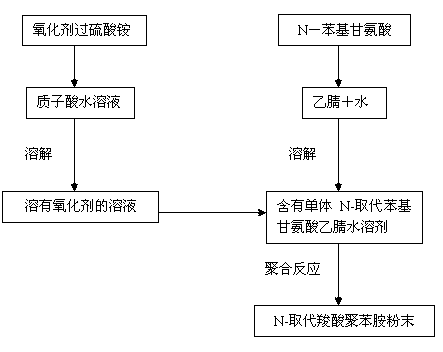
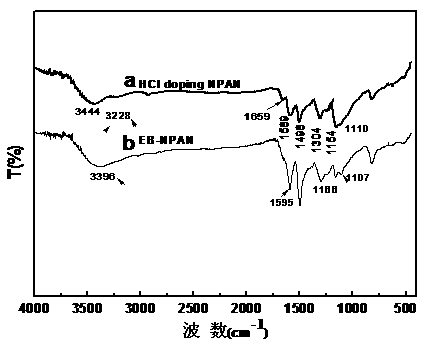
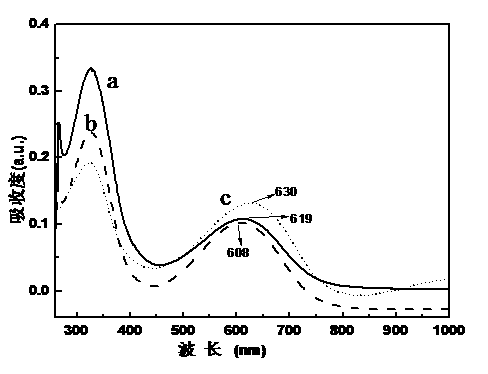
Chemical oxidation preparation method for novel N-substituted carboxyl polyaniline
The invention discloses a chemical oxidation preparation method for novel N-substituted carboxyl polyaniline. According to the method, the N-substituted carboxyl polyaniline polymer is prepared through a chemical oxidation method by taking N-phenylglycine as a monomer, and the method comprises the following steps: dissolving a certain amount of N-phenylglycine (N-AN) monomer in a mixed solution of acetonitrile and water in a certain volume; dissolving a certain amount of oxidant ammonium persulfate (NH4)3S2O3 in a prepared hydrochloric acid aqueous solution in a certain size; and slowly dripping the solution dissolved with the oxidant ammonium persulfate into a monomer, so that the monomer is completely reacted, and treating to obtain the N-substituted carboxyl polyaniline powder. The polymer prepared by the method has the yield of 89 weight percent and the electric conductivity of 1.5*10<-1>S / cm, and the N-substituted carboxyl polyaniline has excellent dissolving performance. The obtained polymer powder can be applied to conductive high polymer materials in the fields of secondary batteries, sensors, solar cells and the like.
Owner:EAST CHINA JIAOTONG UNIVERSITY
Hydrocarbon type polymer electrolyte, membrane/electrode assembly, and fuel cell power source
InactiveUS20080032173A1Low costImprove ionic conductivitySolid electrolytesActive material electrodesPolymer electrolytesFuel cells
An alkylenesulfonic group and / or an alkylenesulfo-ether group is introduced as an ionic conductivity-imparting group into a polyazole such as a polyimidazole, a polyoxazole, or a polythiazole each having good resistance to oxidation. The resulting polymer yields an electrolyte, an electrolyte membrane, and a membrane electrode assembly which are available at low cost, contains ionic conductivity-imparting groups stable over extended periods of time and satisfactorily resistant to oxidative degradation. This enables long-term continuous use of mobile cell power sources, dispersed cell power sources, and cell power sources for mobile units.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Method for preparing high-molecular weight aliphatic polycarbonate
