A catheter system integrating ultrasound imaging and laser ablation
An ultrasound imaging and ablation technique, which is used in the field of intravascular imaging and vascular stenosis treatment, and can solve the problems of dissection or perforation, and the inability to determine the distal end of the ablation catheter.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
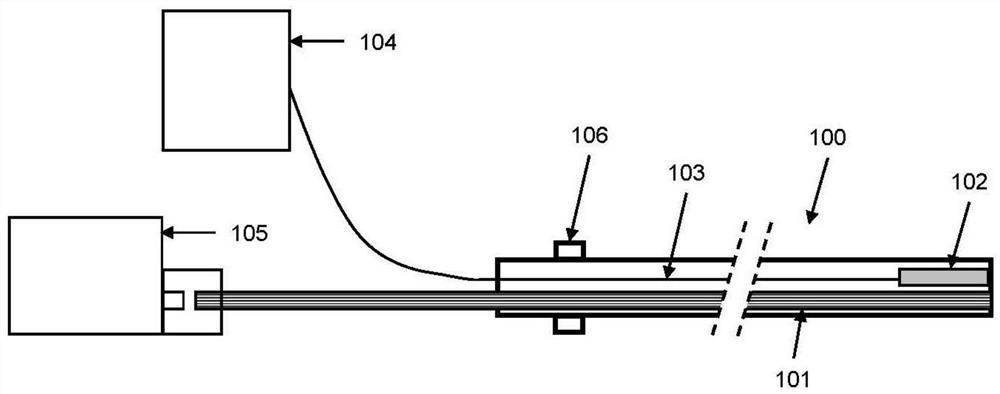
[0050] figure 1 A schematic diagram of a catheter system integrating ultrasound imaging and laser ablation is shown. The catheter system is in the form of a catheter 100 to facilitate access to the patient's blood vessels. The left end of the catheter 100 is called the proximal end of the catheter, and the right end of the catheter 100 is called the distal end of the catheter 200. The system contains an optical waveguide 101, an ultrasound imaging probe 102 and an ultrasound Signal channel 103. The proximal end of the optical waveguide 101 is connected to the pulsed laser light source 105 , and the distal end of the optical waveguide 101 terminates at the end face of the distal end 200 of the catheter. The proximal end of the ultrasonic signal channel 103 is connected to the ultrasonic imaging engine 104, the excitation signal sent from the ultrasonic imaging engine 104 is transmitted to the ultrasonic imaging probe 102 through the ultrasonic signal channel 103, and the elect...
Embodiment 2
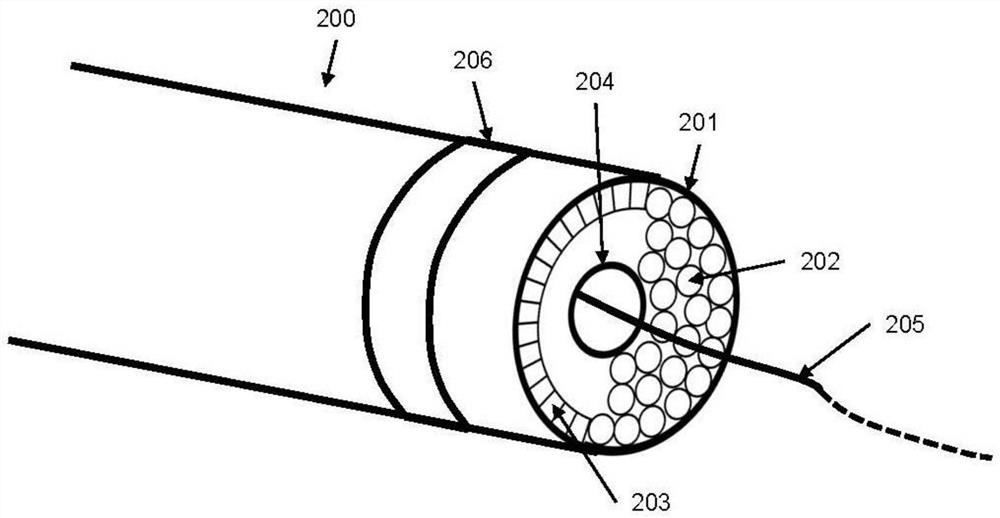
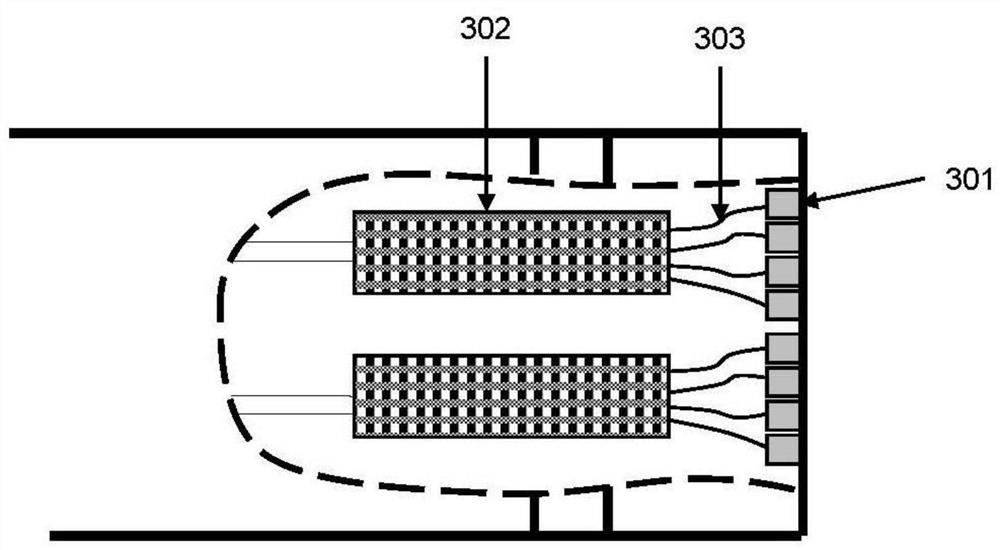
[0056] Figure 4 A schematic diagram of the distal end of the catheter of a catheter system integrating ultrasound imaging and laser ablation is shown. Different from the preferred embodiment 1, the array elements 203 are arranged in a ring along the pipe wall 404 of the