Tomato bacterial wilt resistance gene Slalpha-KGDH E2 and application thereof
One-KGDHE2, tomato bacterial wilt technology, applied to tomato bacterial wilt resistance gene Slα-KGDHE2 and its application field, can solve problems such as difficult large-scale promotion and application, limited breeding progress, time-consuming and labor-intensive costs, and achieve important research value , increased gene expression, and broad application prospects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] Example 1 Genetic analysis of resistance to bacterial wilt of tomato 'ZRS-7'
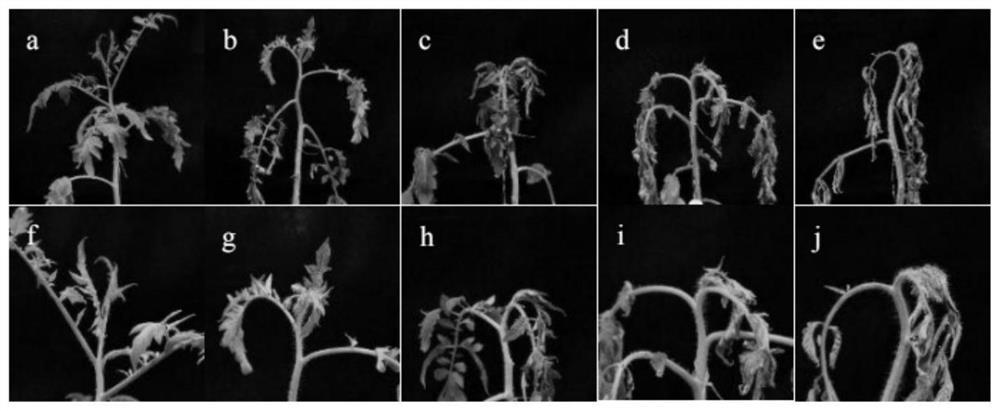
[0038] The F1 generation was obtained by crossing the resistant variety 'ZRS-7' with stable and extreme disease-resistant traits and the susceptible variety 'HTY-9' as parents. The results showed that the F1 generation was susceptible to bacterial wilt, but the disease index was lower compared with the susceptible parents; 2 A total of 156 plants were counted, and the resistance and susceptibility traits were separated. The disease rate was 72.22% and the disease index was 58.8%. The onset time of most of the susceptible plants of the F2 generation was about 2 days later than that of the susceptible parents; some of the F2 generation plants were resistant to the disease, the onset time was delayed, and symptoms began to appear at 10dpi. Due to the complexity of the genetic law of bacterial wilt resistance, it was determined that the resistance to bacterial wilt of 'ZRS_7' tomato was recessiv...
Embodiment 2
[0039] Example 2 Localization of the main resistance gene of 'ZRS-7' tomato bacterial wilt resistance
[0040] 25 highly disease-resistant and highly susceptible plants were selected from the F2 generation segregation population, and the genomic DNA was extracted and mixed in equal amounts to construct a disease-resistant pool (R-pool) and a disease-susceptible pool (S-pool) respectively. -7' and 'HTY-9' were the two parental pools plus the disease-resistant pool and the susceptible pool, a total of four samples were subjected to whole-genome sequencing. Through BSA-seq analysis, compare the difference of SNP-index and Indel-index between the offspring and the reference parent and the distribution of ΔSNP / Indel-index between the two offspring, and perform regional positioning of target traits based on SNP and Indel markers, taking into account the distribution of differential loci The degree of difference with Δindex locates the main resistance gene in the candidate interval o...