The invention relates to a method for preparing high-molecular weight aliphatic polycarbonate. The method is characterized in that diphenyl carbonate and aliphatic diol are taken as raw materials, and then subjected to two-step reaction of melting ester exchange and polycondensation in a zinc-based catalysis system to obtain the high-molecular weight aliphatic polycarbonate. The zinc-based catalyst takes zinc halide, zinc glutarate and zinc acetate as active components, the active components are loaded on the surface of an inorganic mesoporous material and an organic polymer material to obtain the catalyst, and the carrier mass accounts for 0-95 wt% of that of the catalyst mass. The method has the characteristics of fast reaction rate and high yield, in the invention, diphenyl carbonate and aliphatic diol are rapidly subjected to ester exchange and polycondensation to obtain the high-molecular weight aliphatic polycarbonate. A synthesis polymer is a white solid, the color is good, the number-average molecular weight is more than 100000, the polymer can be used as plastic, and the polymer yield can reach as high as 95%. The method has the advantages of simple process, large synthesis polymer molecular weight, and high yield, and has good industrial application prospect.
Owner:CHENGDU ORGANIC CHEM CO LTD CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Rotatable head for forming spiral extrusions
InactiveUS7247012B2Increase sealing forceAvoid pollutionConfectioneryFilament/thread formingEngineeringBelleville washer
A polymer extrusion crosshead assembly for forming a spirally-striped extrusion. The assembly includes conventional components for admitting, turning, and accelerating primary molten polymer toward a novel rotating die sub-assembly. A body element includes an axial counterbore for receiving a manifold supply block in communication with a source of secondary striping polymer. A wear plate is attached to the manifold block. The die sub-assembly includes a striping die having an annular passage for conveying the primary polymer to form an extruded tube or a core material coating. The die is loaded against the wear plate by a Belleville washer. The die includes one or more striping nozzles in communication with the manifold block for injecting secondary striping polymer into the annular stream of primary polymer flowing through the die, creating a longitudinal stripe of striping polymer. Rotating the die while extruding both polymers yields a helically striped (spiral) extrusion.
