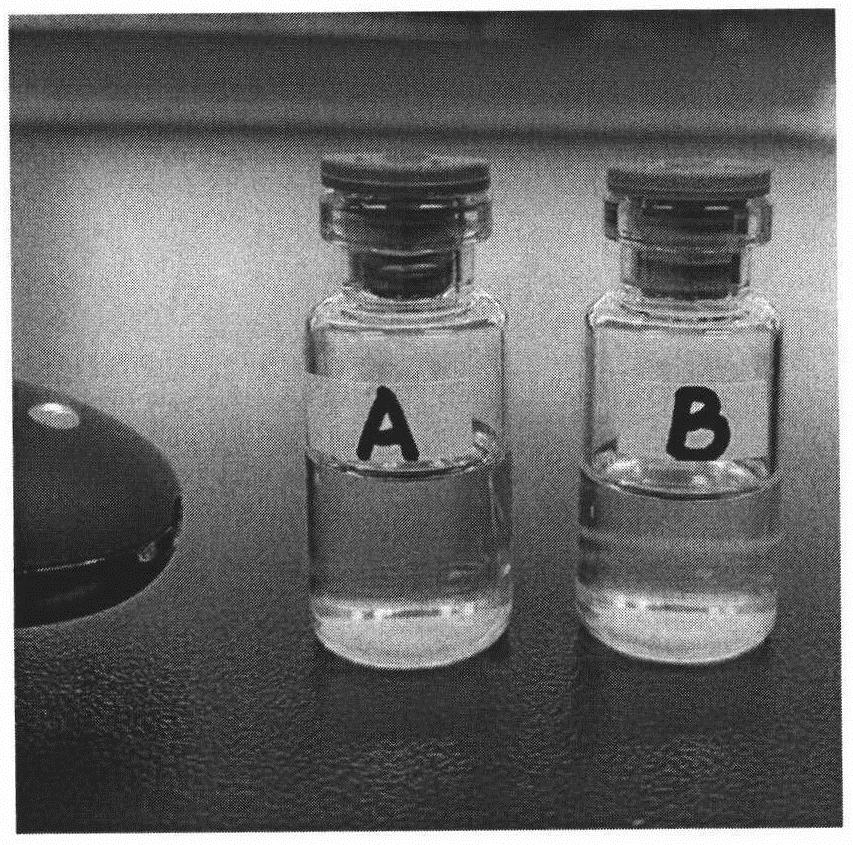
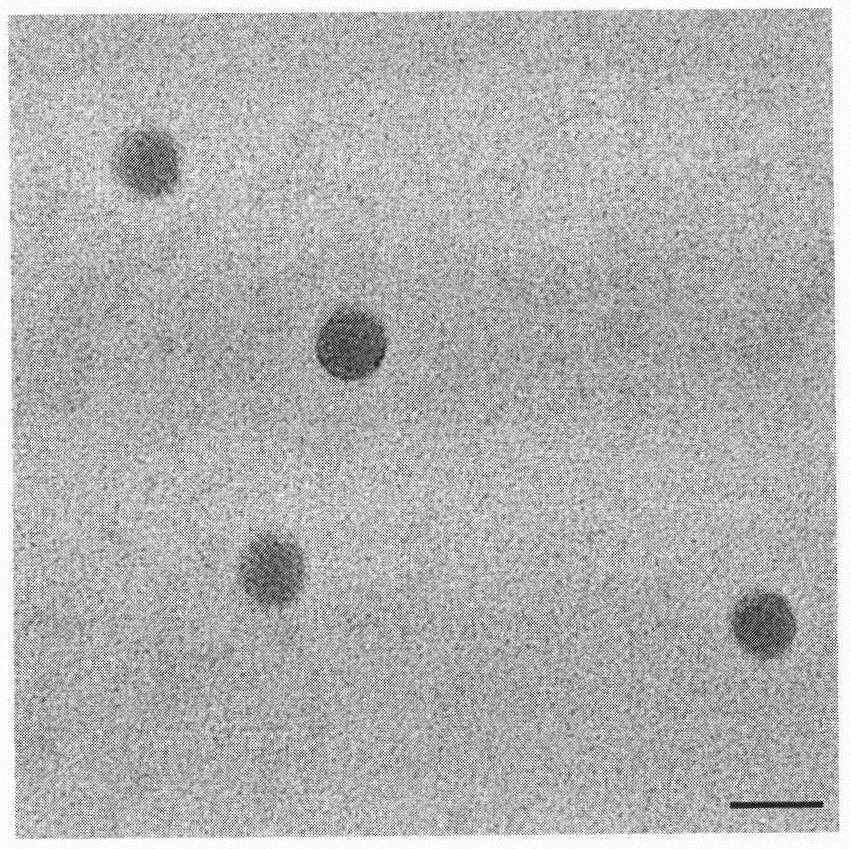
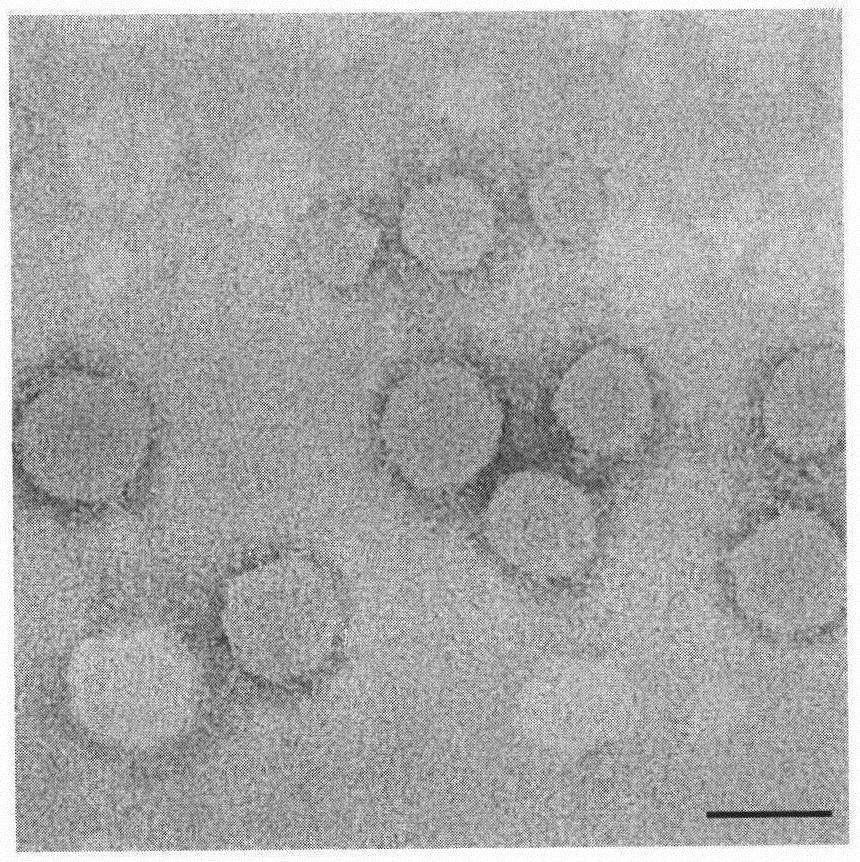
Carrier for transmembrane delivery of molecules and preparation method of carrier
A carrier and molecular technology, applied in non-active ingredient medical preparations, active ingredient-containing medical preparations, pharmaceutical formulations, etc., can solve the limited loading capacity of hydrophilic drugs, easy adhesion, and efficient cholesterol transmembrane characteristics Issues such as not being able to achieve better
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0093] diethylene glycol As a linking group, couple cholesterol and phosphate groups to form a new carrier material with the structure:
[0094]
[0095] The specific synthesis process is as follows: Take 10 g of cholesterol, 8 g of p-toluenesulfonyl chloride, and 50 ml of pyridine to dissolve, stir and react at room temperature for 24 hours, track the reaction by thin-layer chromatography, separate and purify to obtain product A. Take 5g of product A, 20g of diethylene glycol, dissolve in 90mL of epoxyhexacycline, heat and reflux at 120°C for 10h, follow the reaction by thin layer chromatography, separate and purify to obtain product B. Take 1.6g of product B, add 6g of tetrabutyl disodium hydrogen phosphate, dissolve it with 16mL of chloroform, add 2mL of trichloroacetonitrile under the condition of stirring in an ice bath, react for 30min, separate and purify to obtain the final product, the product is white solid.
[0096] The linking group of embodiment 1 is changed...
Embodiment 2
[0098] 1,6-hexanediol As a linking group, couple cholesterol and phosphate groups to form a new carrier material with the structure:
[0099]
