Three-layer bionic skin scaffold based on 3D printing technology and preparation method thereof
A 3D printing and 3D printer technology, which is applied in medical science, prosthesis, additive processing, etc., can solve the problem of non-subcutaneous tissue simulation, achieve low immunogenicity, good mechanical properties, and avoid secondary damage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0072] 1. Preparation of hybrid bioink
[0073] Get freeze-dried GelMA (52% grafting rate) and dissolve in the PBS solution of 45 ℃, then add photoinitiator LAP and photoresist phenol red (MV absorber), make by 8%GelMA, 0.3%LAP Mixed bio-ink with 0.05% photoresist, keep the EP tube containing the ink in a 45°C water bath and wait for printing, and the above operation is protected from light.
[0074] 2. 3D printed three-layer bionic skin scaffold
[0075](1) 3D printing
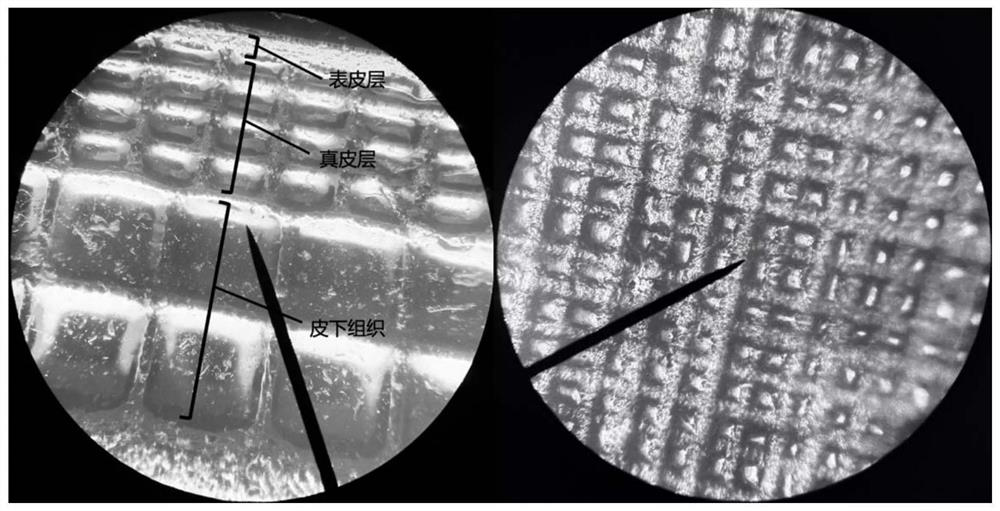
[0076] The three-dimensional model of the above-mentioned three-layer bionic scaffold is used as a model (the epidermis of the skin scaffold model is a dense structure with a height of 400 μm; the dermis is a six-hole structure with a diameter of 200 μm and a height of 1200 μm; the subcutaneous tissue layer is a structure with six holes with a diameter of 400 μm , height 1000 μm; overall length 10600 μm, width 10600 μm, height 2600 μm), import the pre-designed skin scaffold STL file into the DLP photocuring...
Embodiment 2
[0080] 1. Preparation of hybrid bioink
[0081] Get freeze-dried GelMA (52% grafting rate) and HAMA (33% grafting rate) and dissolve them in the PBS solution at 45°C, then add photoinitiator LAP and photoresist phenol red (UV absorber), A mixed bio-ink composed of 8wt% GelMA, 1wt% HAMA, 0.3wt% LAP and 0.05wt% photoresist was prepared, and the EP tube containing the ink was kept in a 45°C water bath for printing, and the above operations were protected from light.
[0082] 2. 3D printed three-layer bionic skin scaffold
[0083] (1) 3D printing
[0084] The three-dimensional model of the above-mentioned three-layer bionic scaffold is used as a model (the epidermis of the skin scaffold model is a dense structure with a height of 400 μm; the dermis is a six-hole structure with a diameter of 200 μm and a height of 1200 μm; the subcutaneous tissue layer is a structure with six holes with a diameter of 400 μm , height 1000 μm; overall length 10600 μm, width 10600 μm, height 2600 μm...
Embodiment 3
[0088] 1. Preparation of hybrid bioink
[0089] Get freeze-dried GelMA (52% grafting rate) and HAMA (33% grafting rate) and dissolve them in the PBS solution at 45°C, then add photoinitiator LAP and photoresist phenol red (UV absorber), A mixed bio-ink composed of 8wt% GelMA, 1.5wt% HAMA, 0.3wt% LAP and 0.05wt% photoresist was prepared, and the EP tube containing the ink was kept in a 45°C water bath for printing, and the above operations were protected from light .
[0090] 2. 3D printed three-layer bionic skin scaffold
[0091] (1) 3D printing
[0092] The three-dimensional model of the above-mentioned three-layer bionic scaffold is used as a model (the epidermis of the skin scaffold model is a dense structure with a height of 400 μm; the dermis is a six-hole structure with a diameter of 200 μm and a height of 1200 μm; the subcutaneous tissue layer is a structure with six holes with a diameter of 400 μm , height 1000 μm; overall length 10600 μm, width 10600 μm, height 260...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Elastic modulus | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Young's modulus | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Young's modulus | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com