Method for reducing content of H2O2 and MDA in non-heading Chinese cabbages after low-temperature stress
A headed cabbage, H2O2 technology, which is applied in the directions of botanical equipment and methods, gardening methods, gardening tools/equipment, etc., can solve the problems of weak resistance to low temperature stress of non-heading cabbage, and achieves increased low temperature stress resistance, realization of The effect of protection and environmental pollution-free
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
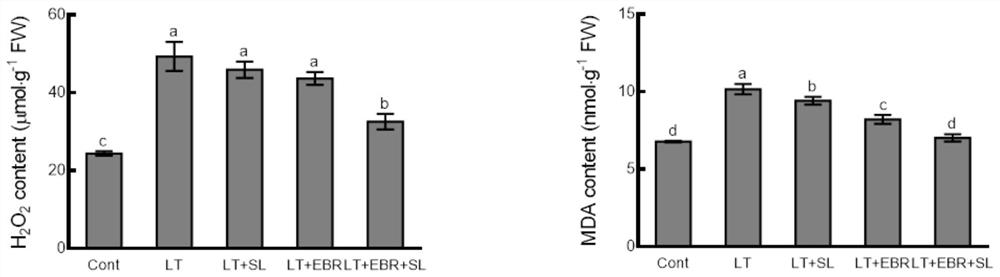
[0026] Effect of mixed solution on non-heading Chinese cabbage seedlings under low temperature 2 o 2 and the effect of MDA content
[0027] According to Solebol "Hydrogen peroxide H 2 o 2 ) content detection kit "instructions for the determination of H in the sample 2 o 2 content. The content of MDA in the samples was determined by the thiobarbituric acid method. Depend on figure 1 It can be seen that after low temperature, non-heading Chinese cabbage seedling leaves H 2 o 2 The contents of MDA and MDA increased significantly, and the contents of both sprayed with EBR or SL alone would decrease to varying degrees, while the contents of the two in the leaves of plants sprayed with EBR and SL decreased significantly, and there was little difference between them and normal temperature.
[0028] At the same time, hydrogen peroxide (H 2 o 2 ) is a kind of active oxygen, which can cause oxidative damage to plant cells, and the increase of its content will increase membran...
Embodiment 2
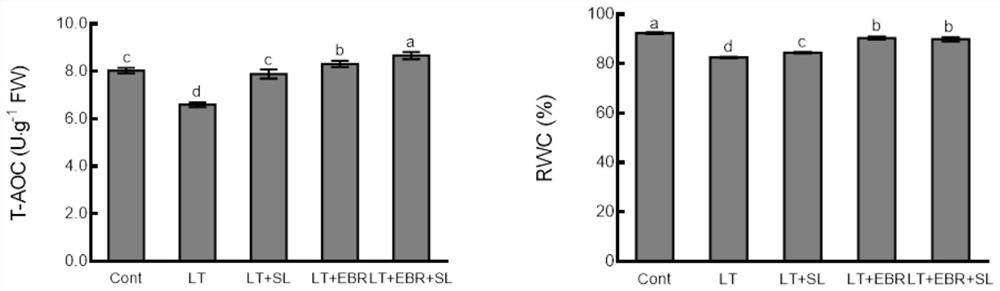
[0032] Effects of Mixture on T-AOC and RWC Contents of Non-heading Chinese Cabbage Seedlings at Low Temperature
[0033] The determination of total antioxidant capacity refers to the total antioxidant level composed of various antioxidant substances and antioxidant enzymes in the sample. After 5 days of low temperature treatment, the total antioxidant capacity (T-AOC) detection kit was used by Suleibao. The collected plant leaves were assayed. The relative water content of plant leaves is an important indicator of the water status of plant tissues, and it is of special significance for the selection of resistance to reverse breeding; it is measured by dry and fresh weight of leaves. Its test results are as figure 2 , the total antioxidant capacity (T-AOC) and relative water content (RWC) of non-heading cabbage seedling leaves were significantly reduced, and the contents of both spraying EBR or SL alone would increase to varying degrees, while the mixed spraying of EBR and T...
Embodiment 3
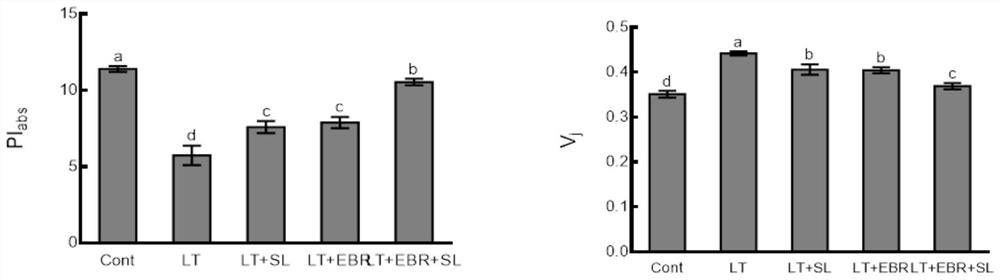
[0035] Effects of Mixture on Photosynthetic Mechanism of Non-heading Chinese Cabbage Seedlings at Low Temperature
[0036] After 5 days of low temperature treatment, the fluorescence emitted by chlorophyll in the plant leaves after 30min dark adaptation was measured with a continuous excitation fluorometer plant efficiency instrument (PEA, Hansatech, UK). The detection results are as follows: image 3 .
[0037] V j It can reflect the degree of closure of active reaction centers when illuminated for 2ms. P.I. abs It is the photosynthetic performance index, which can reflect the state of the photosynthetic mechanism of the plant. The parameter is sensitive and can well reflect the influence of stress on the photosynthetic mechanism. As can be seen from the figure above, after low temperature, PI abs The sharp decrease indicates that the low temperature has an impact on the photosynthetic apparatus. After spraying EBR or SL alone, there is a slight increase, but it is much d...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com