Method of establishing double-detection sensor for antibiotics based on aptamers
A technology for establishing methods and aptamers, which can be used in biochemical equipment and methods, biological testing, microbial determination/inspection, etc., and can solve the problems of high instrument cost and low detection sensitivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
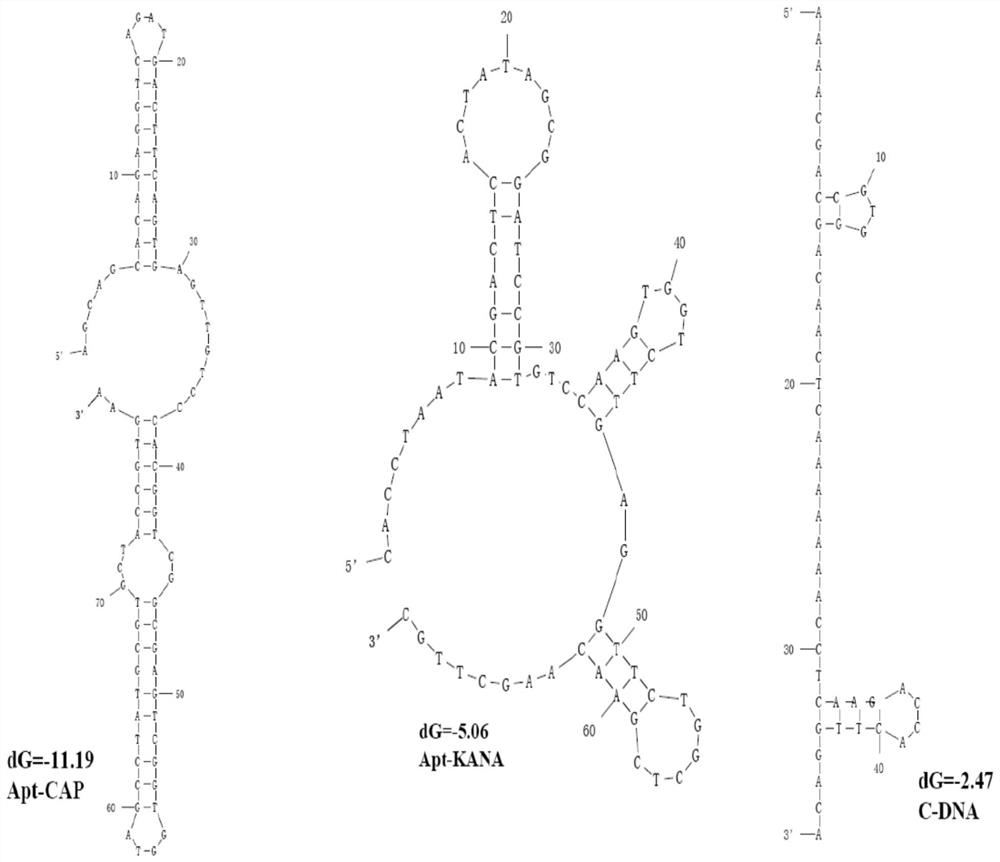
[0060] Example 1: Synthesize the following sequence, the shown chloramphenicol nucleic acid aptamer and kanamycin aptamer
[0061] 1.CAP-aptamer:
[0062] Chloramphenicol Aptamer (Apt-CAP):
[0063] 5'-AGCAGCACAGAGGTCAGATGACTTCAGTGAGTTGTCCCACGGTCGGCGAGTCGGTGGTAGCCTATGCGTGCTACCGTGAA-3'
[0064] Kanamycin aptamer (Apt-KANA):
[0065] 5'-CACCTAATACGACTCACTATAGCGGATCCGTGTCCAAGTGGTCTTGAGGTTCTGGCTCGAACAAGCTTGC-3'
[0066] Apt-CAP corresponds to the above quotation (C1): 5'-AGCAGCACAGAGGTCAGATG-3'
[0067] Apt-CAP corresponds to the following quote (C2): 5'-CCTATGCGTGCTACCGTGAA-3'
[0068] Apt-Kana corresponds to the upper citation (K1): 5’-CACCTAATACGACTCACTATA-3’
[0069] Apt-Kana corresponds to the following quotation (K2): 5'-CTGGCTCGAACAAGCTTGC-3'
Embodiment 2
[0070] Embodiment 2: the establishment of antibiotic double detection system
[0071] The buffer used in the experiment:
[0072] F1 buffer solution: Tris (Tris) 10 mM, sodium chloride (NaCl) 100 mM, ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid disodium (EDTA Na2) 1 mM, pH 8.0.
[0073] F2 buffer: Tris (Tris) 20mM, sodium chloride (NaCl) 200mM, ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid disodium (EDTA Na2) 1mM, Triton X-100 0.02%, pH 7.8 .
[0074] 1×B buffer solution: Tris (Tris) 50mM, Magnesium chloride (MgCl2) 1mM, Sodium chloride (NaCl) 200mM, Potassium chloride (KCl) 5mM, Triton X-100) 0.02% , pH 7.4.