Owner:CANGEN HLDG
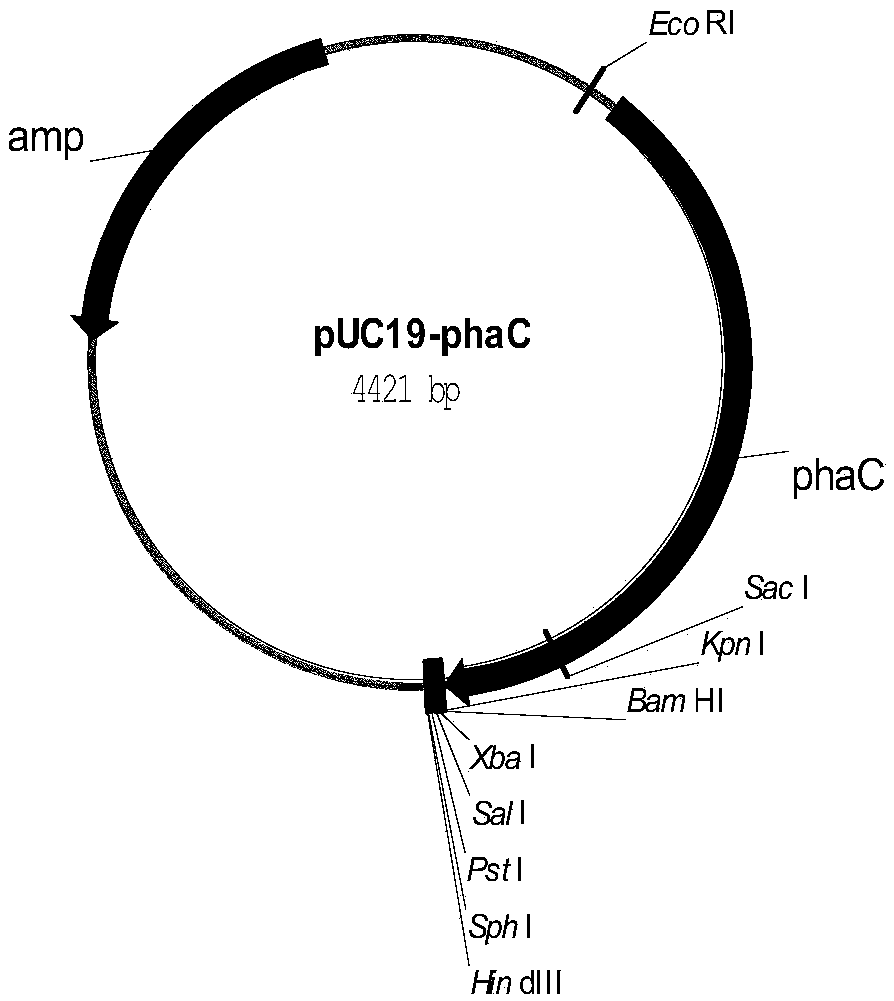
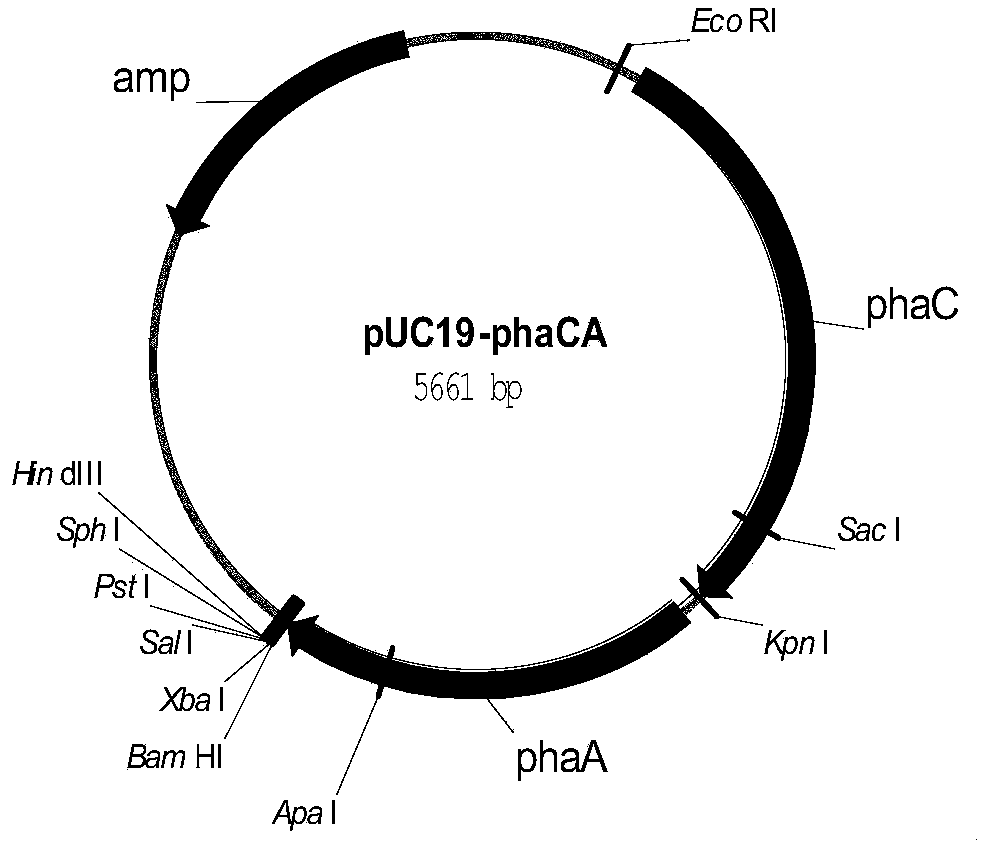
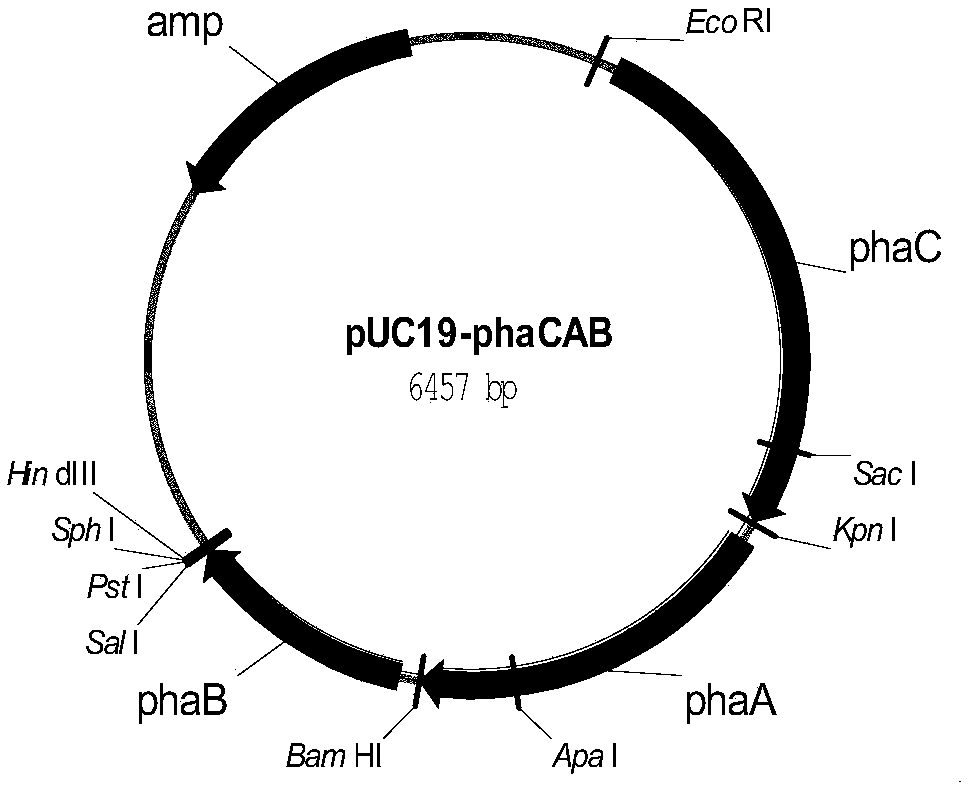
Genetic engineering bacteria for producing lactic acid and 3-hydroxybutyrate copolyester, construction method and application thereof
The invention discloses genetic engineering bacteria for producing lactic acid and 3-hydroxybutyrate copolyester, and a construction method and application thereof. The genetic engineering bacteria for producing lactic acid and 3-hydroxybutyrate copolyester are obtained by the following steps: knocking out the poxB gene, pflB gene and aceEF gene of a recipient bacterium; and increasing the contentof protein encoded by the phaA gene, phaB gene, phaC gene and pct gene. With the genetic engineering bacteria, lactic acid and 3-hydroxybutyrate copolyester can be synthesized by the use of glucose and acetic acid, and the polymer yield of the recombinant bacteria in the shake-flask culture can reach a high level. The ratio of lactic acid to 3-hydroxybutyrate monomer can be controlled by changingthe concentration of glucose and acetic acid. The invention has a good application prospect.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Preparation method of chlorogenic acid uniformly-imprinted microspheres
InactiveCN104403045AUniform particle sizeReduce sizeOther chemical processesPolymer scienceFunctional monomer
The invention discloses a preparation method of chlorogenic acid uniformly-imprinted microspheres, which comprises the following steps: dissolving chlorogenic acid and functional monomer MMA (methacrylic acid) in a mole ratio of 1:3-1:5 in an acetonitrile-toluene-DMSO (dimethyl sulfoxide) mixed solution, oscillating at room temperature for 3-7 hours, adding a crosslinking agent DVB (divinylbenzene) and a right amount of initiator AIBN (2,2'-azobisisobutyronitrile), transferring the mixture into a glass ampoul, introducing nitrogen for 5-15 minutes, sealing the ampoul, carrying out rotary