Process for continuously preparing N, N-dimethyl-1, 3-propane diamine by using micro-mixing and fixed bed reactors
A technology of fixed bed reactor and dimethylaminopropionitrile, which is applied in the field of preparing N, can solve the problems of low production efficiency and long process reaction time, and achieve the effects of low cost, improved hydrogenation efficiency, and improved mass and heat transfer
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
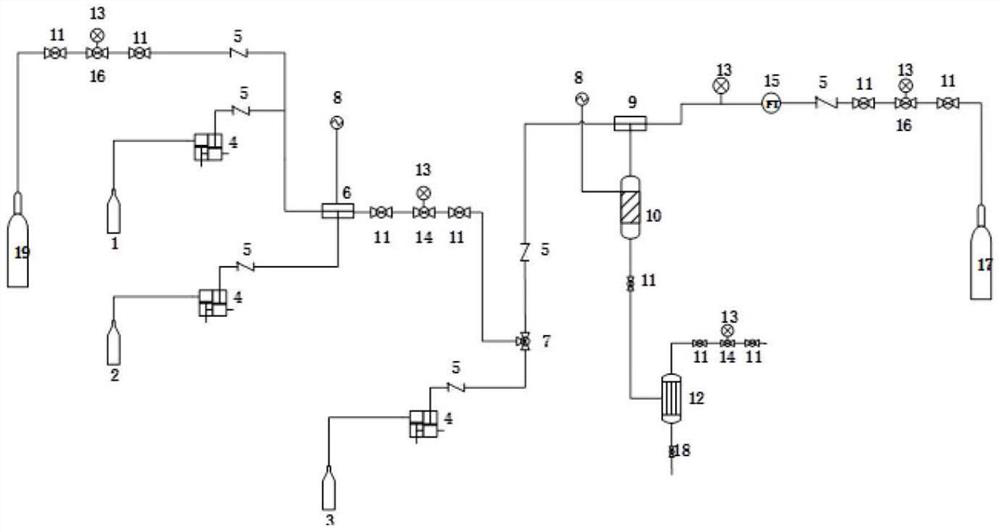
[0024] (1) Firstly, the catalyst Raney-Ni is loaded into the reactor 10 . (2) Open the nitrogen cylinder 19, purge the whole system, discharge the air, set the pressure on the micro-mixing reactor 6 through the nitrogen pressure reducing valve 16: 2MPa, and set the temperature by the temperature controller 8: 35°C. The pressure of the fixed bed reactor 10 is set by the hydrogen cylinder 17 through the pressure reducing valve 16 to the system to set the hydrogen pressure: 3MPa, and the hydrogen flow rate is controlled by the mass flow controller 15, and the temperature is set by the temperature controller 8 to 70°C. (3) Use two double-plunger micropumps 4 to transport dimethylamine (100%) and acrylonitrile (99%) to the micro-mixing reactor 6 with a molar ratio of 1.1:1 for reaction, and the residence time is 1 min Under certain conditions, continuous reaction makes the reaction liquid that contains dimethylaminopropionitrile, and the mass fraction of dimethylaminopropionitrile ...
Embodiment 2
[0026] Using the production method of Example 1, the difference is that the concentration of 40% dimethylamine aqueous solution is used, the concentration of acrylonitrile is 99%, the molar ratio of dimethylamine to acrylonitrile is 1.5:1, the reaction temperature is 25°C, and the reaction pressure is The residence time of 1MPa is 0.5min, the catalyst for hydrogenation is: ethanol solution of 4% NaOH, the content of dimethylaminopropionitrile in the hydrogenation raw material is 35%, the content of NaOH is 0.5%, and the molar ratio of hydrogen to dimethylaminopropionitrile is 5:1 , the reaction temperature is 65°C, the reaction pressure is 4MPa, the residence time is 40min, the hydrogenation catalyst is: Raney Ni, the conversion rate of acrylonitrile is 99.8%, and the yield of N,N-dimethyl-1,3-propanediamine is 98.6% %.
Embodiment 3
[0028] Using the production method of Example 1, the difference is that the concentration of dimethylamine in methanol is 30%, the concentration of acrylonitrile is 99%, the molar ratio of dimethylamine to acrylonitrile is 1.2:1, and the reaction temperature is 30°C. The pressure is 2 MPa and the residence time is 2 minutes. The hydrogenation catalyst is: methanol solution of 10% NaOH, the content of dimethylaminopropionitrile in the hydrogenation raw material is 28%, the content of NaOH is 2.5%, and the molar ratio of hydrogen to dimethylaminopropionitrile is 20:1 , the reaction temperature is 55°C, the reaction pressure is 3MPa, the residence time is 60min, the hydrogenation catalyst is: Raney Ni, the conversion rate of acrylonitrile is 99.8%, and the yield of N,N-dimethyl-1,3-propanediamine is 98.1 %.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com