Processing technology of stone composite board
A processing technology and composite panel technology, which is applied in the field of building decoration materials, can solve the problem of single function of stone composite panels
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
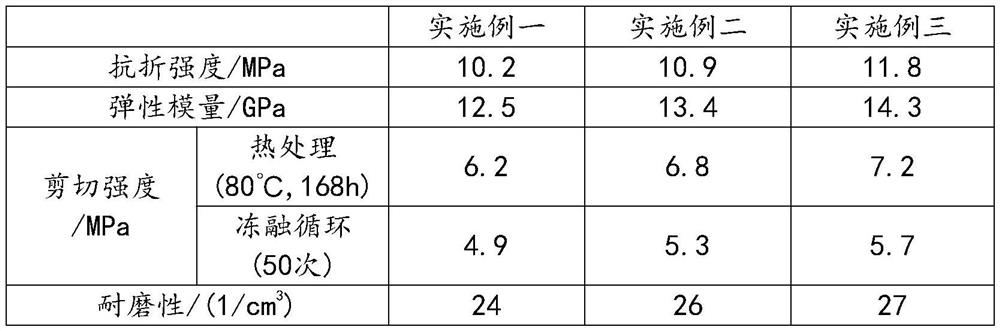
Embodiment 1
[0030] A processing technology for a stone composite board, comprising the following steps:
[0031](1) Polish the surface of the marble sheet with an emery grinding head, so that the surface roughness of the marble sheet reaches below 20 μm, then clean and dry the marble sheet;
[0032] (2) Coating adhesive on one side of the marble, and then bonding the substrate on the surface of the marble. The substrate is mixed uniformly with the following raw materials in parts by weight and then injected into the mold. After curing for 28 days, it is prepared: Portland cement 60 10 parts, 10 parts of stone waste, 15 parts of quartz sand, 0.6 parts of water reducing agent, 12 parts of bisphenol A epoxy resin, 2 parts of polyvinyl acetate, 3 parts of methyl silicone oil, modified fatty amine curing agent DG5930.5 0.5 parts of 2,4,6-tris(dimethylaminomethyl)phenol, 4 parts of aluminum borate whiskers, 3 parts of tetraacicular zinc oxide whiskers, 5 parts of polyvinyl alcohol fibers, and 1...
Embodiment 2
[0044] A processing technology for a stone composite board, comprising the following steps:
[0045] (1) Polish the surface of the marble sheet with an emery grinding head, so that the surface roughness of the marble sheet reaches below 20 μm, then clean and dry the marble sheet;
[0046] (2) Coating adhesive on one side of the marble, and then bonding the substrate on the surface of the marble. The substrate is mixed uniformly with the following raw materials in parts by weight and then injected into the mold. After curing for 28 days, it is prepared: sulphoaluminate cement 70 parts, 14 parts of stone waste, 22 parts of quartz sand, 0.7 parts of water reducer, 16 parts of bisphenol A epoxy resin, 3 parts of polyvinyl acetate, 5 parts of methyl silicone oil, modified fatty amine curing agent DG5932 parts , 1 part of 2,4,6-tris(dimethylaminomethyl)phenol, 6 parts of aluminum borate whiskers, 5 parts of tetraacicular zinc oxide whiskers, 8 parts of polyvinyl alcohol fibers, 15 p...
Embodiment 3
[0058] A processing technology for a stone composite board, comprising the following steps:
[0059] (1) Polish the surface of the marble sheet with an emery grinding head, so that the surface roughness of the marble sheet reaches below 20 μm, then clean and dry the marble sheet;
[0060] (2) Coating adhesive on one side of the marble, and then bonding the substrate on the surface of the marble. The substrate is mixed uniformly with the following raw materials in parts by weight and then injected into the mold. After curing for 28 days, it is prepared: Portland cement 80 18 parts of stone waste, 30 parts of quartz sand, 0.8 parts of water reducer, 20 parts of bisphenol A epoxy resin, 4 parts of polyvinyl acetate, 8 parts of methyl silicone oil, 4 parts of modified fatty amine curing agent, 1 part of 2,4,6-tris(dimethylaminomethyl)phenol, 8 parts of aluminum borate whiskers, 6 parts of tetraacicular zinc oxide whiskers, 10 parts of polyvinyl alcohol fibers, 20 parts of glass be...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Surface roughness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Compressive shear bond strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Compressive shear bond strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com