polymerization at 60 DEG C for 24 hours, precipitating with methanol, precipitating with tetrahydrofuran, and filtering. The uniformly-imprinted microspheres with the diameter of about 2.5 mu m are prepared by using chlorogenic acid as the template molecule by a precipitation polymerization process. The polymer yield is 35-40%; and the molecularly imprinted polymer has uniform particle size and proper size, can be conveniently used as a liquid chromatography separation material and for preparation, separation and purification, and has the advantages of favorable separation efficiency, high extraction yield and wide application prospects.
Owner:JISHOU UNIVERSITY
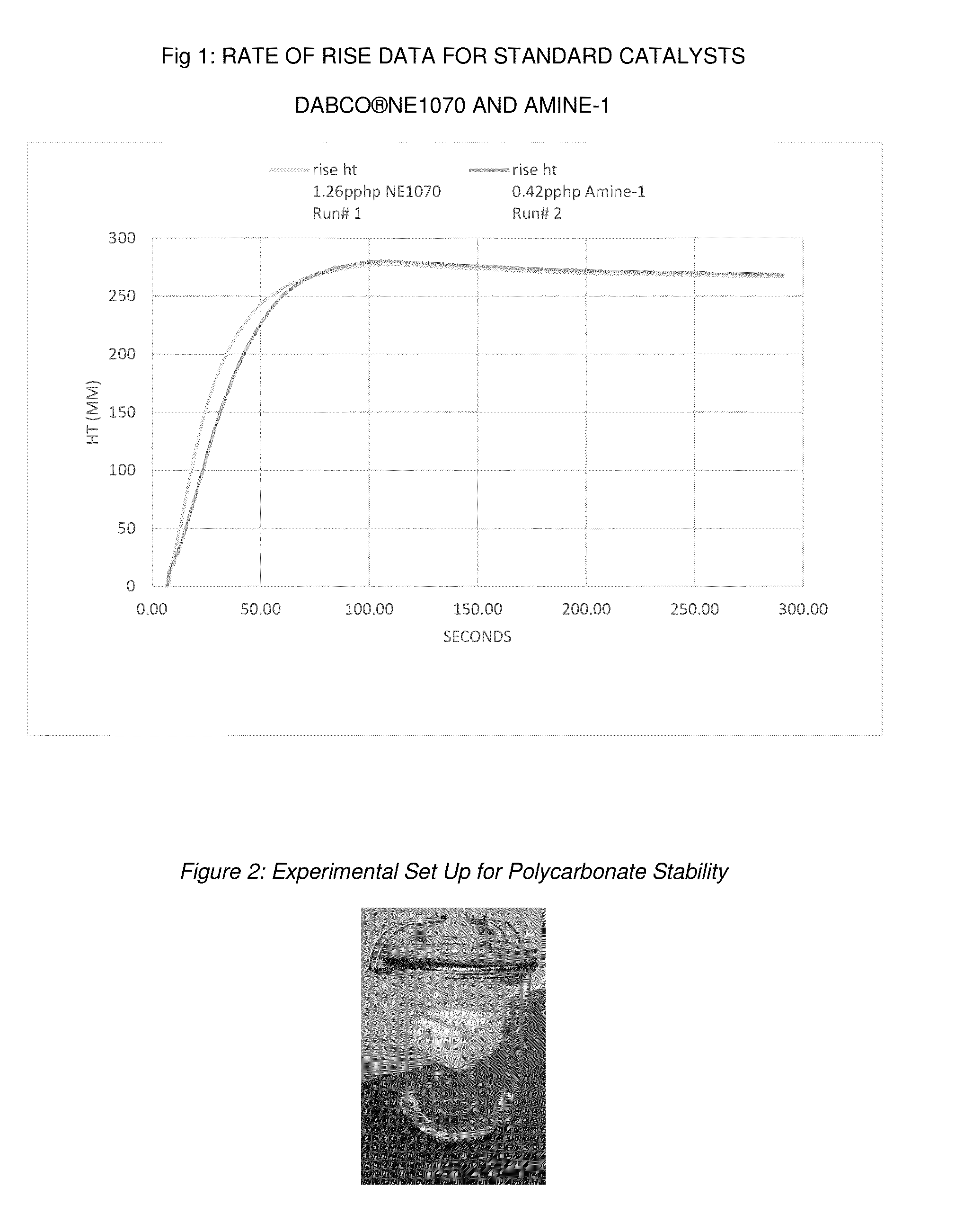
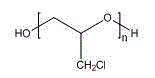
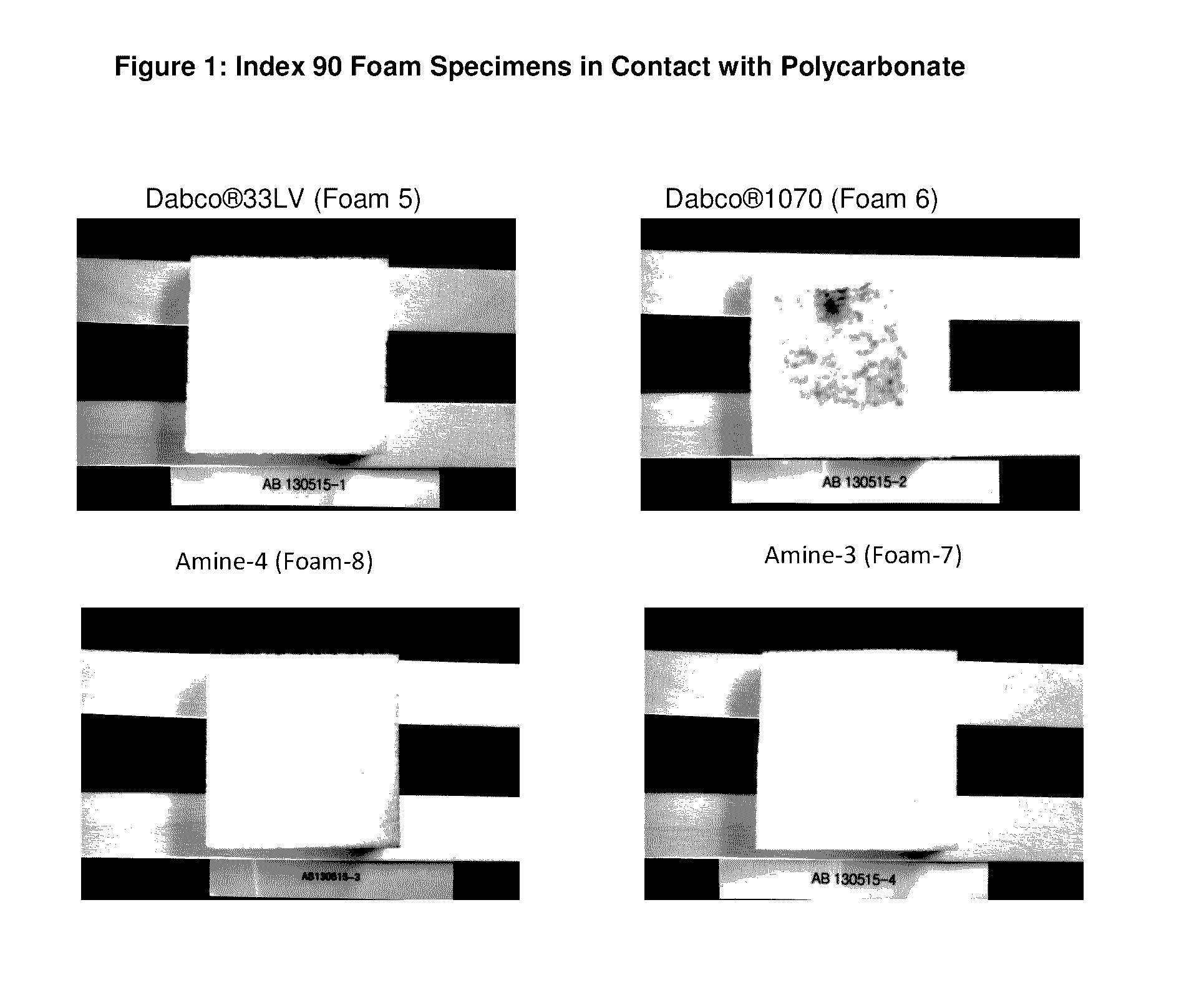
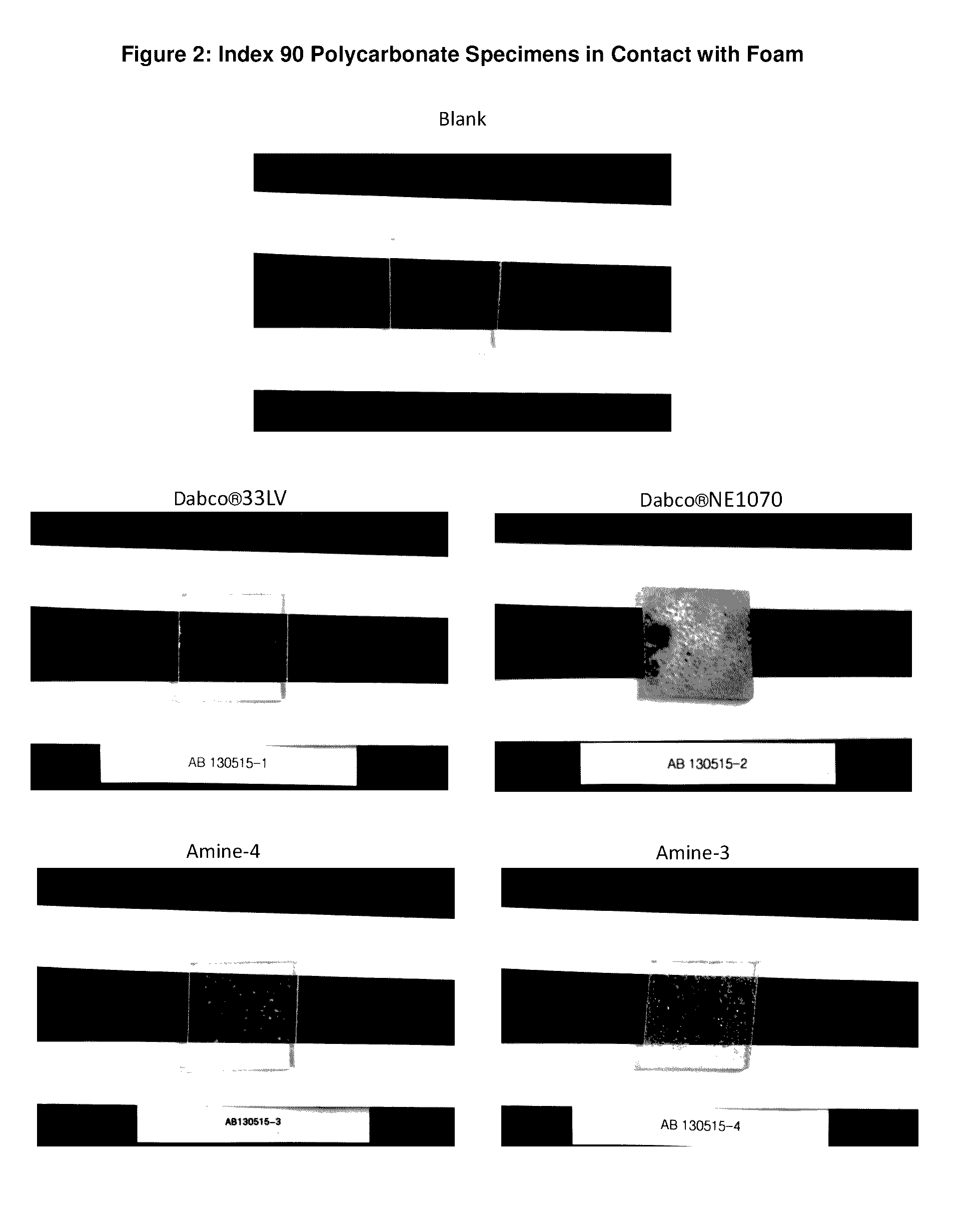
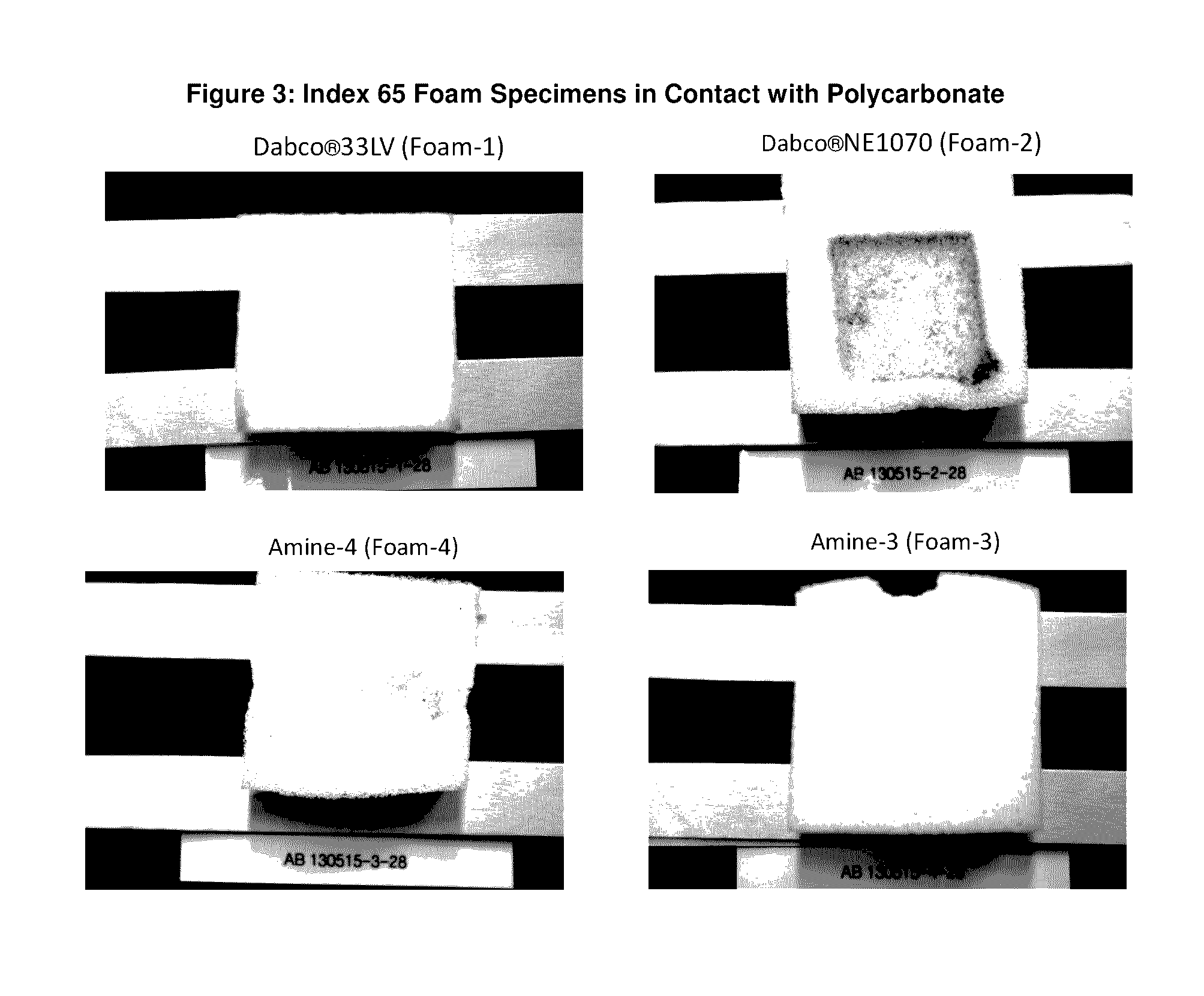
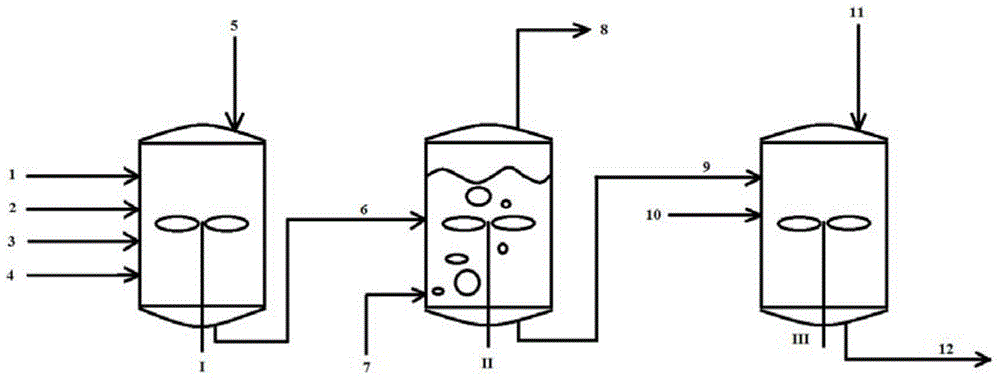
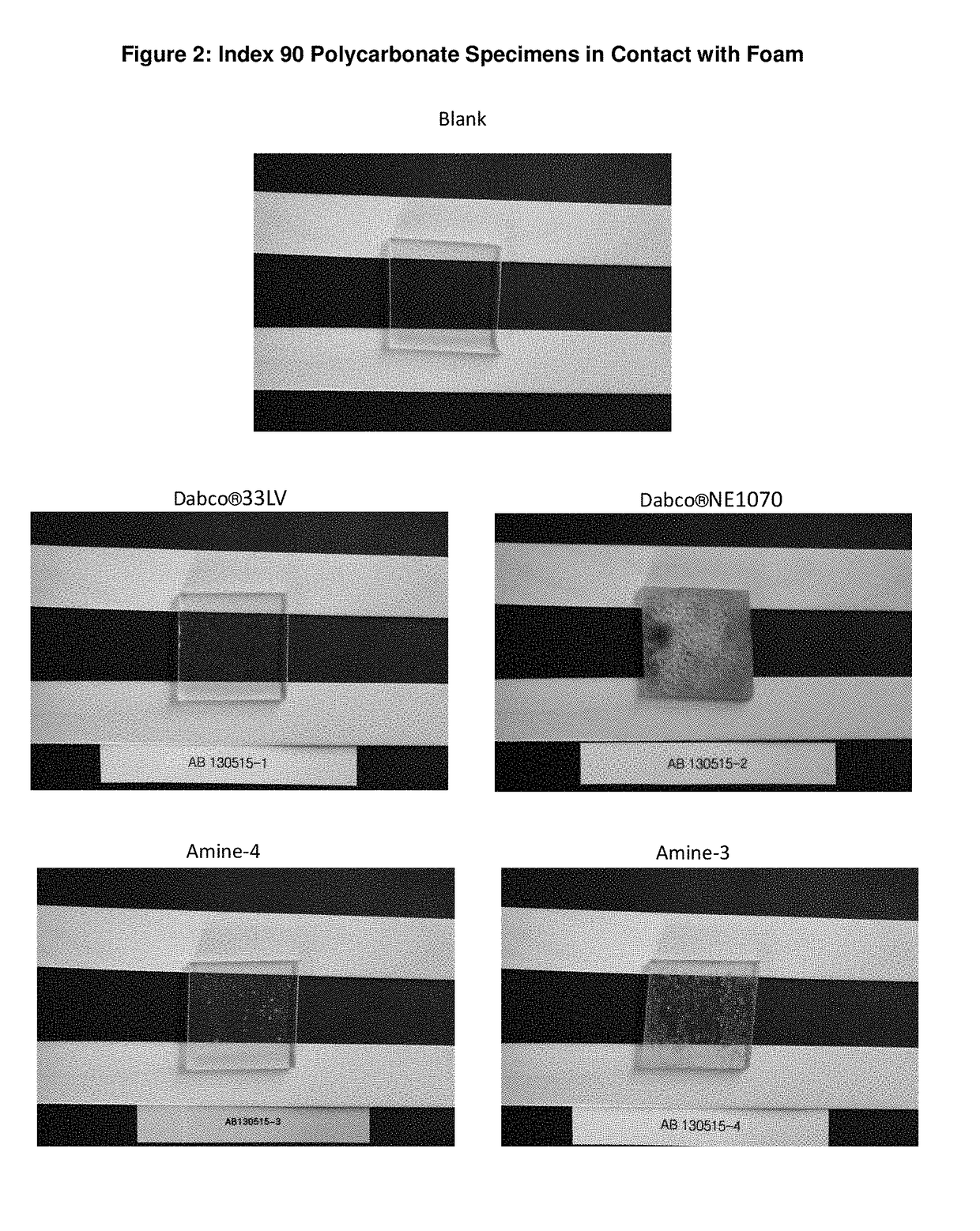
Low Emissions Polyurethane Foam Made with Isocyanate Reactive Amine Catalyst
InactiveUS20160075817A1Reduce amine emissionReduce turnCarboxylic acid nitrile preparationOrganic compound preparationPolymer yieldAqueous solution
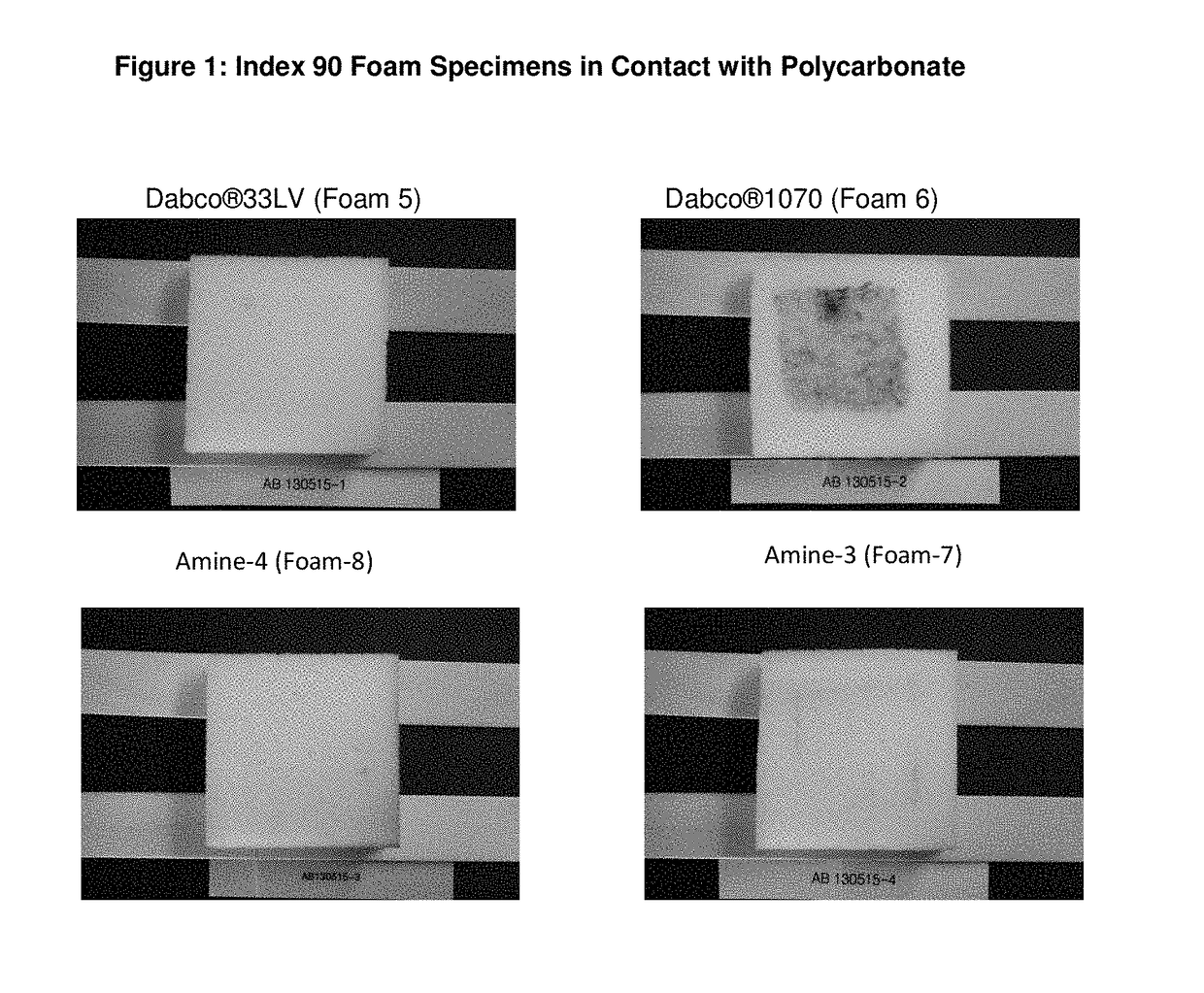
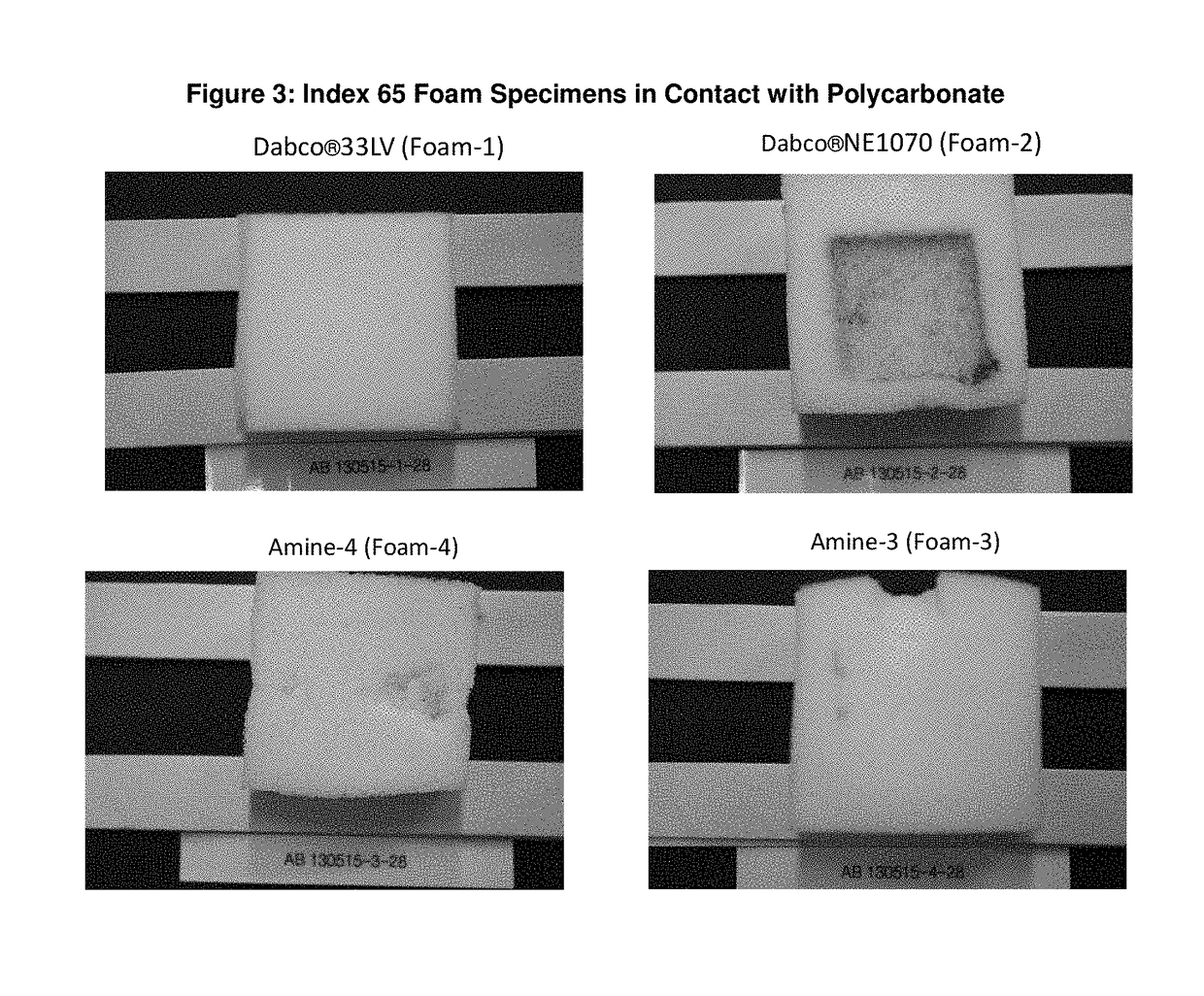
Tertiary amine catalysts having isocyanate reactive groups that are capable of forming thermally stable covalent bonds able to withstand temperatures from 120° C. and higher and up to 250° C. are disclosed. These catalyst can be used to produce polyurethane foam having the following desirable characteristics: a) very low chemical emissions over a wide range of environmental conditions and isocyanate indexes (e.g., indexes as low as 65 but higher than 60) ; b) sufficient hydrolytic stability to maintain the catalyst covalently bound to foam without leaching of tertiary amine catalyst when foam is exposed to water or aqueous solutions even at temperatures higher than ambient (temperature range 25° C. to 90° C.); and c) stable contact interface between the polyurethane polymer and other polymers (for example polycarbonate) with minimal migration of tertiary amine catalyst from polyurethane polymer to other polymers yielding no noticeable polymer deterioration at the point of contact even under conditions of heat and humidity.
