Method for producing pickled vegetables
A kimchi and subspecies technology, applied in the direction of microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, microorganisms, etc., can solve the problems of uncontrollable ripening and eating time, long fermentation cycle, unstable quality of kimchi, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0073] Example 1: Screening, identification and preservation of ethanol-resistant Pediococcus VCQWZ3-L7
[0074] Specific steps are as follows:
[0075] 1. Screening
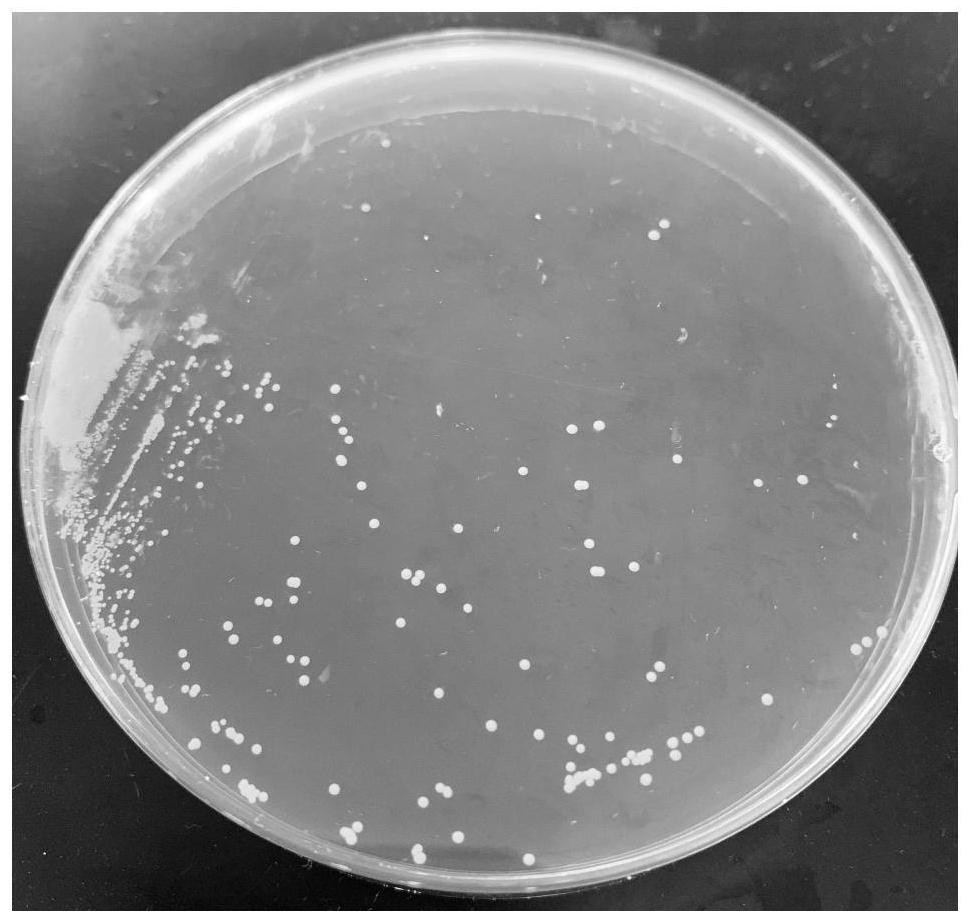
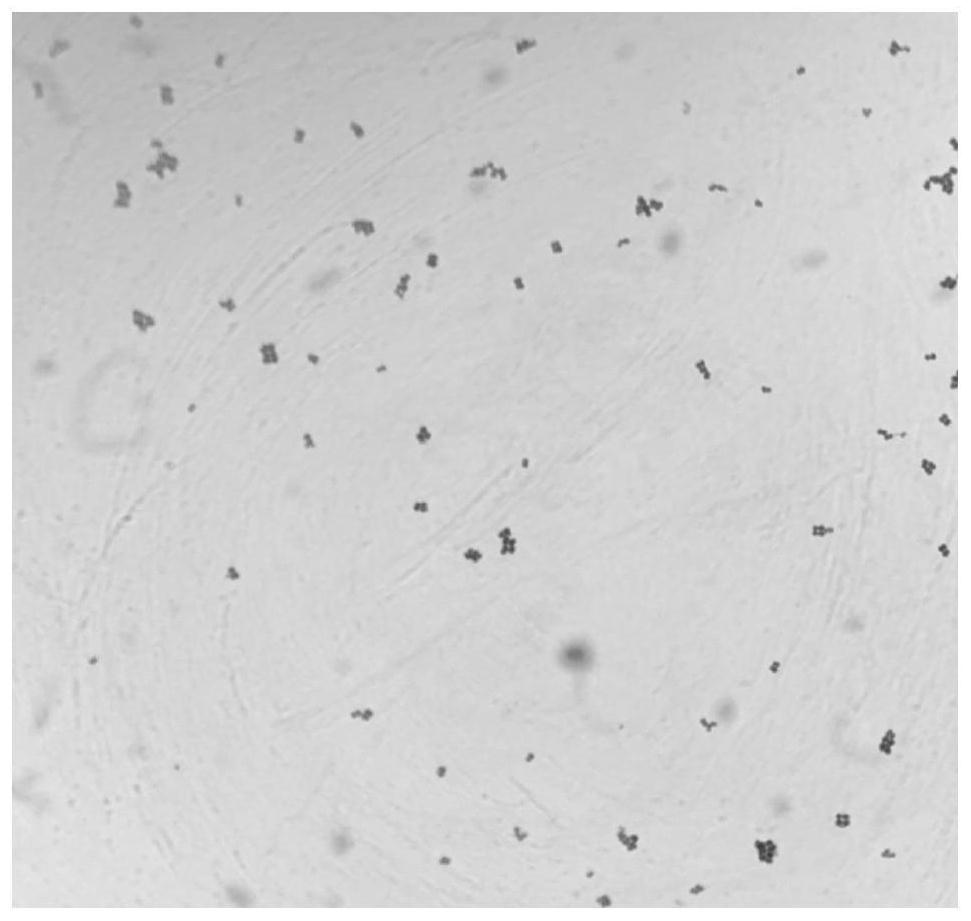
[0076] Taking pickle water from Chongqing as a sample, it was diluted 10 times with sterile saline to 10 -6 , and then take 100 μL dilution factor of 10 -4 、10 -5 、10 -6 Spread the diluted liquid on the MRS solid medium, culture it upside down at 37°C for 48 hours, observe and record the colony shape; pick the colonies of different shapes on the MRS solid medium to separate them by streaking, and culture them at 37°C for 48 hours , pick the single colonies of different shapes on the MRS solid medium again and separate them by streaking until the pure single colonies with the same shape are obtained; observe the colony morphology of the single colonies, and perform microscopic examination, Gram staining and physiological analysis on the obtained colonies. For the investigation of biochemical characteristics,...