[0075] 2×B buffer: Tris (Tris) 100mM, Magnesium chloride (MgCl2) 2mM, Sodium chloride (NaCl) 400mM, Potassium chloride (KCl) 10mM, Triton X-100) 0.02% , pH 7.4.
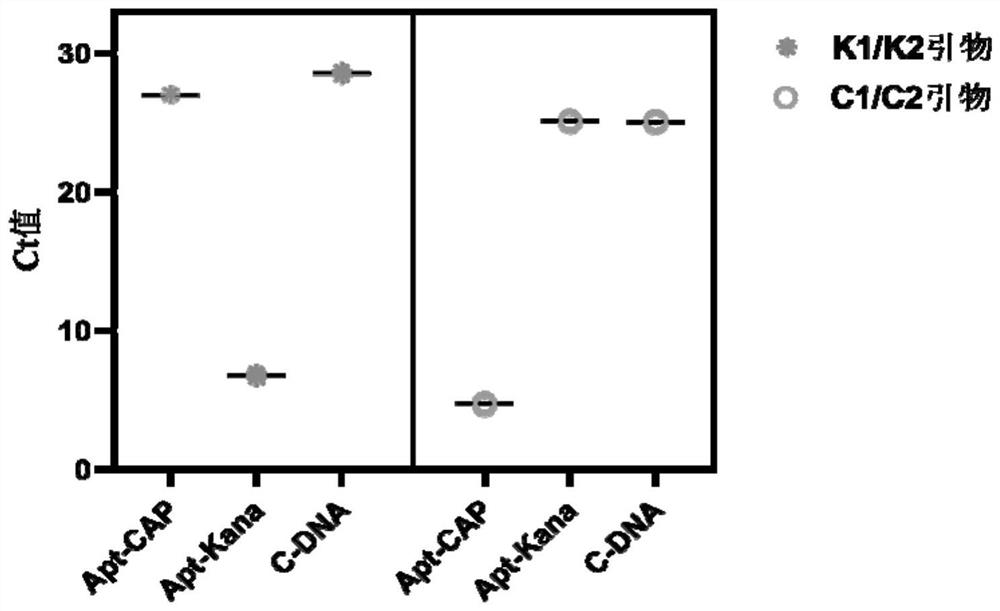
[0076] 2.1 Dual detector feasibility verification experiment
[0077] 2.1.1 Predict the secondary structure of the two aptamers by mfold simulation respectively, and check the data to determine the sequence of the complementary re...
Embodiment 3
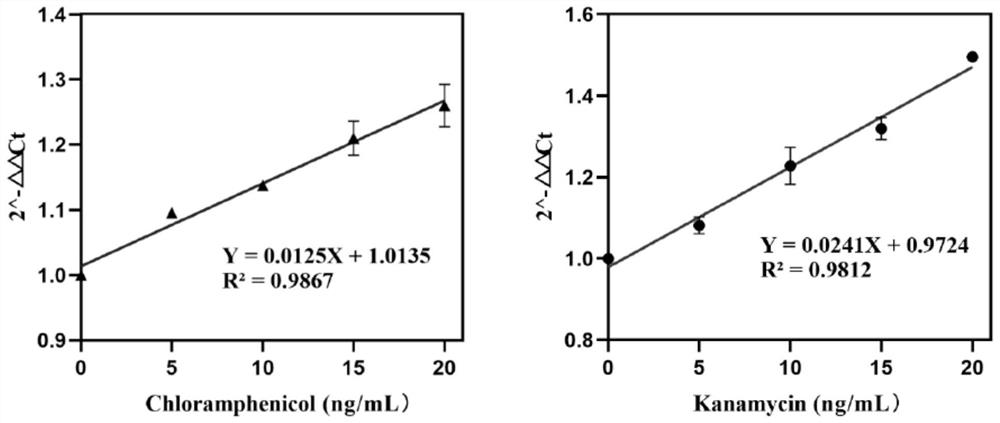
[0093] Embodiment 3. The mensuration of detector linear interval and detection limit
[0094] Add chloramphenicol and antibiotics with gradient final concentration to the reaction system as the experimental group, and add sterile water as the blank group. The standard curve was drawn with the antibiotic concentration as the abscissa and the 2^-ΔΔCt values of the experimental group and the blank group as the ordinate. The standard curve of chloramphenicol concentration and 2^-ΔΔCt value is y=0.0125X+1.0135, correlation coefficient R 2 =0.9867, the linear detection range is from 0ng / ml to 20ng / ml. From 10 groups of blank groups without chloramphenicol, calculate the standard deviation SD of the fluorescence values of 10 groups, according to the standard curve formula y=0.0125X+1.0135 obtained above, the value calculated by 3SD / k is the minimum detection limit . The standard deviation SD of the blank group was 0.047, which was brought into the standard curve, and the minim...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com