Owner:EVONIK DEGUSSA GMBH
Method for preparing vinyl chloride pasty resin
A process for preparing a vinyl chloride paste resin comprises the following steps: homogenizing a vinyl chloride monomer in an aqueous medium together with an oil-soluble polymerization initiator to form a first aqueous dispersion, and subjecting the first dispersion to a micro-suspension polymerization wherein a second aqueous dispersion containing a vinyl chloride monomer and a surface active agent is added to the reaction system in such a manner that the addition is started after starting the polymerization but by the time the polymerization conversion of the initially charged monomer reaches 30%, and is terminated by the time the polymerization conversion of the initially charged monomer reaches 95%. The process has an improved productivity since the heat removing area of a jacket of a reactor is prevented from lowering during the polymerization to increase the amount of heat removed and since the polymer yield per unit volume of the reactor is increased.
Owner:KANEKA CORP
Method for preparing polyepichlorohydrin by catalyzing epichlorohydrin polymerization by using three-element iron catalyst
The invention discloses a method for preparing polyepichlorohydrin by catalyzing epichlorohydrin polymerization by using a three-element iron catalyst, belonging to the field of polymer preparation and solving the problem of low activity of the catalyst for synthesizing polyepichlorohydrin from polymerization, and small molecular weight and wide PDI distribution of the obtained product in the prior art. The three-element iron catalyst (iron compound, alkyl aluminum compound or electron donor) is adopted to catalyze epichlorohydrin homopolymerization to obtain the polyepichlorohydrin, of which the molecular weight is 10000 above, the polymer color is light and the PDI distribution is 1.2 or so; and the reaction is easy to control. The catalyst is easy to prepare and has the advantage of high polymer yield. The iron compound is iron naphthenate, iron neodecanoate, iron isooctoate or the like; the organic aluminum compound is triisobutylaluminum, triethyl aluminum, sesquialuminum or the like; and the electron donor is tri-ortho-methylphenyl phosphite, diethyl phosphite, tributyl phosphate or the like.
Owner:山东菏泽玉皇化工有限公司
Hydrocarbon type polymer electrolyte, membrane/electrode assembly, and fuel cell power source
InactiveCN101117382AStable power generationIncrease output powerSolid electrolytesCell electrodesContinuous useElectrical battery
An alkylenesulfonic group and / or an alkylenesulfo-ether group is introduced as an ionic conductivity-imparting group into a polyazole such as a polyimidazole, a polyoxazole, or a polythiazole each having good resistance to oxidation. The resulting polymer yields an electrolyte, an electrolyte membrane, and a membrane electrode assembly which are available at low cost, contains ionic conductivity-imparting groups stable over extended periods of time and satisfactorily resistant to oxidative degradation. This enables long-term continuous use of mobile cell power sources, dispersed cell power sources, and cell power sources for mobile units.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Preparation method of halogenated polymer
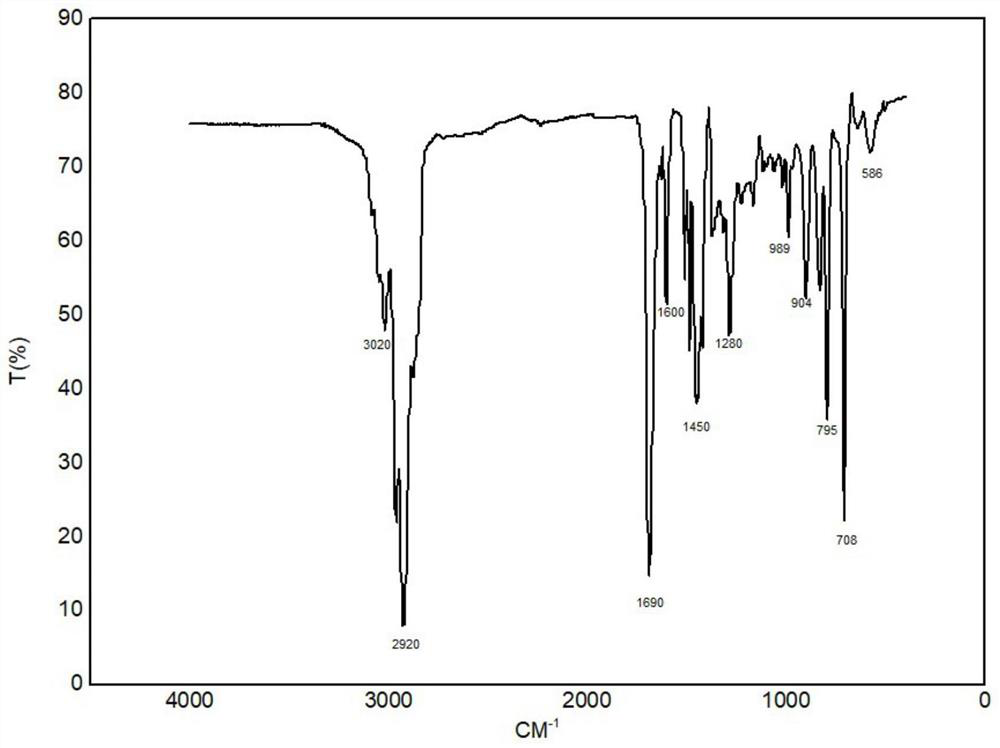
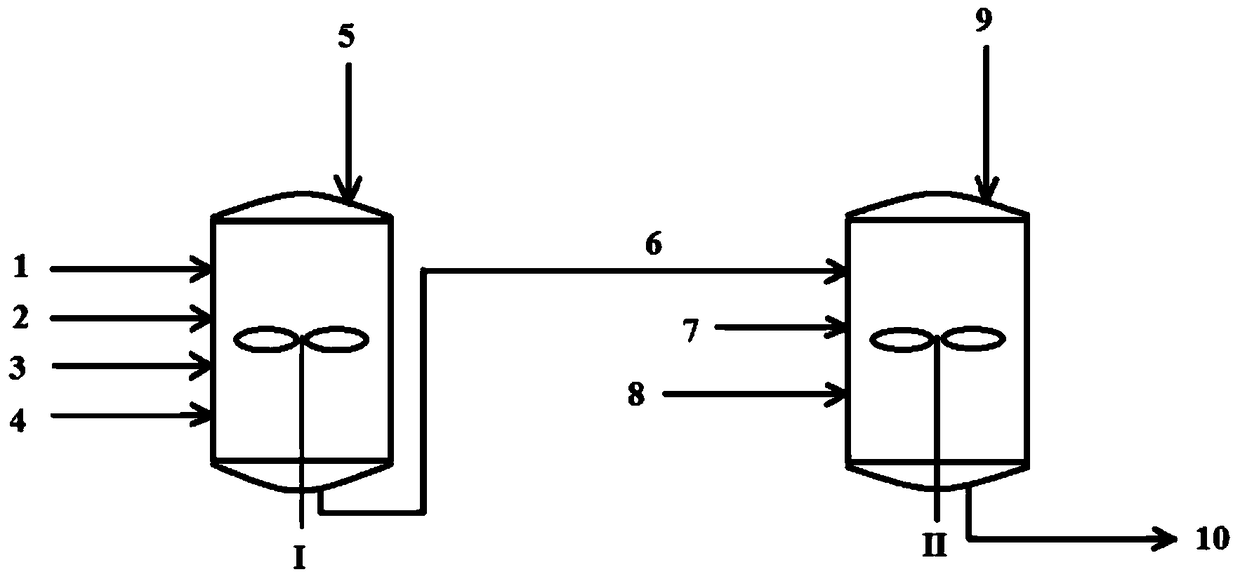
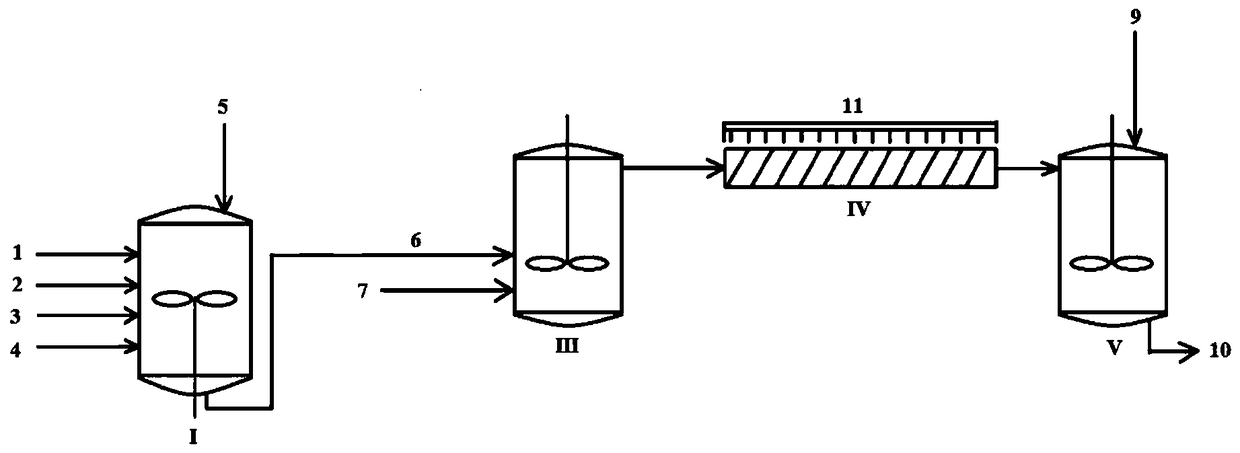
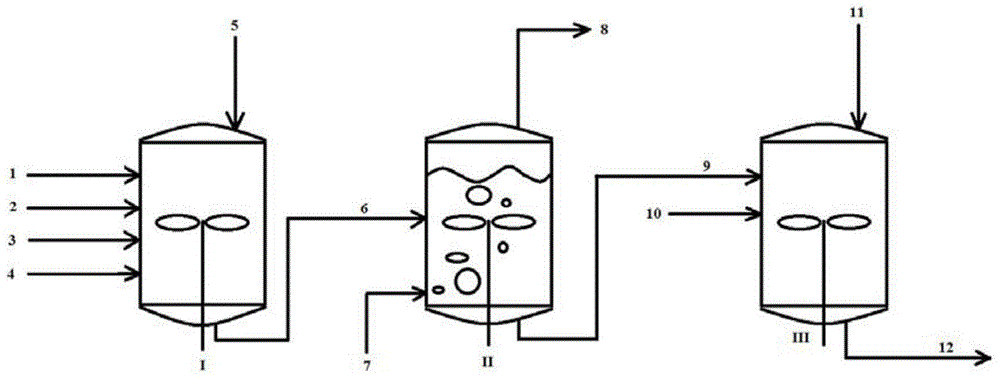
