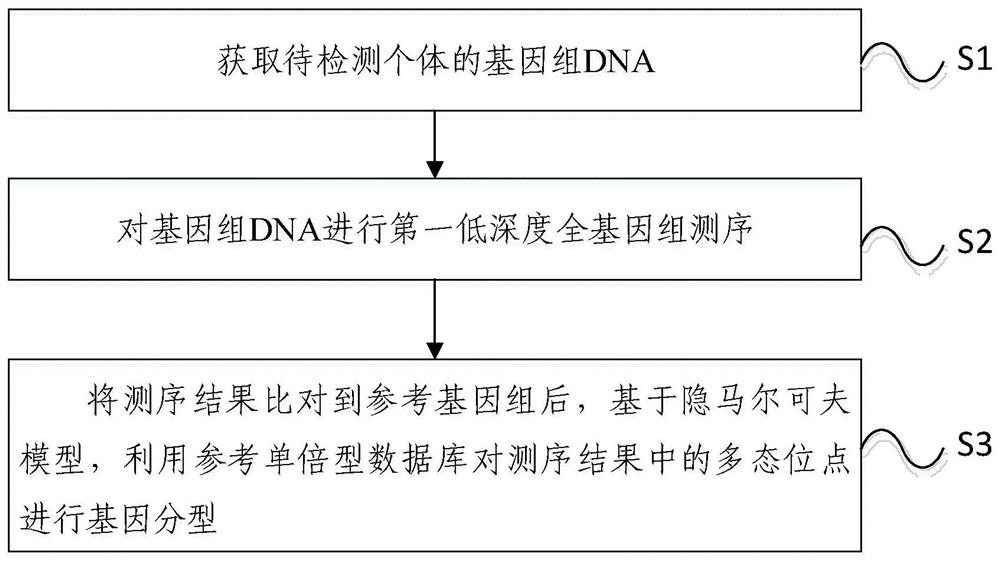
Method and device for detecting SNP marker sites based on low-depth sequencing
A technology of deep sequencing and marking loci, applied in the field of genetics, can solve problems such as wrong typing results, filling that cannot guarantee high accuracy, poor timeliness, etc., and achieve high accuracy results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0059] 1. Experimental materials
[0060] Using 3000 individual ear tissue samples from the core breeding herd of Duroc, the genome was extracted and diluted to 40ng / μL.
[0061] 2. Experimental method
[0062] 2.1 Low-depth DNA library construction and sequencing
[0063] This example uses Tn5 digestion to carry out DNA library construction instructions, specifically:
[0064] (1) Embed Tn5 proenzyme with specific Tn5ME-A / Tn5Merev and Tn5ME-B / Tn5MErev joints at 72°C for 2 hours to obtain Tn5 working enzyme with cut-paste activity, dilute the working enzyme to 16.5ng / μL, In 4 μL 5x TAPS-MgCl 2 , Digest 50ng of genome in the reaction system of 2μL dimethylformamide (DMF) and Nuclease-free water, the condition is 55℃ for 10min.
[0065] (2) Add 3.5 μL of 0.2% SDS to each reaction, and incubate again at 55° C. for 10 min. Subsequently, a PCR reaction was carried out, and 96 different indexes were included in the primers to distinguish individuals.
[0066] The PCR program i...
Embodiment 2
[0076] This example is used to illustrate the accuracy and timeliness of the method for detecting SNP marker sites provided by the present invention.
[0077] 1. Experimental materials
[0078] Genomes were extracted from blood samples of 3000 individuals in Huiyang bearded chicken and Lingnan yellow chicken distant-origin deep hybrid family and diluted to 40 ng / μL.
[0079] 2. Experimental method
[0080]The basic methods of low-depth DNA library construction and sequencing steps, polymorphic site identification and screening, reference haplotype database construction, candidate sample mutation typing and accuracy assessment are the same as in Example 1. The differences include: the average sequencing depth of each individual is about 0.8×; the reference genome uses the chicken GRCg6a (INSDC Assembly GCA_000002315.5, Mar 2018) version; since the genome heterozygosity and complexity of the hybrid population is much higher than that of the pure line population, Therefore, the...
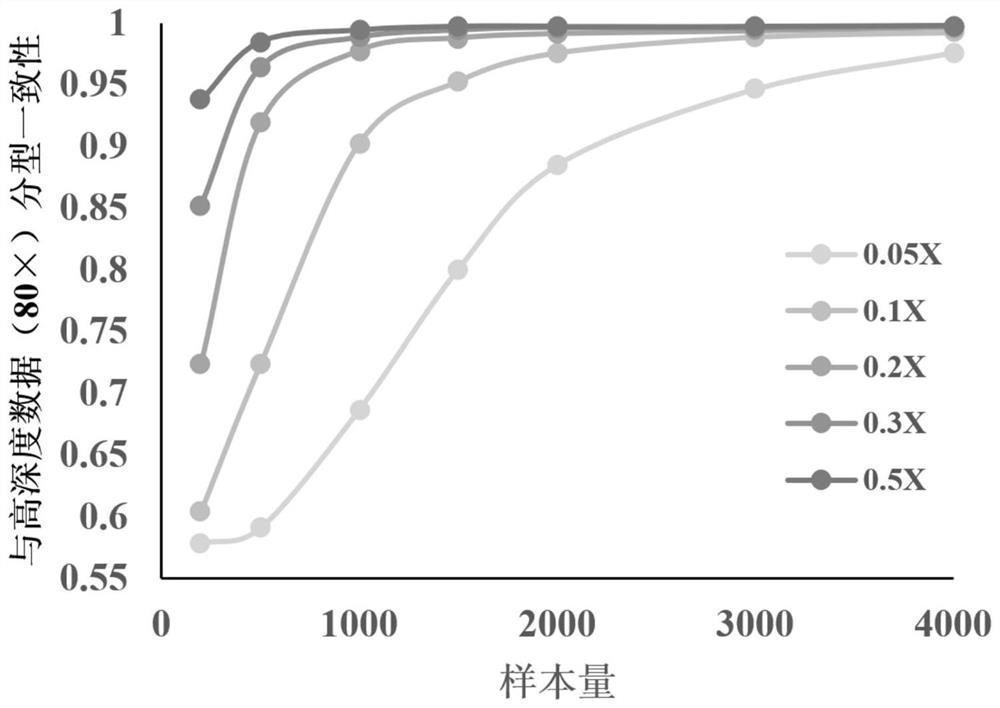
Embodiment 3
[0084] This example is used to illustrate the influence of the sequencing depth and sample size of each sample on the accuracy of genotyping during the construction of the reference haplotype database.
[0085] The experimental materials and experimental methods used in this embodiment are the same as those in Example 2. In the construction of the reference haplotype database, different reference sample sizes (200, 500, 1000, 1500, 2000, 3000, 4000) and the sequencing depth of each sample (0.05×, 0.1×, 0.2×, 0.3×, 0.5 ×), the accuracy was assessed by comparing the final obtained genotyping results with the high-depth data.
[0086] The result is as image 3 shown. It can be seen from the figure that the average sequencing depth of each sample reaches more than 0.2×, and when the sample size exceeds 1500, the accuracy of genotyping is basically stable (maintained above 98.78%), and no longer increases with the sequencing depth and number of samples. Significant changes occur...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com