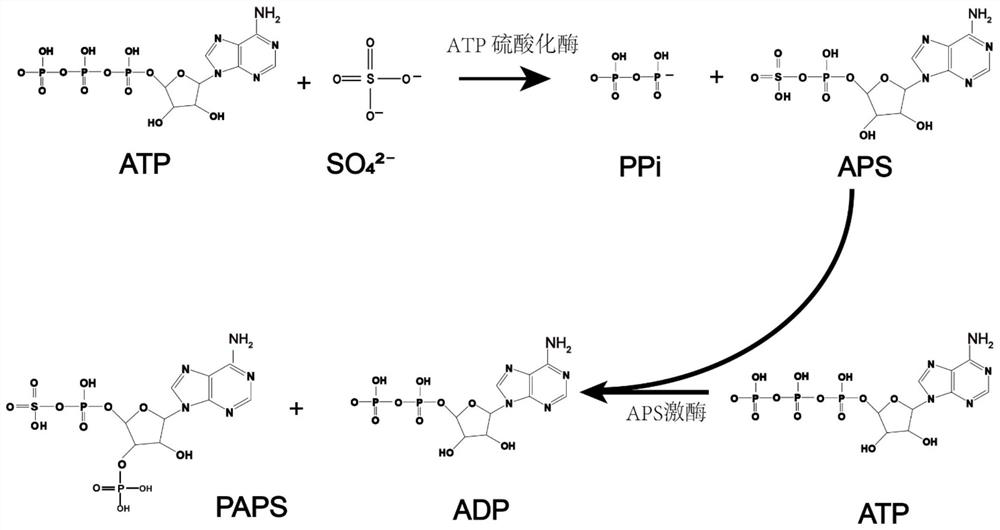
Method for synthesizing PAPS based on construction of bifunctional enzyme
A bifunctional enzyme and kinase technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, biochemical equipment and methods, enzymes, etc., can solve the problems of expensive PAPS, limited application, limited purity of PAPS, etc., to reduce costs, simplify acquisition, shorten The effect of the transfer mass transfer process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
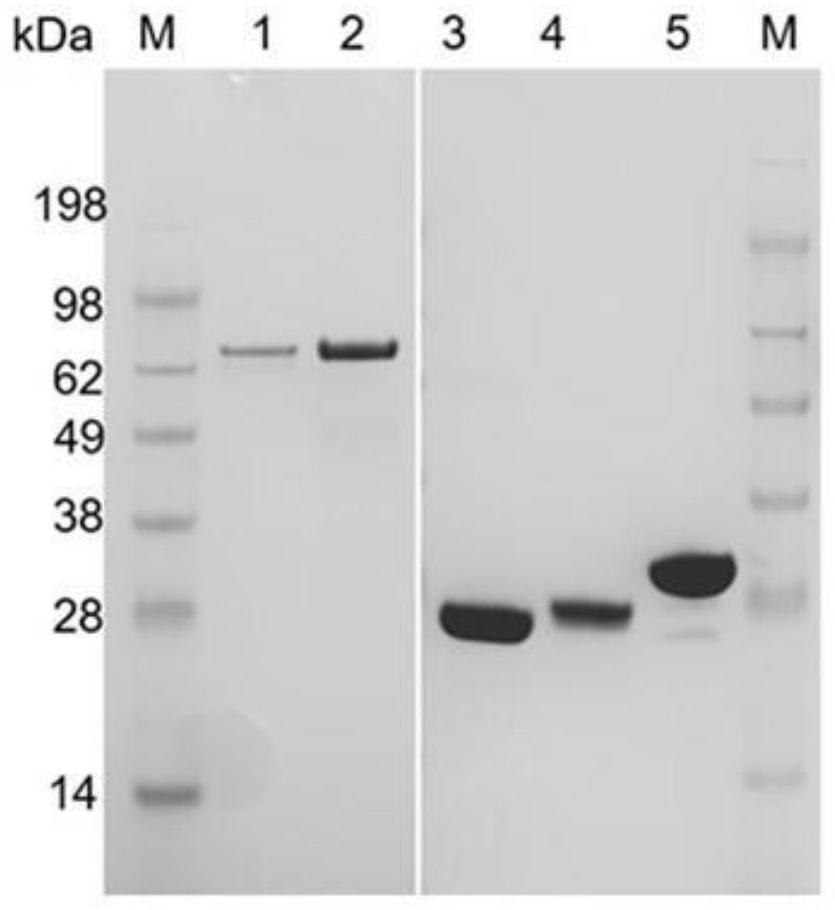
[0072] Example 1: Expression and purification of ATP sulfurylase and APS kinase
[0073] ATP sulfurylase derived from Saccharomyces cerevisiae (Gene ID 853466), ATP sulfurylase derived from Penicillium chrysogenum (GenBank number CAP86100.1), and ATP sulfurylase derived from Kluyveromyces lactis ( Gene ID is 2894185), codon optimization was carried out according to the codon preference rule of Escherichia coli, and the optimized nucleotide sequence was connected between the Nde I and Hind III restriction enzyme sites of plasmid pET28a (+) to obtain recombinant plasmid.
[0074] APS kinase derived from Penicillium chrysogenum (Gen Bank No. U39393.1), APS kinase derived from Escherichia coli (Gen Bank No. M74586.1), and APS kinase derived from Saccharomyces cerevisiae (Gene ID 853869) were selected. , APS kinase of Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Gen Bank No. QGK78545.1), codon optimization was carried out according to the codon preference rule of Escherichia coli, and the optimize...
Embodiment 2
[0079] Example 2: Comparison of ATP sulfurylase and APS kinase from different sources
[0080] After constructing the ATP sulfurylase gene derived from Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Kluyveromyces lactis, and Penicillium chrysogenum on the carrier to obtain the target protein, add equimolar protein 0.1mM to the catalytic system, and the catalytic system is 50-100mM Tris -HCl buffer pH 7.0~8.5, then add 5mM ATP, 4mM MgSO 4 , catalyzed at 35-40°C for 60 hours, using high-performance liquid chromatography to detect the generation of APS, after comparison, the specific enzyme activity of ATP sulfurylase derived from Saccharomyces cerevisiae is higher, and it is more advantageous.
[0081] After obtaining APS kinase proteins from Escherichia coli, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Penicillium chrysogenum, and Mycobacterium tuberculosis, ATP sulfurylases from Saccharomyces cerevisiae were catalyzed and compared together. Add APS kinase from different sources and ATP sulfurylase from Saccharomyc...
Embodiment 3
[0084] Example 3: Enzyme activity assay comparison of bifunctional enzymes with different linker sequences
[0085] Construction of a bifunctional enzyme: ATP sulfurylase derived from Saccharomyces cerevisiae and APS kinase derived from Escherichia coli were fused into one fragment according to genetic manipulation (the sequence of the two enzymes does not affect its expression), and different fusions were added to the linker part The linker sequence (linker) is fused into a fragment, so that both enzymes maintain a certain spatial position, and the catalysis is more orderly. Specifically, the stop codon of the previous gene is removed, directly connected to the linker, and then connected to another gene The sequence of the linker can be SEQ ID NO.1-5 (respectively GGGGGS, EAAAAK, GMALP, GA2PA3PAKQEA3PAPA2KAEAPA3PA2KA, KESGSVSSEQLAQFRSLD), and the number of repetitions n=1 is compared here.
[0086] Expression conditions: Pick a single colony and culture overnight in LB medium...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com