The invention discloses a preparation method of a halogenated monoolefine-conjugated diene copolymer. The method comprises steps as follows: under the cationic polymerization condition, monoolefine shown in a formula II and conjugated diene shown in a formula III are contacted with components in an initiator system in a mixed solvent of alkane and haloalkane, halogenated alkane in a solution obtained through polymerization is replaced with alkane, besides, after unreacted monomers are removed, a product is contacted with a compound containing halogen for a halogenating reaction, the initiator system contains a compound capable of providing carbocation, lewis acid and an activator, and the activator is selected from a compound shown in the formula I-1 and a compound shown in a formula I-2. By means of the method, the polymerization efficiency can be remarkably improved, and the higher polymer yield is obtained; the polymer with higher molecular weight can also be obtained. By means of the method, the polymer redissolving process required with a slurry polymerization method is omitted, and the production process is simplified.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Reactive amine catalysts for polyurethane applications
ActiveUS20160347901A1Reduce amine emissionReduce turnUrea derivatives preparationOrganic compound preparationPolycarbonateAqueous solution
Tertiary amine catalysts having isocyanate reactive groups that are capable of forming thermally stable covalent bonds able to withstand temperatures up to 120° C. are disclosed. These catalyst can be used to produce polyurethane foam having the following desirable characteristics: a) very low chemical emissions over a wide range of environmental conditions and isocyanate indexes (e.g. indexes as low as 65 but higher than 60) while meeting all physical property requirements; b) sufficient hydrolytic stability to maintain the catalyst covalently bound to foam without leaching of tertiary amine catalyst when foam is exposed to water or aqueous solutions even at temperatures higher than ambient (temperature range 25° C. to 90° C.); and c) stable contact interface between the polyurethane polymer and other polymers (for example polycarbonate) with minimal migration of tertiary amine catalyst from polyurethane polymer to other polymers yielding no noticeable polymer deterioration at the point of contact even under conditions of heat and humidity.
Owner:EVONIK OPERATIONS GMBH
Double metal cyanide-rare earth compound composite catalyst for CO2-epoxypropane copolymerization
The invention provides a double metal cyanide-rare earth compound composite catalyst for CO2-epoxypropane copolymerization. In the catalyst, the mol ratio of the metal Co, Fe, Ni or Cr to La, Pr, Nd, Yb, Lu or Y of rare earth is 1:1-1:16. When the catalyst is used for the CO2-epoxypropane copolymerization, the weight content of cyclic carbonate ester in a reaction mixture is less than 2 percent, the polymer yield in a crude product is improved by more than 30 percent compared with the condition that only the double metal cyanide is used as the catalyst, and the maximum catalysis efficiency can reach 52kg of polymer in 1g of compound DMC (Dimethyl Carbonate). In the copolymer, the content of carbonic ester is more than 35 percent, and the content of Mn is more than 100,000g / mol.
Owner:中科应化(长春)科技有限公司
Amphiphilic polymeric micro-spherical material uniform in grain size, preparation method and application
ActiveCN109942737AFix stability issuesSolve yieldWater contaminantsWater/sewage treatment by sorptionHydrophilic monomerDivinylbenzene
The invention discloses an amphiphilic polymeric micro-spherical material uniform in grain size, a preparation method and an application and belongs to the field of high molecular materials and solvesthe problems that an existing preparation method is hard to regulate grain size, low in polymer yield, poor in application effect and the like. The preparation method comprises the following steps: by taking N-vinyl pyrrolidone and divinylbenzene as a monomer, dispersing an emulsion uniformly in a water phase by a certain way; strengthening affiliation of the hydrophobic monomer divinylbenzene and the hydrophilic monomer N-vinyl pyrrolidone to increase the yield by means of proper water phase composition and proportion; and carrying out polymerization in conditions of a strict temperature androtating speed and the like to finally obtain the amphiphilic polymeric resin material uniform in grain size. Through serial representation and application evaluation, the material has very excellentamphiphilic performance, has a wide broad enriching and separating property to organic matters in a water body, and can be separately applied to the fields of analysis, detection, water treatment projects, household water purification and the like according to the grain sizes.
