High-temperature gas heat pump system with mechanical supercooling function
A gas heat pump, high temperature technology, applied in heat pumps, mechanical equipment, refrigerators, etc., can solve problems such as power consumption, large irreversible loss of heat exchange, and inability to ensure the uniformity of temperature difference fields.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
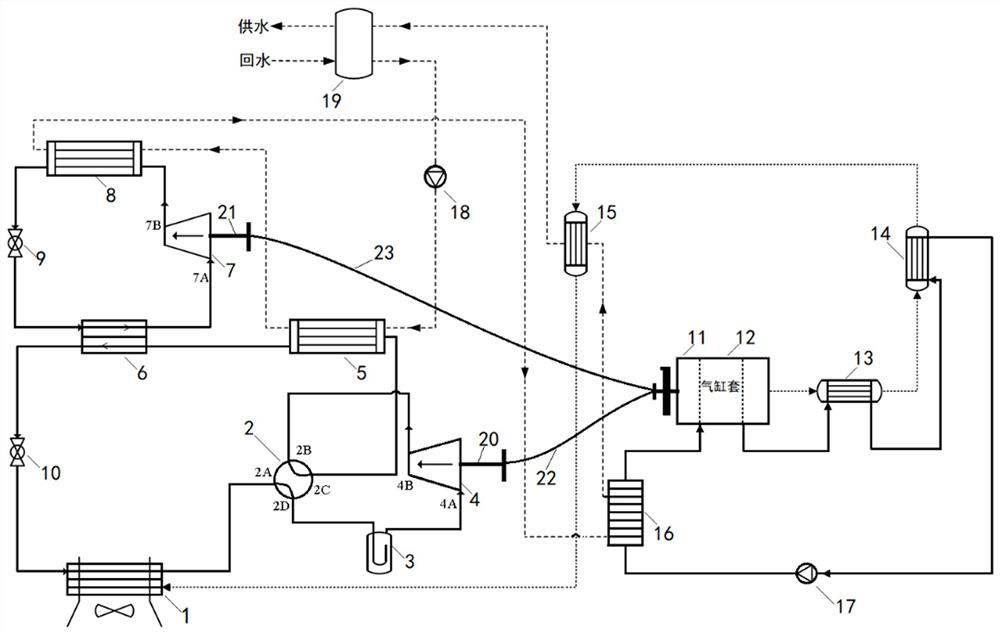
[0035] A high temperature gas heat pump system with mechanical subcooling, including heat pump subsystem, internal combustion engine subsystem, linkage unit and water supply flow path, the structure is as follows figure 1 shown.
[0036] The heat pump subsystem is composed of a heat pump main cycle and a mechanical sub-cooling sub-cycle; The refrigerant channel of the machine 4, the first condenser 5, the high temperature channel of the subcooler 6 and the first throttle valve 10 are sequentially connected in series through pipelines, and the first throttle valve 10 is connected with the low temperature evaporator 1 The refrigerant channels are connected to form a cycle; the subcooler 6 is arranged at the outlet of the first condenser 5 for further condensation and supercooling of the refrigerant; The low-temperature channel of the subcooler 6, the second compressor 7, the second condenser 8, and the second throttle valve 9 are sequentially connected in series through pipelin...
Embodiment 2
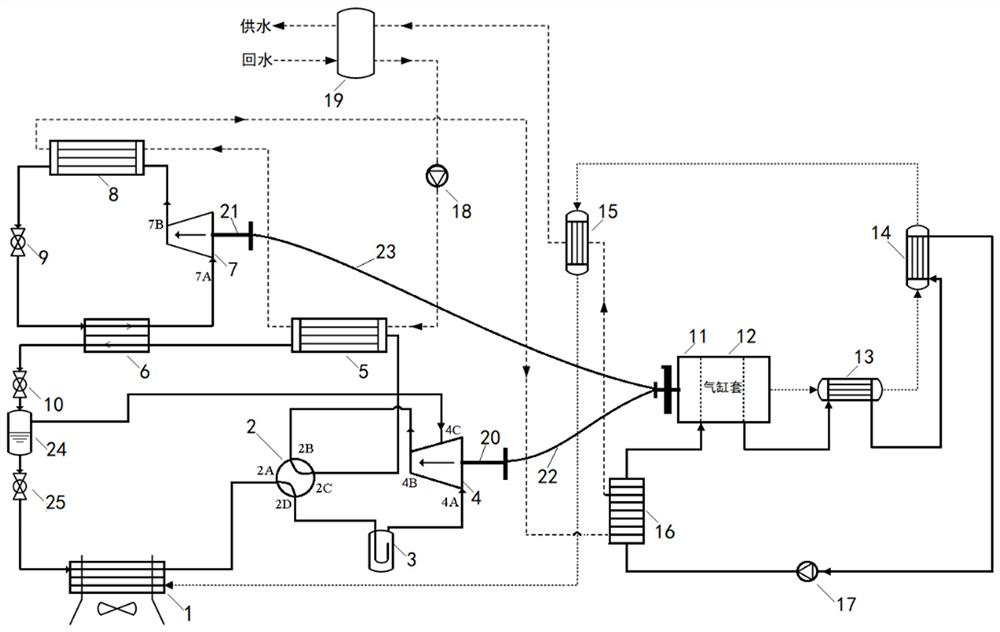
[0060] A high temperature gas heat pump system with mechanical subcooling, including heat pump subsystem, internal combustion engine subsystem, linkage unit and water supply flow path, the structure is as follows image 3 shown.