Embodiment 2
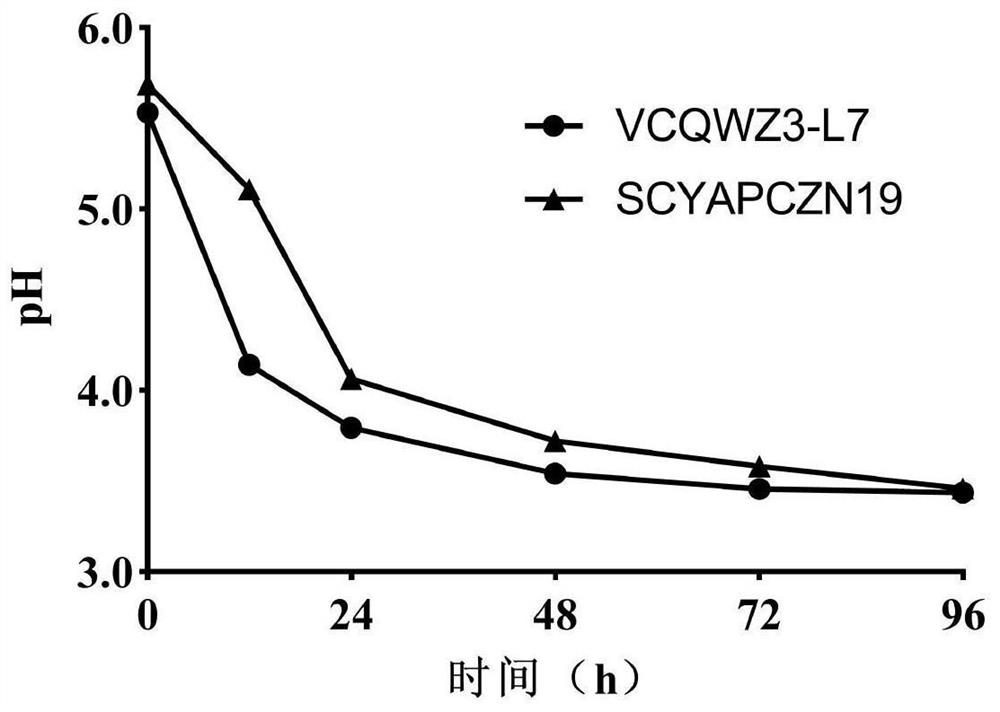
[0084] Example 2: Fermentation characteristics of ethanol-resistant Pediococcus VCQWZ3-L7
[0085] Specific steps are as follows:
[0086] The ethanol-resistant Pediococcus VCQWZ3-L7 and the ethanol-resistant Pediococcus SCYAPCZN19 obtained in Example 1 were respectively streaked on the MRS solid medium, cultured at 37°C for 48 hours, and single colonies were obtained; single colonies were picked and inoculated in the MRS liquid culture cultured at 37°C for 18 hours to activate, and two generations of continuous activation to obtain the activation solution; the activation solution was inoculated into the MRS liquid medium at an inoculum amount of 2% (v / v), and cultured at 37°C for 18 hours. 100g of white radish, 4g of pepper, 6g of garlic, 6g of ginger, 6g of table salt, 4g of white sugar and 100mL of water were prepared; the white radish, pepper, garlic and ginger were cleaned to remove impurities from the skin, and blanched in boiling water instantly. Wash 3 times with ster...
Embodiment 3
[0095] Embodiment 3: the production of kimchi starter
[0096] Specific steps are as follows:
[0097] The ethanol-resistant Pediococcus VCQWZ3-L7 obtained in Example 1, Lactobacillus plantarum ZH008 and Leuconostoc enterococci subsp. enterica Q3-16 were respectively streaked on the MRS solid medium and cultured at 37°C for 48 hours to obtain single Bacterial colonies; pick single colonies and inoculate them in MRS liquid medium respectively, culture them at 37°C for 18 hours for activation, and activate two generations continuously to obtain activation solution; inoculate the activation solution at an inoculum amount of 2% (v / v) in In the MRS liquid medium, culture at 37° C. for 18 hours to obtain a bacterial liquid.
[0098] The bacterial solution obtained by cultivating Lactobacillus plantarum ZH008 and Leuconostoc enterococci subsp. The viable bacteria ratio of -16 was 2:1, and starter A was obtained.
[0099] The bacterial liquid obtained by culturing Leuconostoc enter...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com