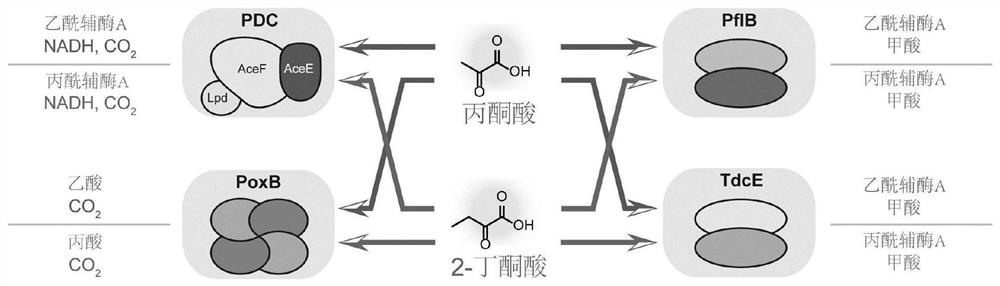
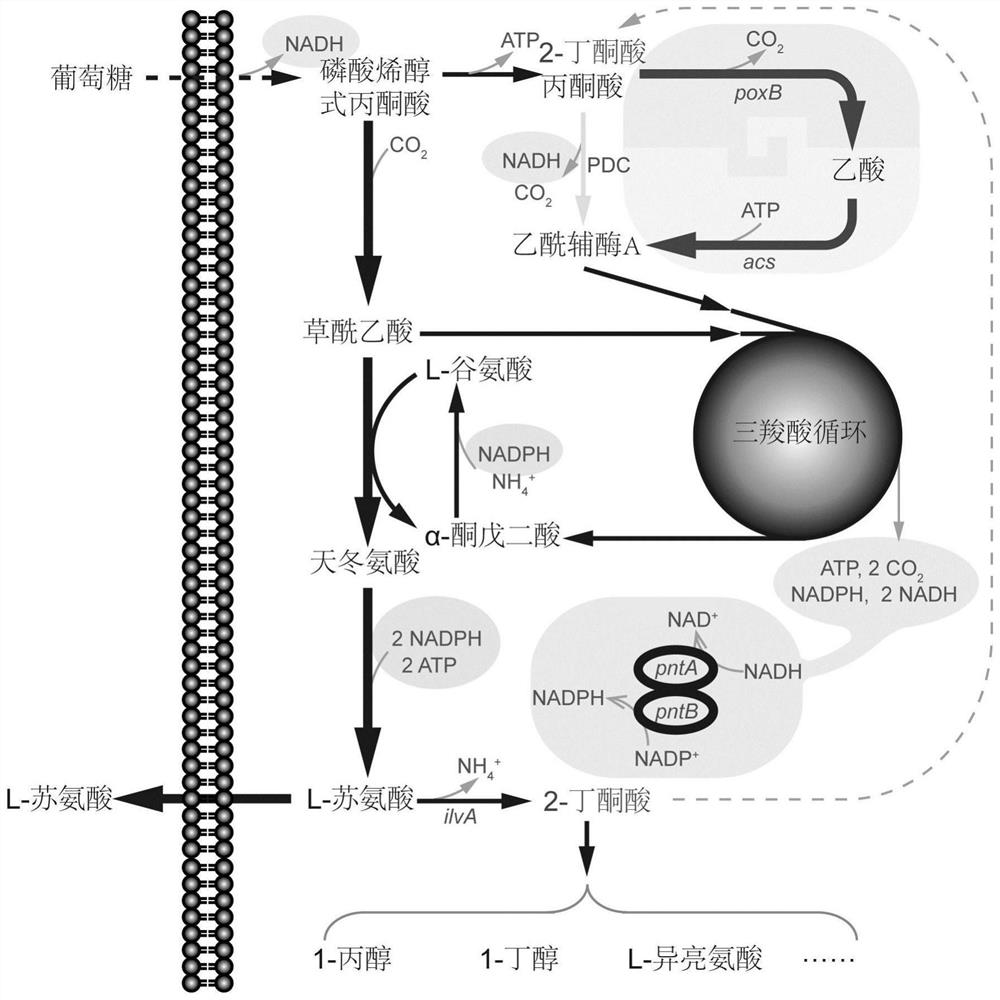
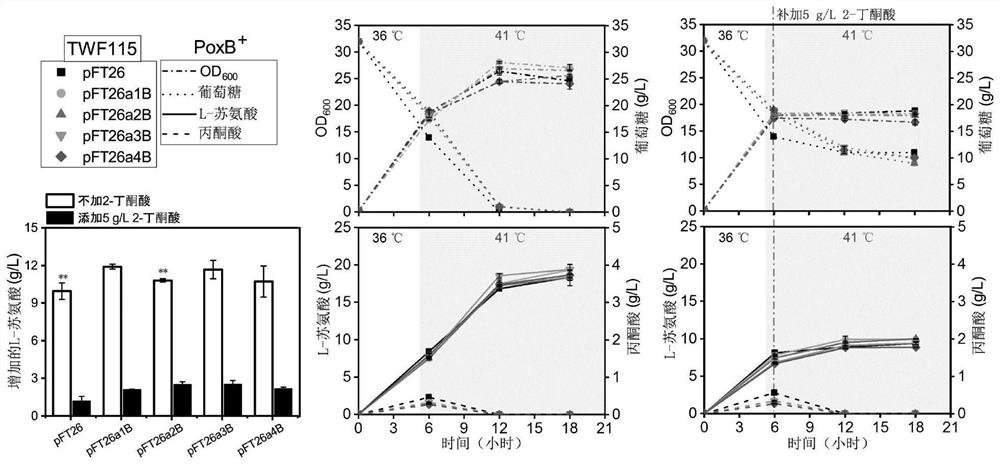
Mutant pyruvate oxidase and use thereof in metabolic detoxification of 2-butanone acid
A technology of pyruvate oxidase and pyruvate, which is applied in the field of genetic engineering and microbial fermentation, can solve the problem that the output of L-threonine cannot meet the needs of industrial production, achieve good detoxification effect, reduce metabolic toxicity, and reduce the The effect of high object preference
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0049] The construction of embodiment 1 bacterial strain and expression vector
[0050] All bacterial strains, plasmids and primers used in this application have been summarized in Table 1 and Table 2. Escherichia coli DH5α was used as a host for constructing plasmids, and its genomic DNA was used as a template for gene cloning.
[0051] (1) Plasmid construction: The construction of the plasmid was accomplished using the ClonExpress II one-step cloning kit (purchased from Novizyme) and conventional molecular biology techniques.
[0052] Plasmid pFT26: Using the plasmid pFT24 as a template, use the primer pair FW26-mF / FW26-mR to amplify the DNA fragment to be preserved from the plasmid pFT24, digest it with DpnI and transfer it into DH5α competent cells by chemical transformation to obtain the circular plasmid pFT26 . Overexpression of a thermosensitive circuit cI based on plasmid pFT24 ts -P RL , knockdown of TetR repressor and P LtetO-1 obtained from the promoter.
[00...
Embodiment 2
[0076] Example 2 Effect of adding different amounts of 2-OBA on the production of L-threonine by Escherichia coli TWF105