[0061] Compared with embodiment 1, the first compressor 4 described in embodiment 2 is an air supplementary enthalpy increasing compressor, in addition to having a suction port 4A and an exhaust port 4B, an air supplement port 4C is also added; at this time, the heat pump A flash tank 24 is provided in the main cycle for the separation of liquid refrigerant and gaseous refrigerant after throttling once. The flash tank 24 has a liquid inlet, a liquid outlet and a gas outlet; the first section The flow valve 10 is first connected with the liquid inlet of the flash tank 24, the liquid outlet of the flash tank 24 is connected with the inlet of the third throttle valve 25, and the outlet of the third throttle valve 25 is It is connected with the refriger...
Embodiment 3
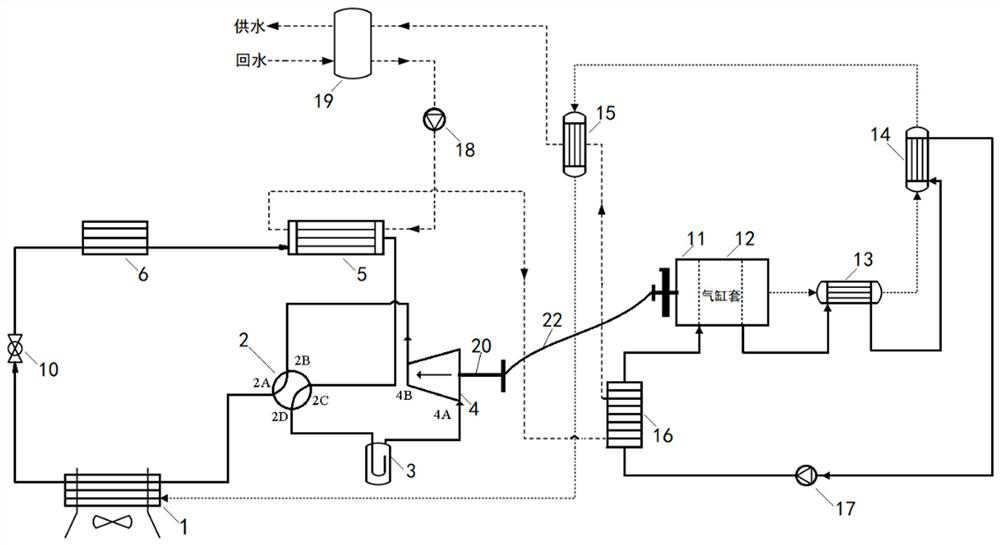
[0065] A high temperature gas heat pump system with mechanical subcooling, including heat pump subsystem, internal combustion engine subsystem, linkage unit and water supply flow path, the structure is as follows Figure 4 shown.
[0066] Compared with Example 1, the heat pump subsystem remains unchanged. Since the engine waste heat belongs to the high-temperature waste heat range, the high-temperature flue gas of the engine can be further used to increase the heating temperature.
[0067] The second flue gas heat exchanger 15 is eliminated in the internal combustion engine subsystem, which is composed of the engine 11, the flue gas flow path and the coolant circulation flow path;
[0068] The flue gas flow path includes the exhaust pipe of the engine 11, the flue gas channel of the three-way catalytic converter 13, the flue gas channel of the first flue gas heat exchanger 14, and the low-temperature evaporation The flue gas channel of device 1;
[0069] The coolant circulat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com