[0100] The specific synthesis steps are as follows: after dissolving 5 g of cholesterol, 4 g of p-toluenesulfonyl chloride, and 30 ml of pyridine, the mixture was stirred and reacted at room temperature for 24 hours. Take 5g of product A, 20g of hexanediol, dissolve it in 90mL of epoxyhexacycline, heat and reflux at 120°C for 10h, follow the reaction by thin layer chromatography, separate and purify to obtain product B. Take 0.9g of product B, add 6g of tetrabutyl disodium hydrogen phosphate, dissolve it with 8mL of chloroform, add 1.1mL of trichloroacetonitrile under ice-bath stirring conditions, react for 30min, separate and purify to obtain the final product, the product is white solid.
[0101] The linking group of embodiment 2 is changed into: The carrier material can still be synthesized according to the synthesis steps...
Embodiment 3
[0103] Weigh 100 mg of the final product of Example 2 and dissolve it in 16 mL of chloroform to form an oil phase; weigh 20 mg of triptorelin acetate and dissolve it in 1200 μL of purified water to form an inner aqueous phase 1; 600 μL of 200 mM calcium nitrate solution, pH 5.0, forming the inner water phase 2; adding the inner water phase 1 and the inner water phase 2 to the oil phase at the same time, ultrasonically forming a water-in-oil emulsion, removing chloroform under reduced pressure, drying to remove residual water, and forming a carrier.
[0104] It was analyzed by high performance liquid chromatography, and the drug loading and encapsulation efficiency of the preparation were monitored respectively according to the following formulas. The drug loading and encapsulation efficiency of the carrier prepared in Example 3 are shown in Table 1.
[0105]
[0106]
[0107] Drug loading and encapsulation efficiency of Table 1 Example 3
[0108]
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com