Embodiment 3
[0041] Example 3 Screening, Prediction and Verification of Candidate Genes
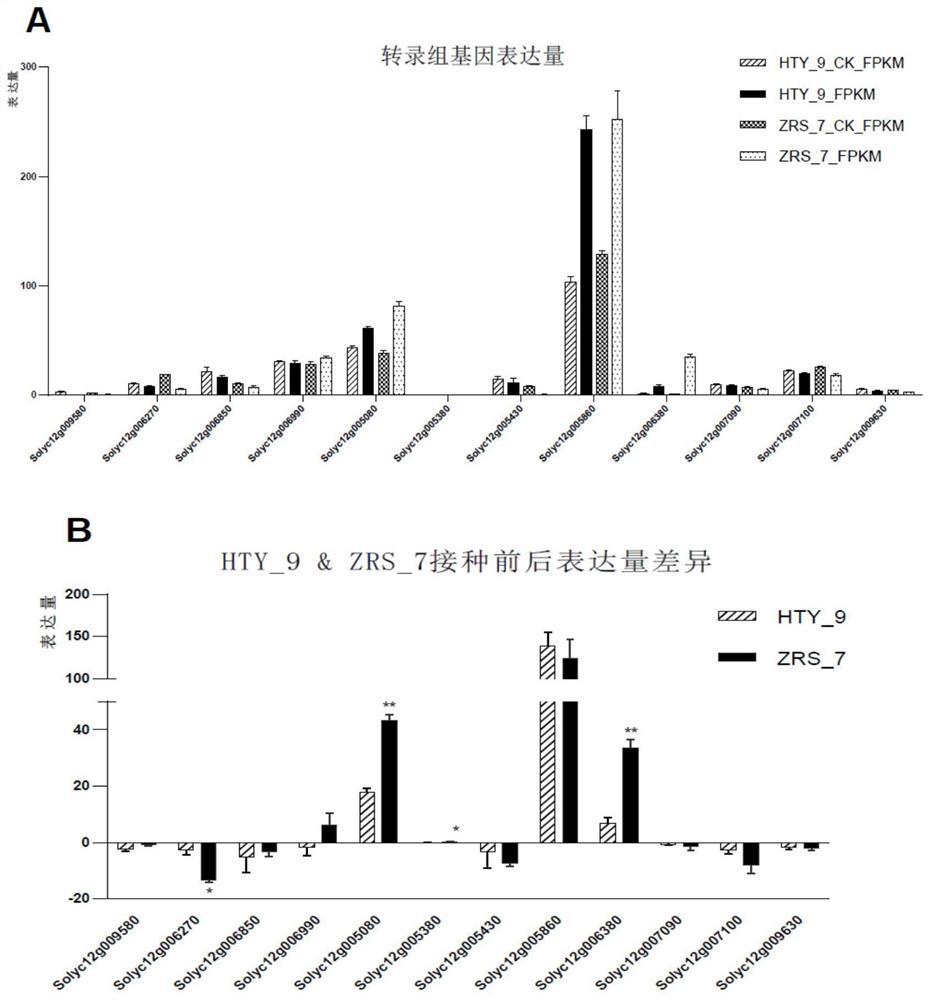
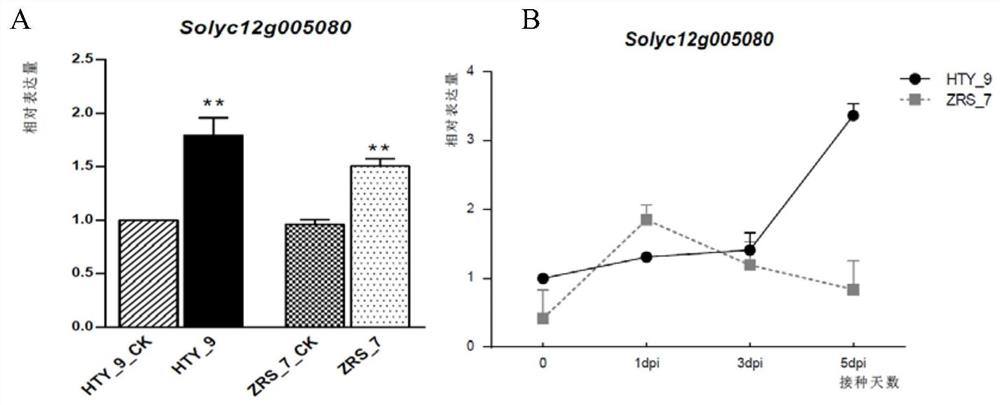
[0042] Based on the preliminary positioning results, combined with transcriptome sequencing for further screening of resistant genes. The stems of the two parents and the highly resistant and susceptible plants in the F2 generation were sampled and RNA was extracted for library construction and transcriptome sequencing. The expression of the 12 genes obtained by screening in transcriptome sequencing (such as figure 2 Shown in A and B), further use fluorescent quantitative PCR to verify the candidate genes, combined with SNP mutation types, gene function annotation and KEGG pathway analysis, and target one of the candidate genes Slα-KGDH E2 (Solyc12g005080), which is involved in Synthetic and metabolic pathways of various secondary metabolites, which play a key role in the tricarboxylic acid cycle. Slα-KGDH E2 has a C→T mutation in the promoter region, which is predicted to form a MIKC-type MADS tra...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com