catheter. The guide wire channel 204 remains in the middle of the catheter 100 . And the optical waveguide 101 , such as but not limited to the optical fiber 202 , is closely arranged between the ultrasonic sensor array 301 and the guide wire channel 204 . The ultrasound sensor and optical fiber 202 are designed to image the entire cross-section of the vessel wall, and the optical fibers 202 are also arranged concentric with the longitudinal axis of the catheter 100 . Such a design eliminates the need to re-rotate the proximal end of the catheter to image different quadrants of the vessel wall or perform ablation. However, the disadvantage of this is that the exit end face of the optical fiber 202 is far aw...
Embodiment 3
[0058] Figure 5 A schematic diagram of the distal end of the catheter of another catheter system integrating ultrasound imaging and laser ablation is shown. Similar to the preferred embodiment 2, the guide wire channel 204 remains in the middle of the catheter 100 . The difference is that, in the design of this preferred embodiment, the array elements 203 are arranged in a ring along the outer wall of the guide wire channel 204 . The optical fibers 202 are closely arranged between the ultrasonic sensor array 301 and the catheter wall 404 . This design can make the end face of the optical fiber 202 as close to the blood vessel wall as possible, so as to ablate the stenotic tissue close to the blood vessel wall. Since the ultrasonic sensor array 301 is far away from the vessel wall, when controlling the ultrasonic beam, the elevation angle of the scanning surface may need to be changed, such as but not limited to 45° or 50°. Another limitation of this design is that the spac...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com