A strain of P. lilacinus and its application in the control of flea beetle
A technology for flea beetle, lilac violacea, applied in the directions of applications, fungi, microorganism-based methods, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026]Embodiment 1: Isolation and screening of P. lilacensis PlSC59A3 bacterial strain
[0027] Inoculate the slant bacteria of the tested strain on the PDA plate, harvest the conidia after cultivating for 2-3 weeks, suspend the conidia with 0.05% Tween-80 solution, measure the spore concentration by the hemocytometer method, adjust the suspension to 10 8 spores / mL concentration, use the dipping method to soak the flea beetle adults in the conidia suspension for 10s, take out the test insects, dry them, place them in a petri dish with wet filter paper at the bottom, and replace the cabbage leaves every day , and observe the changes of the test insects, pick out the dead adult insects, moisten the culture, etc. when the insects grow moldy, they are determined as dead insects. For every treatment of 10 adults, repeat 3 times. Mortality and adjusted mortality are formally calculated according to:
[0028] Mortality (%) = number of dead insects / number of insects before treatmen...
Embodiment 2
[0034] Embodiment 2: Identification of P. lilacensis PlSC59A3 bacterial strain
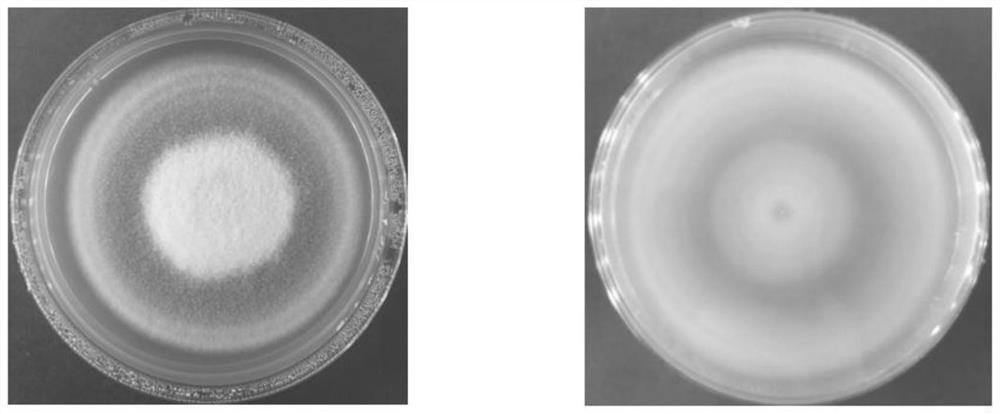
[0035] The slants of the P. lilacinium PlSC59A3 strain obtained from the screening in Example 1 were inoculated on a PDA plate, cultured at 27±1° C., and the changes in colony growth were observed. like figure 1 As shown, the initial stage of the colony is white, the surface is fluffy; the colony is cultivated to the 7th day, the colony is round, the center is slightly raised, the middle of the surface is white, the edge is lavender, fluffy, the back is lavender, and the diameter is (42.30± 0.07) mm.
[0036] The obtained P. lilacinium PlSC59A3 bacterial strain of embodiment 1 screening is under an optical microscope, such as figure 2 As shown, the hyphae are septated, branched, transparent, and the width is (2.87±0.11) μm; the conidia are unicellular, oval to round, chain-like, smooth, colorless to pale yellow, 2 μm to 4 μm wide, with bottleneck-shaped irregular branches or whorled branches o...
Embodiment 3
[0038] Embodiment 3: the conidia production of P. lilacensis PlPlSC59A3 bacterial strain
[0039] Plate culture: Take the preserved slant strains, scrape a small amount of conidia and inoculate them on a PDA plate, culture them in an incubator at 27±1°C for 7-14 days, and scrape the conidia on the surface of the colonies for later use.
[0040] Production of pure powder of conidia: suspend the above conidia with 0.05% Tween-80 solution, inoculate them into PD seed culture solution, culture them in shake flasks in an incubator at 27±1°C for 2 days to form seed solution, and inoculate the seed solution On rice culture medium (in plastic bags or solid fermentation tanks), the inoculum amount is about 10% (v / m), fermented at 27±1°C for about 2 weeks, and the conidia powder is collected with a spore separator, packaged and refrigerated, and used for later use .
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com