Owner:NANJING UNIV +1
Bimodal high density polyethylene and production process thereof
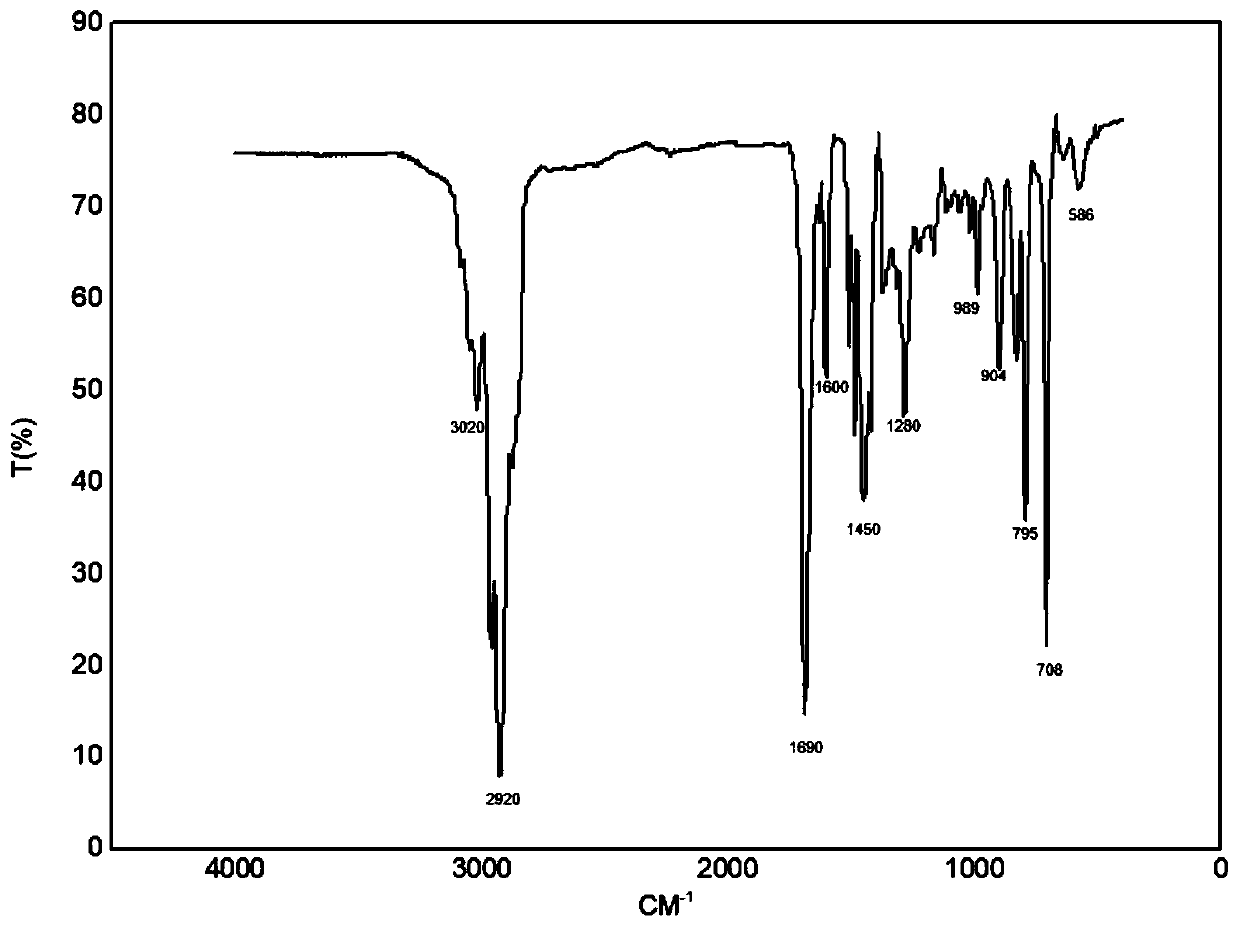
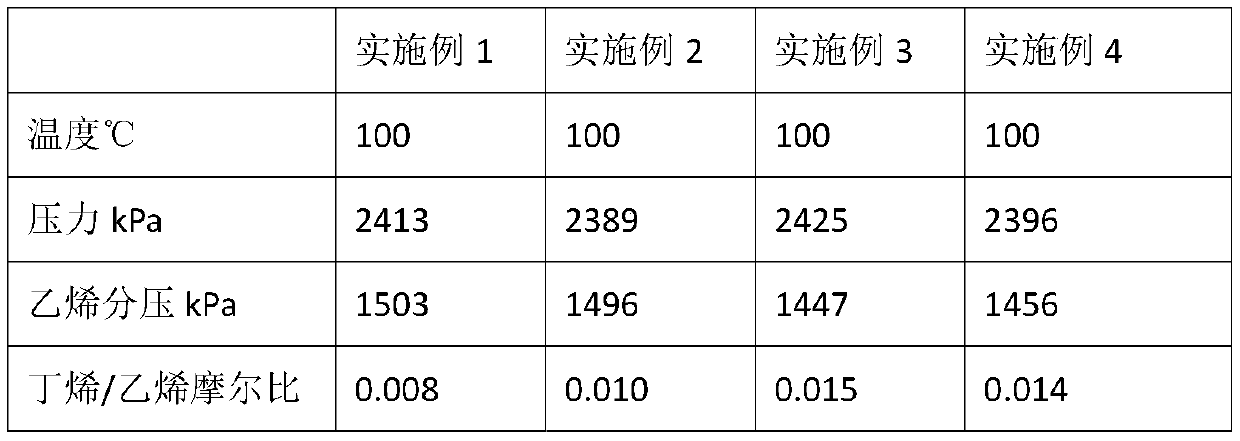
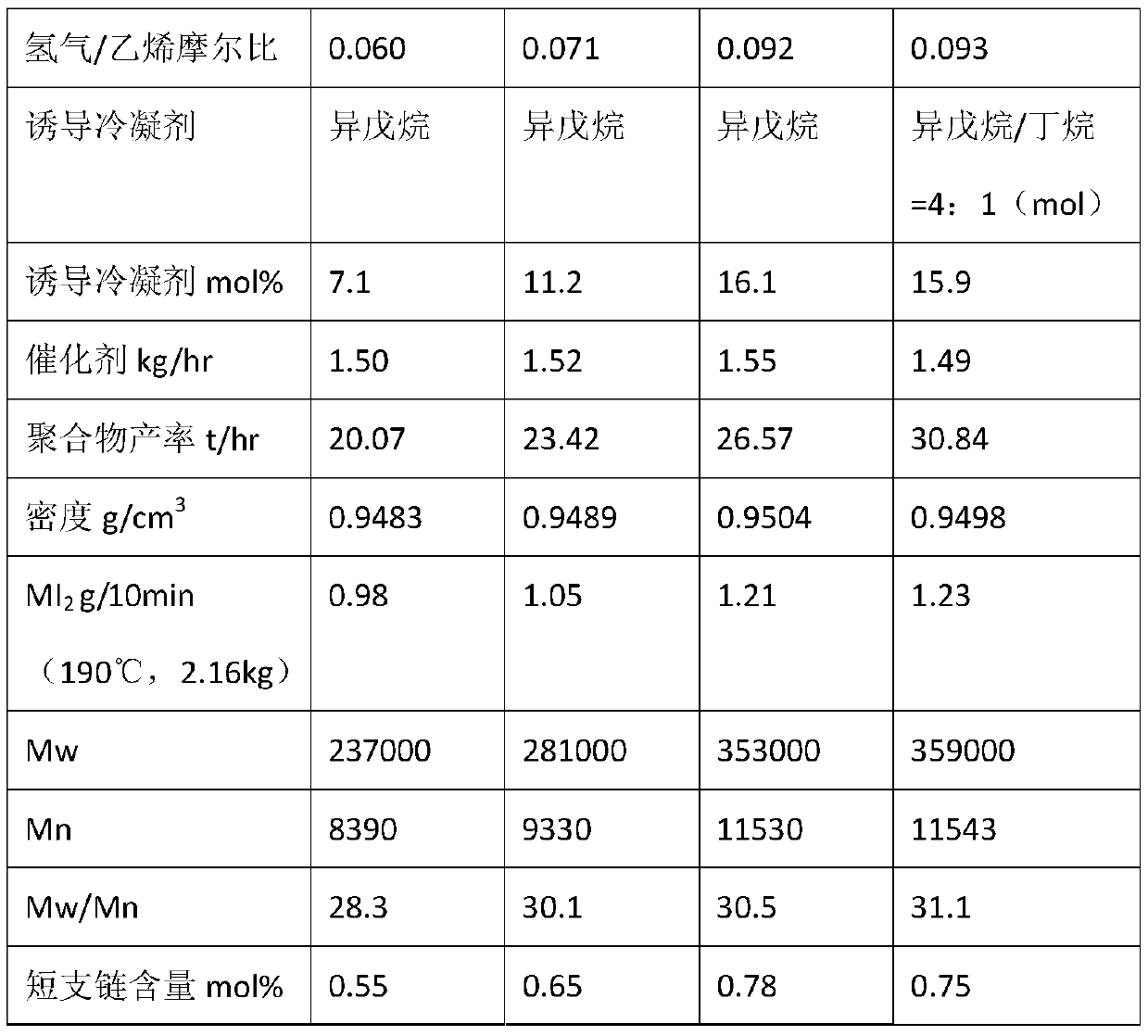
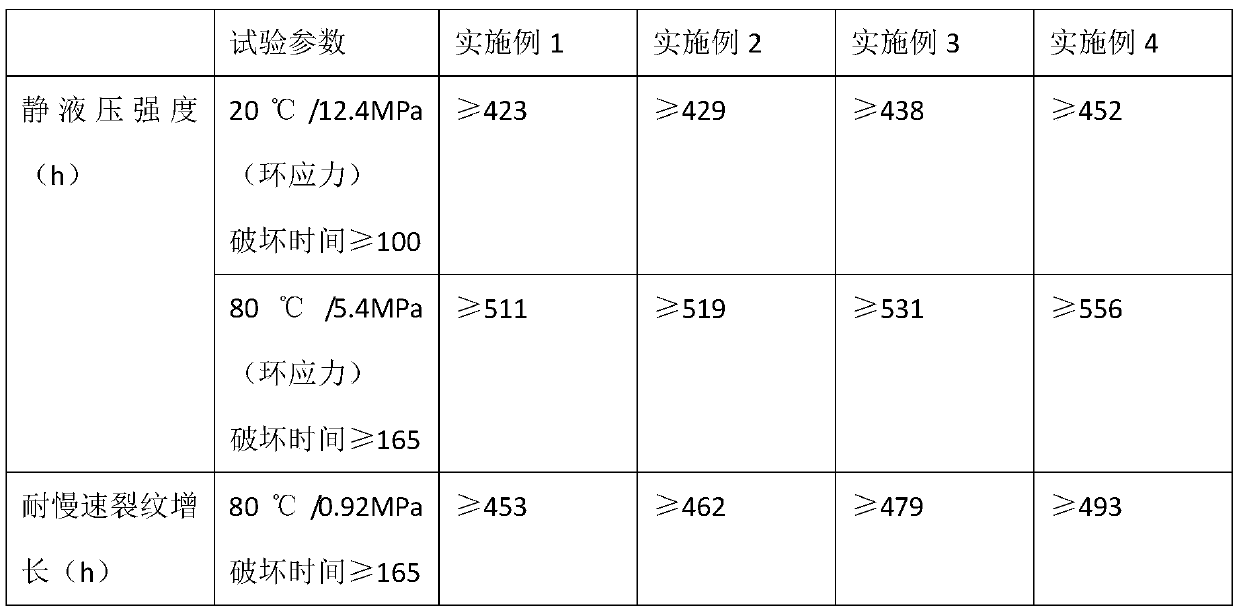
The invention discloses a bimodal high density polyethylene and a production process thereof. In the presence of hydrogen and an induced condensing agent (ICA), contacting ethylene and at least one (C4-C20) alpha-olefin with a bimodal catalyst in a single gas phase reactor to prepare the bimodal high density polyethylene. The content of hydrogen and the induced condensing agent in the reactor is adjusted to adjust the comonomer content and the polymer yield. A pipe prepared from the bimodal high density polyethylene has good hydrostatic strength and slow crack growth resistance.
Owner:JIUTAI ENERGY ZHUNGEER CO LTD
Method for preparing halogenated polymer
The invention discloses a method for preparing a halogenated monoolefine-conjugated diene copolymer. The method comprises the steps that under the condition of cationic polymerization, monoolefine shown as the formula I, conjugated diene shown as the formula III and all components in an initiator system are in contact in a mixed solvent of alkane and haloalkane, alkane is used for displacement and polymerization to obtain haloalkane in the solution, meanwhile, unreacted monomers are separated out and then are in contact with a halogen containing compound for a halogenating reaction, the initiator system contains a compound, lewis acid and an activating agent capable of providing protons, and the activating agent is selected from a compound shown as the formula I-1 and a compound shown as the formula I-2. According to the method, the polymerization efficiency can be obviously improved, and the higher polymer yield can be obtained. The polymer with the high molecular weight can be obtained; meanwhile, the polymer redissolving process necessary for a slurry polymerization method is omitted, and the production process is simplified. The formula is shown in the specification.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Low emissions polyurethane foam made with isocyanate reactive amine crystals
ActiveUS20170247495A1Reduce amine emissionAvoid contactCarboxylic acid nitrile preparationOrganic compound preparationAqueous solutionPolycarbonate
Tertiary amine catalysts having isocyanate reactive groups capable of forming thermally stable covalent bonds able to withstand temperatures from 120° C. and higher and up to 250° C. are disclosed. These catalyst can be used to produce polyurethane foam having the following desirable characteristics: a) very low chemical emissions over a wide range of environmental conditions and isocyanate indexes (e.g., indexes as low as 65 but higher than 60); b) sufficient hydrolytic stability to maintain the catalyst covalently bound to foam without leaching of tertiary amine catalyst when foam is exposed to water or aqueous solutions even at temperatures higher than ambient (temperature range 25° C. to 90° C.); and c) stable contact interface between the polyurethane polymer and other polymers (for example polycarbonate) with minimal migration of tertiary amine catalyst from polyurethane polymer to other polymers yielding no noticeable polymer deterioration at the point of contact even under conditions of heat and humidity.
