Method for detecting carbon black in polymer material for selective laser sintering
A polymer material and laser sintering technology, applied in the field of additive manufacturing, can solve the problems that are not conducive to the large-scale detection of carbon black industrialization, slow gradient temperature rise, long cycle, etc., to achieve simple and easy detection methods, reduce the difficulty of use, and protect environmental effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0035] The inventor of the present application provides a preparation method for the detection method of carbon black in polymer materials for selective laser sintering through the above-mentioned creative work, the method comprising the following steps:
[0036] Step 1, adding white powder to the material to be tested and stirring at a high speed to obtain a sample to be tested, the weight ratio of the material to be tested to the white powder is 1:1-19;
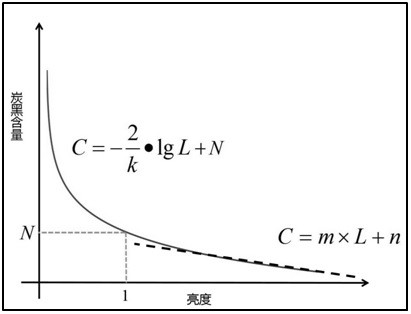
[0037] Step 2, measure the hue value and chromaticity parameter of the sample to be tested, first substitute the hue value into the pre-stored hue value database, and determine the carbon black type of the sample to be tested according to the range of the hue value; then the chromaticity parameter Substituting into the pre-stored standard function model corresponding to the type of carbon black to which the sample to be tested belongs, obtains the content value of carbon black in the sample to be tested; wherein,
[0038] T...
Embodiment 1
[0058] Calibration group 1
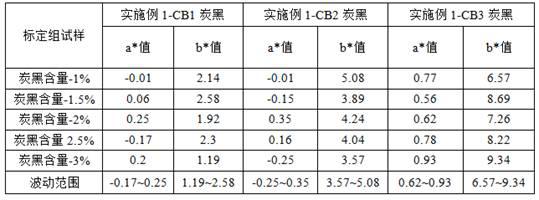
[0059] Take CB1, CB2, CB3 (three different types of carbon black represented by CB1, CB2 and CB3) nylon 12 materials with carbon black contents of 1%, 1.5%, 2%, 2.5%, and 3% respectively. Add 1 part of glass microspheres with a whiteness of 92%, and stir for 5 minutes under the condition of 200 r / min. Measure the L values of each chromaticity parameter of the above-mentioned polymer composite material by a colorimeter, and record the hue parameter a*, b* value simultaneously; Obtain the hue value fluctuation range of the composite material with different carbon black contents, set up a database, see Table 1; The standard linear function model CB1=m1×L1+n1, CB2=m2×L2+n2, CB3=m3×L3+n3 is established by regression analysis, and the relationship between L value and carbon black content can be seen in Table 2;
[0060] Test group 1
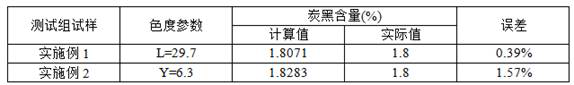
[0061] Take 1 part of finished nylon 12 powder containing carbon black (in order to verify the accuracy of the test, ...
Embodiment 2
[0063] Calibration group 2
[0064] Take 1 part of nylon 6 materials with CB4, CB5 and CB6 carbon black contents of 1%, 2% and 3% respectively, add 2 parts of nylon 6 base material powder respectively, and stir for 5 minutes under the condition of 200r / min. Measure the Y value of each chromaticity parameter of the above-mentioned polymer composite material by a colorimeter, and record the hue parameter a*, b* value simultaneously; Obtain the fluctuation range of the hue value of the composite material with different carbon black contents, set up a database, see Table 3; The standard linear function model CB4=m4×Y4+n4, CB5=m5×Y5+n5, CB6=m6×Y6+n6 is established by regression analysis, and the relationship between the Y value and the carbon black content is shown in Table 4;
[0065] Test group 2
[0066] Take 1 part of finished nylon 6 powder containing carbon black (in order to verify the accuracy of the test, it is known that the type of carbon black is CB6 with a content of ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com