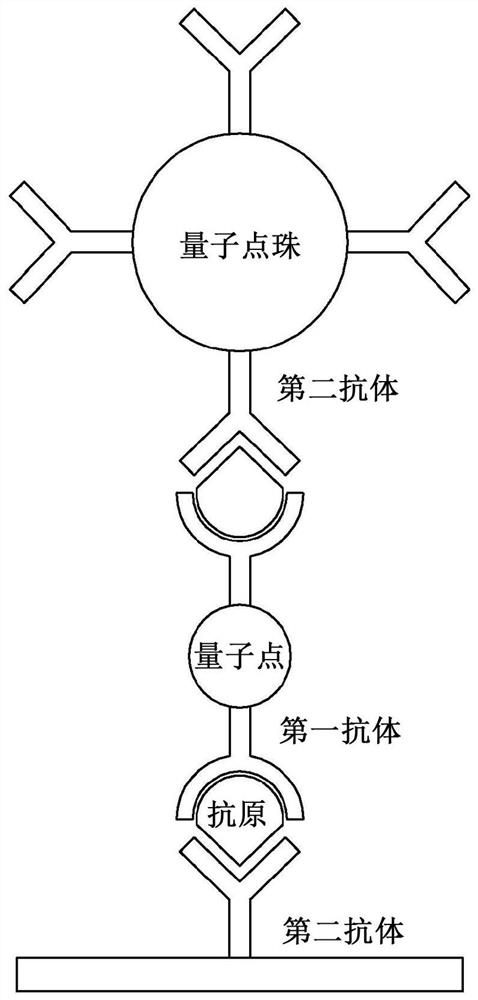
Biosensor comprising linker material and quantum dot beads, and target antigen detection method using same
A detection method, quantum dot technology, applied in the field of biosensors, can solve problems such as limitations, and achieve the effect of amplifying the detection intensity, fast and easy detection and identification, and favorable price competitiveness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation Embodiment 1
[0080] [Preparation Example 1] Preparation of Quantum Dots Having Antibodies on Their Surfaces
[0081] (1) Preparation of fat-soluble quantum dots
[0082] In a three-necked flask, 1.0 g of zinc acetate (Zn(Ac) 2 ), 0.441 g of cadmium oxide (CdO), 20 mL of oleic acid, and 75 mL of octadecene (ODE) were mixed and at 150° C. for 1 hour under a nitrogen atmosphere to remove water. Subsequently, the resulting flask was heated to 300° C., and then 1 mL of trioctyl (TOP) and 0.045 g of selenium (Se) were injected and heated for 3 minutes, whereby quantum dot cores were formed.
[0083] Subsequently, 0.5 mL of dodecanethiol was added into the three-necked flask and reacted for 10 minutes. Then, a solution containing 1 mL of TOP and 0.025 g of sulfur (S) was added to the reaction vessel of the three-necked flask and reacted for 20 minutes, whereby a shell was formed. Then, the resulting core and shell were purified with a mixed solution of ethanol and toluene and dissolved in an o...
preparation Embodiment 2
[0093] [Preparation Example 2] Preparation of Quantum Dot Beads Having Antibodies on Their Surfaces
[0094] (1) Synthesis and surface modification of silica particle substrate
[0095] Silica-based nanoparticles were synthesized by the Stober method. First, the NH 4 OH, EtOH, and H 2 O was stirred in an Erlenmeyer flask at a ratio of 3:60:1 mL, 2 mL of tetraethylorthosilicate (TEOS) was added to the reactant, and the mixture was stirred and reacted at 50° C. for 18 hours or more. Here, the reaction time and mixing ratio can be adjusted according to the desired size. Subsequently, final samples were obtained by centrifugation using ethanol. Herein, silica beads of about 200 nm can be obtained.
[0096] Subsequently, for the reaction between the surface and the quantum dots, as reactive functional groups, 180 μL of 3-mercaptopropyltrimethoxysilane (MPTS) and NH 4 OH and react for 12 to 24 hours. After purification by centrifugation using ethanol, a surface-modified silic...
