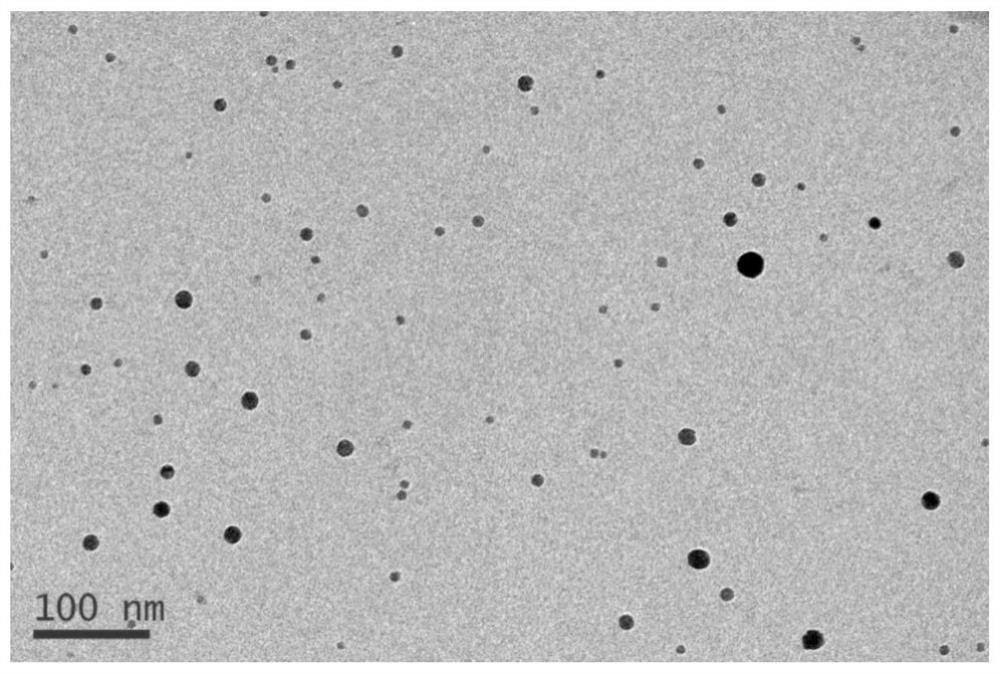
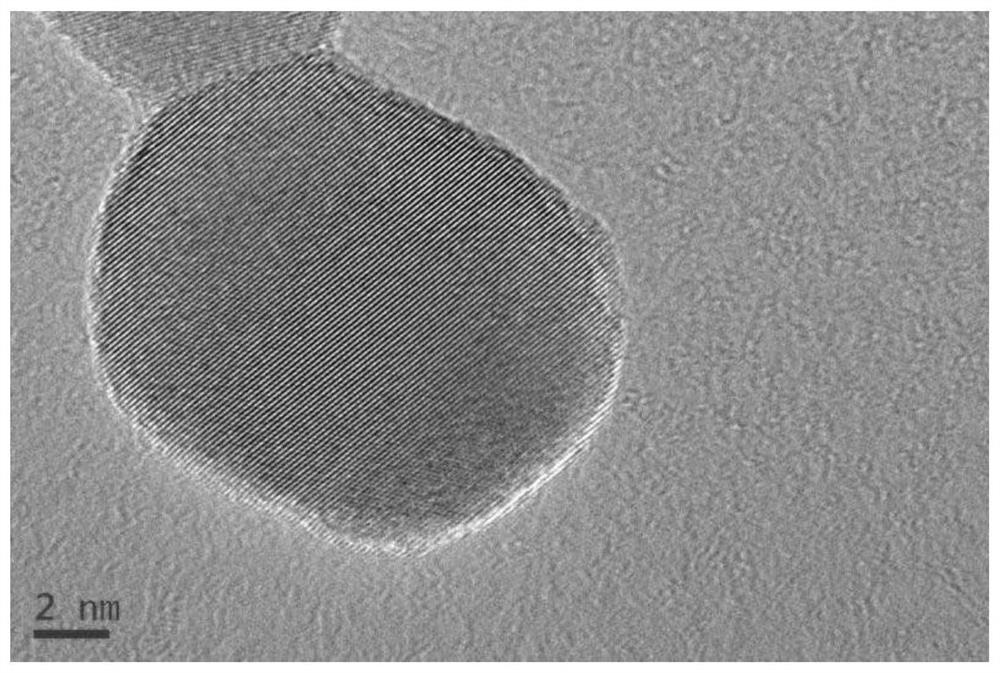
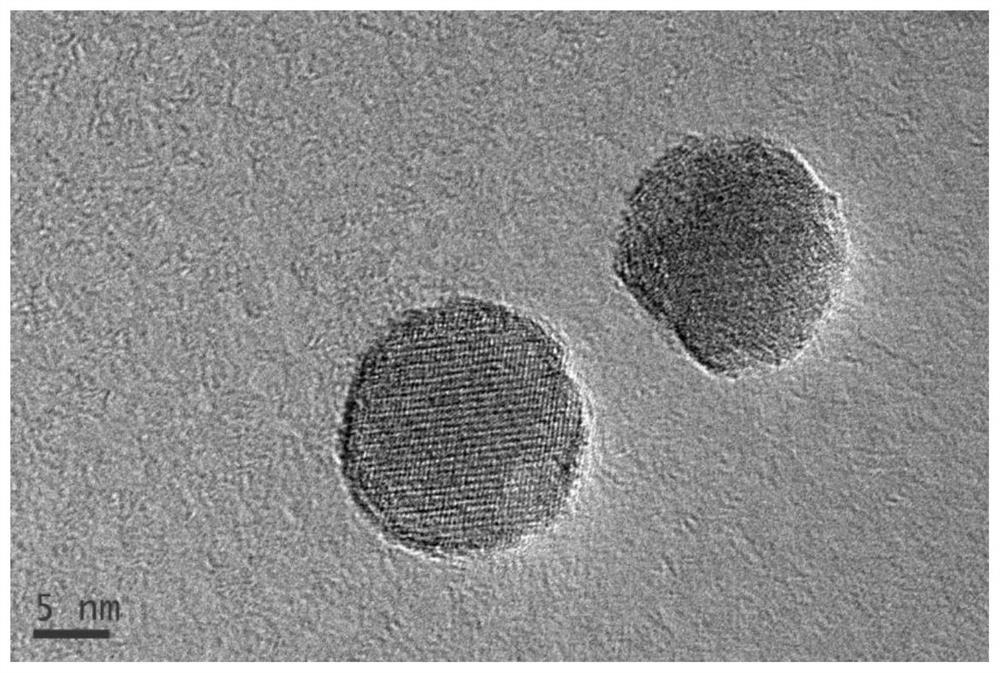
A method for extracting nanometer second phase by using non-aqueous solution electrolysis system
An electrolysis system, a non-aqueous solution technology, used in material analysis using radiation, material analysis using wave/particle radiation, instruments, etc. In order to achieve the effect of selective electrolysis, effective separation and strong repeatability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0049] In this embodiment, the electrolysis system is composed of a ferromagnetic alloy, a power supply, a hollow conical porous inert electrode, a hollow porous conductive inert electrode, an electrolyte storage tank, an electrolytic cell, an ultrasonic device, No. 1 pump, and No. 2 pump.
[0050] Connect the ferromagnetic alloy to the lower part of the hollow porous conductive inert electrode, connect the hollow porous conductive inert electrode to the positive pole of the power supply; connect the hollow porous conductive electrode and the electrolyte storage tank through the No. The electrolytic cell, the vertical distance between the ferromagnetic alloy and the bottom of the electrolytic cell is 3cm, and the distance between the ferromagnetic alloy and the overflow port is 25cm; the hollow conical porous inert electrode is connected to the negative pole of the power supply; the hollow conical is connected through the No. 2 pump and the pipeline Shaped porous inert electrod...
Embodiment 2
[0061] In this embodiment, the electrolysis system consists of a ferromagnetic alloy, a power supply, a hollow conical porous inert electrode, a hollow porous conductive inert electrode, an electrolyte storage tank, an electrolytic cell, an ultrasonic device, No. 1 pump, No. 2 pump and electrolyte composition.
[0062] Connect the ferromagnetic alloy to the lower part of the hollow porous conductive inert electrode, connect the hollow porous conductive inert electrode to the positive pole of the power supply; connect the hollow porous conductive electrode and the electrolyte storage tank through the No. The electrolytic cell, the vertical distance between the ferromagnetic alloy and the bottom of the electrolytic cell is 2cm, and the distance between the ferromagnetic alloy and the overflow port is 22cm; the hollow conical porous inert electrode is connected to the negative pole of the power supply; the hollow cone is connected to the No. 2 pump and the pipeline Shaped porous ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com