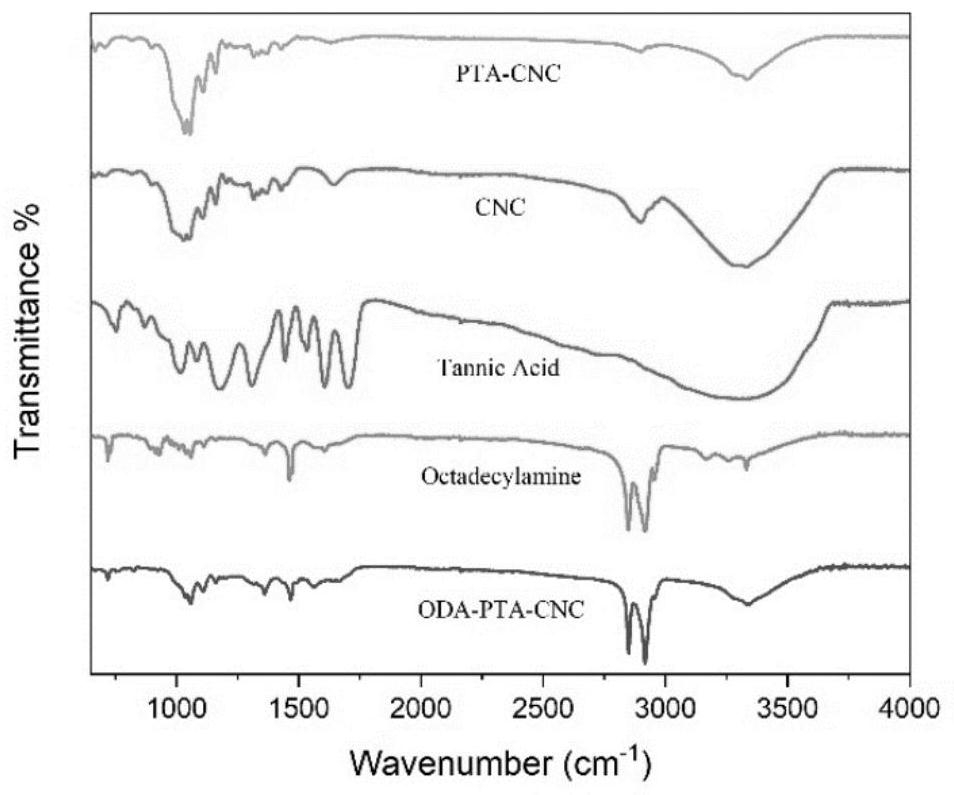
Preparation method of hydrophobic nanocellulose material
A nanocellulose and hydrophobic nanotechnology, applied in the field of preparation of hydrophobic nanocellulose, can solve the problems of hydrophobic coating damage, low durability, low melting point, etc. good biocompatibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0044] A method for preparing hydrophobic nanocellulose, comprising the following steps:
[0045] S1 Add cellulose to concentrated sulfuric acid and heat to 50°C-70°C to stir for hydrolysis, add 10 times the volume of acid deionized water to terminate the reaction, centrifuge the suspension and remove the supernatant, and then centrifuge the lower layer for several times Washing, dialysis with water for 5-10 days after ultrasonication, ultrasonic treatment again to obtain a nanocellulose dispersion, and placing the nanocellulose dispersion in the refrigerated layer of the refrigerator for later use; the cellulose can be pulp cellulose, microcrystalline cellulose and bacterial One or several kinds of cellulose, the dosage ratio of cellulose and sulfuric acid is (15-30) g: (150-300) mL;
[0046] S2 Dilute the nanocellulose dispersion obtained in step S1 with deionized water to a mass concentration of 0.2%-4%, perform ultrasonic treatment on the diluted nanocellulose dispersion f...
Embodiment 1
[0062] Add cellulose to concentrated sulfuric acid, heat and stir for acidolysis, add 10 times the volume of acid deionized water to terminate the reaction, centrifuge the suspension and remove the supernatant, then wash the lower layer of sediment several times by centrifugation, and perform dialysis after ultrasonication Several days, and finally sonicated again to obtain nanocellulose dispersion. Dilute the nanocellulose dispersion obtained in the above steps to a mass concentration of 2%. The nanocellulose dispersion was adjusted to pH 8.5 with 0.01% sodium hydroxide solution, and tris was added to keep the pH constant. According to the nanocellulose / tannic acid mass ratio of 5:1, tannic acid was added to the nanocellulose dispersion, and stirred and reacted for 24 hours in an atmospheric environment. Prepare an octadecylamine ethanol solution with the same volume and mass percentage as the nanocellulose, mix it with the nanocellulose dispersion, stir and react under atmo...
Embodiment 2
[0064] The type, amount and process flow of the materials used are the same as in Example 1, except that octadecylamine is replaced with tetradecylamine to obtain tetradecylamine-polytannic acid-nanocellulose.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com