experiment Embodiment 1
[0106] [Experimental Example 1] Confirmation of Characteristics of Quantum Dots and Quantum Dot Beads
[0107] (1) Zeta potential of quantum dots and quantum efficiency of quantum dots and quantum dot beads
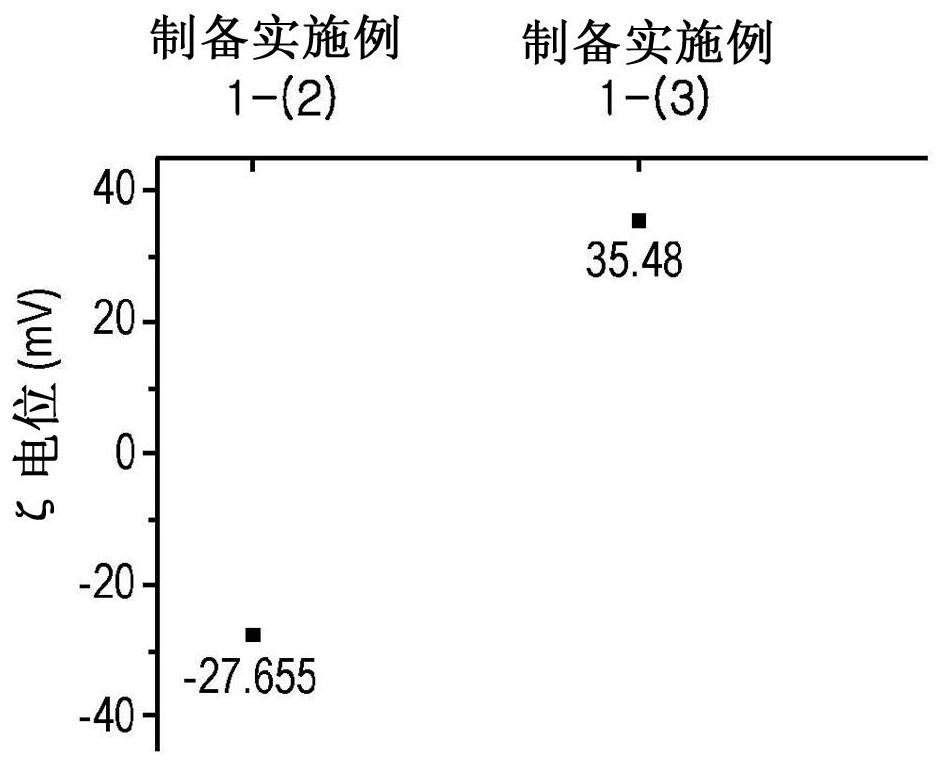
[0108] The zeta potential of the quantum dots of Preparation Examples 1-(2) and 1-(3) was measured using ELS-100ZS (Otsuka), and at figure 2 The results are shown in .
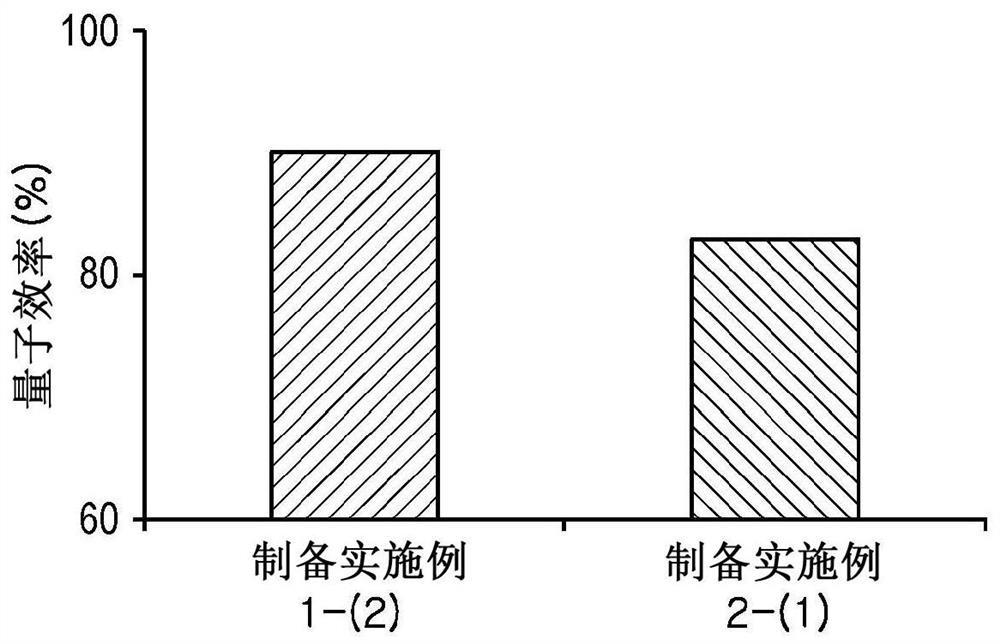
[0109] The quantum efficiencies of the quantum dots of Preparation Example 1-(2) and the quantum dot beads of Preparation Example 2-(3) were measured using QE 2000 (Otsuka Corp.), and image 3 The results are shown in . According to these results, according to one aspect of the present disclosure, the quantum dots and quantum dot beads prepared in Preparation Examples 1-(2) and 2-(3) exhibited quantum efficiencies of 92±3% and 83±3%, respectively And since both are greater than 80%, it shows an excellent effect.
[0110] (3) Confirmation of the size and shape of quantum dots and quantum dot beads
...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| The average diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| The average diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com