[0077] In the fermentation medium, different amounts of 2-OBA were added, and the L-threonin bacteria Escherichia coli TWF105 was fermented in shake flasks to evaluate the inhibitory effect of 2-OBA on L-threonine biosynthesis. Due to the stagnation of cell growth in the early stage of fermentation, which is not conducive to the synthesis of L-threonine, sufficient biomass accumulation was maintained in the early stage of fermentation, and the time point of adding exogenous 2-OBA was set to 6h after the start of fermentation. After adding exogenous 2-OBA for 12h, the increase of L-threonine in the fermentation broth was detected.
[0078] After adding 2-OBA, the amount of L-threonine increased significantly according to the amount of 2-OBA added. With the increase of 2-OBA addition, the increase of L-threonine decreased significantly, and the biosynthesis...
Embodiment 3
[0081] Example 3 Screening of acetic acid bypass pathway expression vector and host
[0082] The acetic acid bypass pathway expression vectors pFT26a1B, pFT26a2B, pFT26a3B and pFT26a4B constructed in Example 1 and the expression vectors pFT26a1, pFT26a2, pFT26a3 and pFT26a4 expressing only ACS were tested for 2-OBA toxicity. The expression vectors were introduced into Escherichia coli and shake-flask fermentation of L-threonine was carried out. The initial fermentation temperature was 36°C, and the temperature was adjusted to 41°C 6 hours after the start of fermentation. In order to ensure cell growth and biomass accumulation in the early stage of fermentation, 5 g / L 2-OBA was added 1 h after the temperature change. Take no addition of 2-OBA as the control group.
[0083] (1) The expression vectors pFT26a1B, pFT26a2B, pFT26a3B and pFT26a4B were respectively introduced into Escherichia coli TWF115. like image 3 As shown, after adding 5g / L of 2-OBA, the growth of the host s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com