Owner:EVONIK OPERATIONS GMBH
Preparation method of proanthocyanidin polymer and proanthocyanidin polymer
PendingCN111675683AHigh degree of polymerizationSimple preparation processOrganic chemistryNatural dyesAqueous acetoneGrape seed
The invention discloses a preparation method of a proanthocyanidin polymer. The preparation method comprises the following steps: preparing a raw material, which is waxberry leaves or grape seeds; preprocessing the raw material to obtain raw material powder; mixing the raw material powder with an acetone water solution to obtain a mixed solution, then adding ascorbic acid into the mixed solution,and carrying out lightproof intermittent oscillation extraction to obtain a mixed feed liquid; performing suction filtration on the obtained mixed feed liquid to obtain filtrate, mixing the filtrate with trichloromethane, and collecting supernatant liquid; adding sodium chloride into the collected supernatant liquid, centrifuging to collect a coarse precipitate; washing the coarse precipitate withwater, and carrying out freeze drying to obtain the proanthocyanidin polymer. The preparation process is simple, the process conditions are mild, the polymer yield is high, the polymerization degreeis high, and the prepared proanthocyanidin polymer can be used for proanthocyanidin structure and biological activity analysis and application, and can also be used for preparing proanthocyanidin oligomers or metal chelating agents.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Preparation method of halogenated polymer
The invention discloses a preparation method of a halogenated monoolefine-alkyl styrol copolymer. The preparation method comprises the steps that monoolefine shown in the formula II and alkyl styrol shown in the formula III make contact with components in an initiator system in alkane under the condition of cationic polymerization, and the obtained solution containing the halogenated monoolefine-alkyl styrol copolymer makes with a compound containing halogen for a halogenating reaction, wherein the initiator system contains a compound capable of providing protons, lewis acid and an activating agent, and the activating agent is selected from the compound shown in the formula I-1 and the compound shown in the formula I-2. By means of the method, polymerization efficiency can be obviously improved, the higher polymer yield is obtained, the polymer with high molecular weight can be obtained, the solvent replacement process and the polymer redissolution process needed in a slurry polymerization are omitted, and the production process is simplified.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Amphiphilic polymer microsphere material with uniform particle size, preparation method and application
ActiveCN109942737BLow costEasy to prepareWater contaminantsWater/sewage treatment by sorptionHydrophilic monomerPolymer science
The invention discloses an amphiphilic polymeric micro-spherical material uniform in grain size, a preparation method and an application and belongs to the field of high molecular materials and solvesthe problems that an existing preparation method is hard to regulate grain size, low in polymer yield, poor in application effect and the like. The preparation method comprises the following steps: by taking N-vinyl pyrrolidone and divinylbenzene as a monomer, dispersing an emulsion uniformly in a water phase by a certain way; strengthening affiliation of the hydrophobic monomer divinylbenzene and the hydrophilic monomer N-vinyl pyrrolidone to increase the yield by means of proper water phase composition and proportion; and carrying out polymerization in conditions of a strict temperature androtating speed and the like to finally obtain the amphiphilic polymeric resin material uniform in grain size. Through serial representation and application evaluation, the material has very excellentamphiphilic performance, has a wide broad enriching and separating property to organic matters in a water body, and can be separately applied to the fields of analysis, detection, water treatment projects, household water purification and the like according to the grain sizes.
Owner:NANJING UNIV +1
A cationic polymerization method
The invention discloses a cationic polymerization method. The method comprises the following steps that on the solution polymerization condition, monoolefine shown in the formula II and conjugated diene shown in the formula II make contact with components in an initiator system in a polymerization solvent, the initiator system contains compounds capable of providing carbocation, lewis acid and an activating agent, the activating agent is selected from a compound shown in the formula I-1 and a compound shown in the formula I-2. Compared with a simple C+ / lewis acid initiator system, the initiating efficiency of the method is remarkably improved, and the higher polymer yield can be obtained at the higher polymerization rate; polymers of different molecular weights can be obtained on different polymerization conditions by adjusting the content and varieties of the activating agent in the initiator system; in addition, the method can perform polymerization under the higher temperature, and energy consumption in the polymerization reaction process is effectively lowered.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Cationic polymerization method
The invention discloses a cationic polymerization method. The method comprises the following steps that on the solution polymerization condition, monoolefine shown in the formula II and conjugated diene shown in the formula II make contact with components in an initiator system in a polymerization solvent, the initiator system contains compounds capable of providing carbocation, lewis acid and an activating agent, the activating agent is selected from a compound shown in the formula I-1 and a compound shown in the formula I-2. Compared with a simple C+ / lewis acid initiator system, the initiating efficiency of the method is remarkably improved, and the higher polymer yield can be obtained at the higher polymerization rate; polymers of different molecular weights can be obtained on different polymerization conditions by adjusting the content and varieties of the activating agent in the initiator system; in addition, the method can perform polymerization under the higher temperature, and energy consumption in the polymerization reaction process is effectively lowered.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
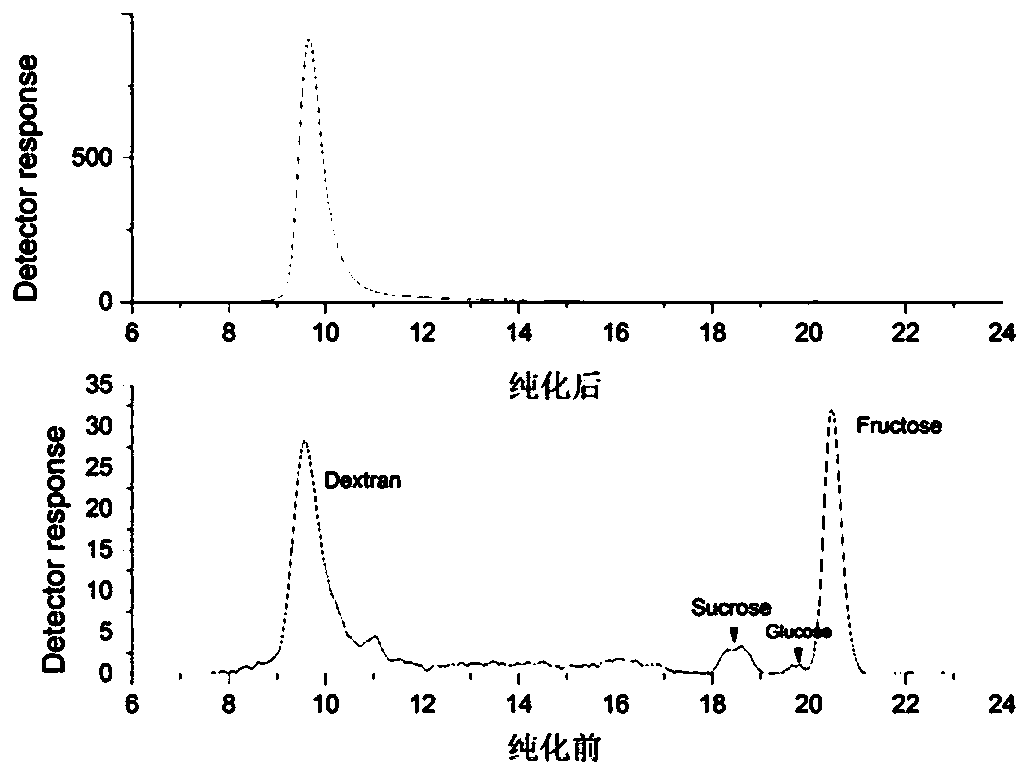
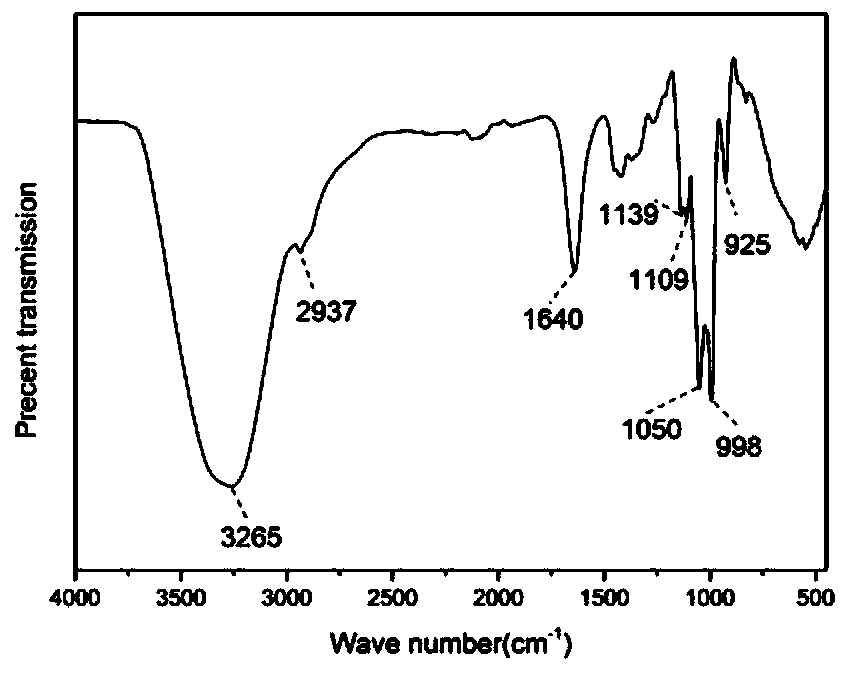
Method for preparing dextran selenium polymers by enzyme means
The invention discloses a method for synthetizing dextran selenium polymers by an enzyme means. According to the method for synthetizing the dextran selenium polymers by the enzyme means, dextran sucrase is used as a catalyst; sucrose and sodium selenite are used as substrates; and then, enzymatic reaction is carried out so as to synthesize the dextran selenium polymers. By catalyzing the sucroseand the sodium selenite by using the dextran sucrase, the method is capable of synthesizing the dextran selenium polymers in one step. Tests have proven that the method for synthesizing the dextran selenium polymers by the enzyme means overcomes the problems of complex reaction steps, intense reaction conditions, relatively many byproducts and the like of chemical synthesis; moreover, the method has the characteristics of being simple in reaction system, wide in raw material source, mild in reaction conditions, relatively high in selenization efficiency, relatively high in selenium polymer yield and the like. In addition, the method is capable of reducing usage of toxic chemical agents as reaction media; moreover, relatively few byproducts are produced so as to facilitate separation and purification, so that, no environmental pollution is caused.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Reactive amine catalysts for polyurethane applications
ActiveUS10100141B2Reduce amine emissionAvoid contactUrea derivatives preparationOrganic compound preparationPolymer yieldPolycarbonate
Tertiary amine catalysts having isocyanate reactive groups that are capable of forming thermally stable covalent bonds able to withstand temperatures up to 120° C. are disclosed. These catalyst can be used to produce polyurethane foam having the following desirable characteristics: a) very low chemical emissions over a wide range of environmental conditions and isocyanate indexes (e.g. indexes as low as 65 but higher than 60) while meeting all physical property requirements; b) sufficient hydrolytic stability to maintain the catalyst covalently bound to foam without leaching of tertiary amine catalyst when foam is exposed to water or aqueous solutions even at temperatures higher than ambient (temperature range 25° C. to 90° C.); and c) stable contact interface between the polyurethane polymer and other polymers (for example polycarbonate) with minimal migration of tertiary amine catalyst from polyurethane polymer to other polymers yielding no noticeable polymer deterioration at the point of contact even under conditions of heat and humidity.
Owner:EVONIK OPERATIONS GMBH
A kind of preparation method of halogenated polymer
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Preparing method of halogenated polymer
The invention discloses a preparing method of a halogenated monoolefine-conjugated diene copolymer. The method comprises the steps that under the cationic polymerization condition, monoolefine shown in the formula II in the description and conjugated diene shown in the formula III in the description make contact with all components in an initiator system in alkane, unreacted monoolefine and conjugated diene in an obtained solution containing the monoolefine-conjugated diene copolymer are removed, then the solution makes contact with a compound including halogen, and a halogenating reaction is carried out, wherein the initiator system includes a compound capable of providing protons, lewis acid and an activating agent selected from a compound shown in the formula I-1 and a compound shown in the formula I-2. By means of the method, the polymerizing efficiency can be remarkably improved, and a higher polymer yield can be achieved; the polymer with a high molecular weight can be obtained. According to the method, the processes of solvent replacement and polymer redissolution necessary in a slurry polymerizing method are omitted, and the production technology is simplified.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com