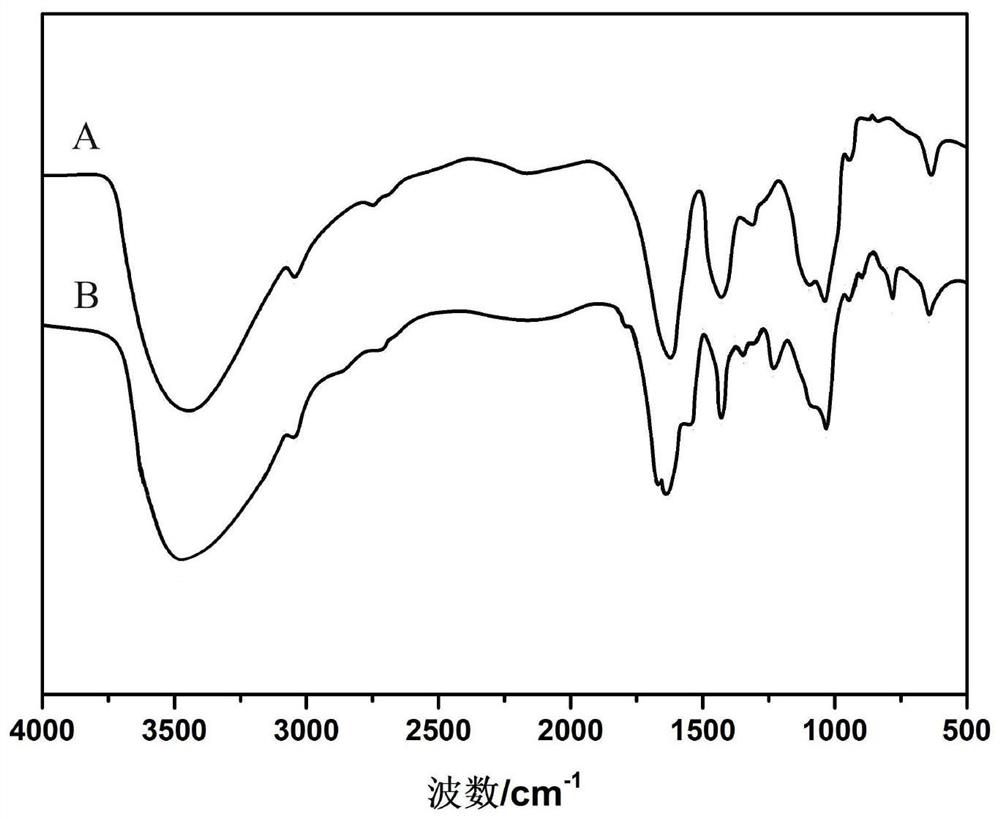
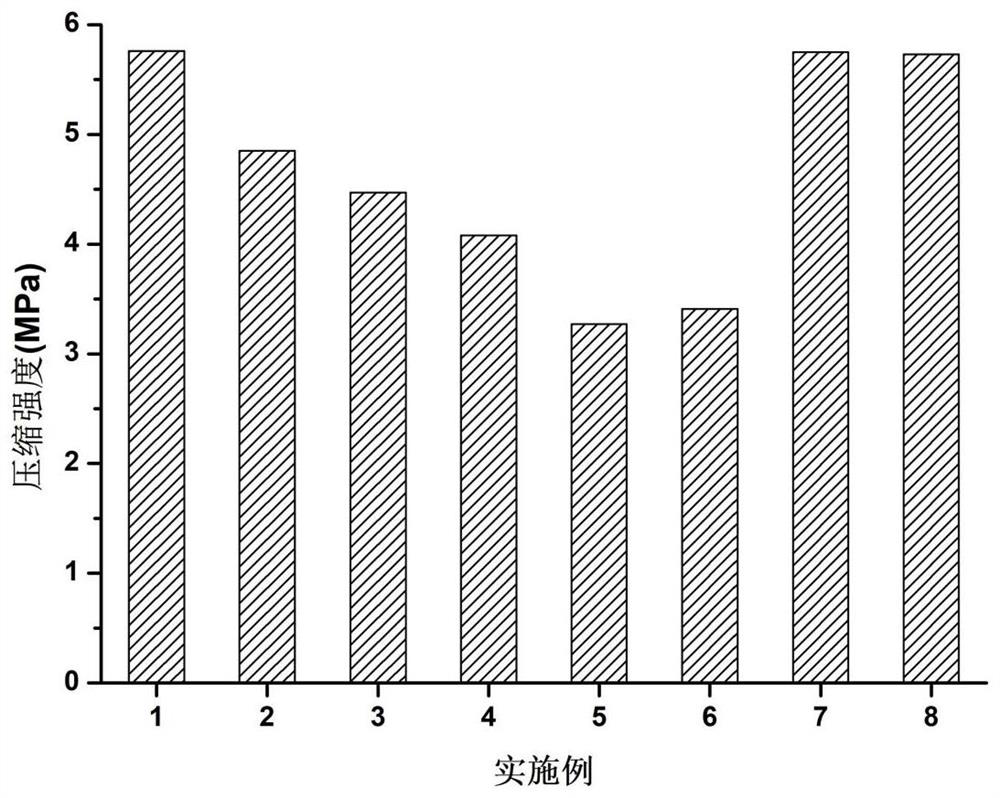
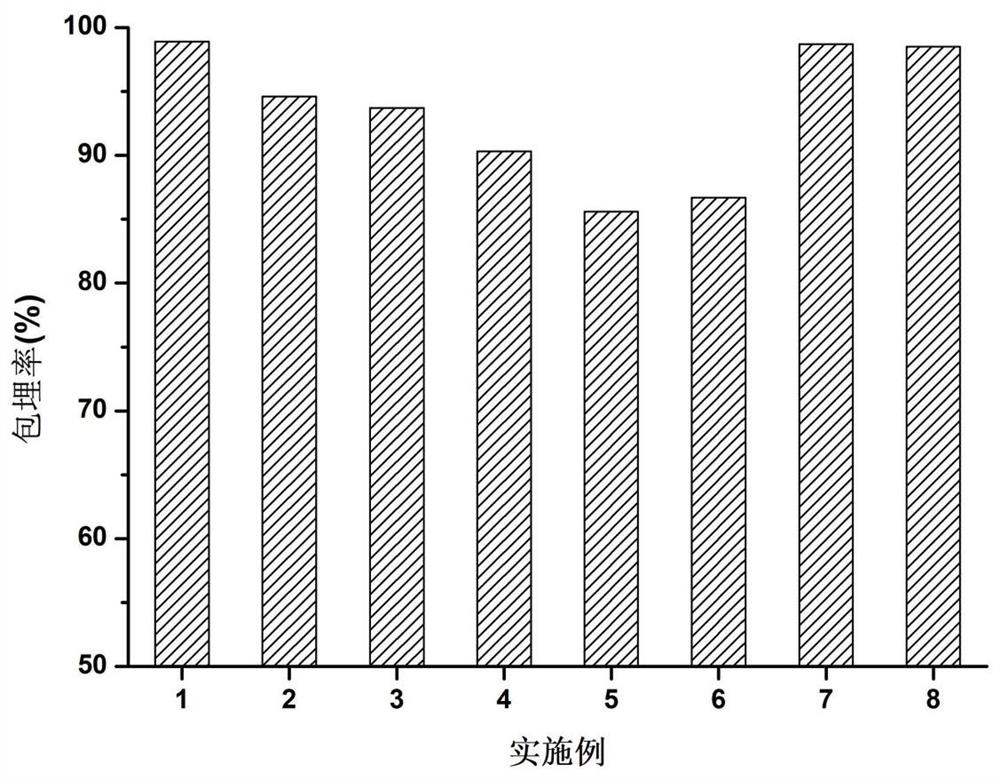
Microorganism preservation method for aerogel immobilization
A technology of immobilizing microorganisms and aerogels, which is applied in the field of microbial preservation, can solve the problems of restricting the application of aerogels, poor toughness, and low strength, and achieve the effect of improving storage stability, increasing strength, and good stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0058] This embodiment provides a method for preserving microorganisms immobilized in airgel, including:
[0059] 1) Dissolve 10g of sodium alginate (viscosity of 350cp) in water to form an aqueous sodium alginate solution with a mass fraction of 4%, adjust the pH to 3.5 with 0.5mol / L sodium hydroxide solution and 0.5mol / L hydrochloric acid solution , adding 9g mass fraction is 4% potassium permanganate solution, 11g acetic acid / tartaric acid mixed solution (the mass fraction of acetic acid in the solution is 5%, the mass fraction of tartaric acid is 6%), add 2g absolute ethanol, avoid light reaction 14h, add 10g of ethylene glycol to terminate the oxidation reaction, then add 1.5g of sodium chloride to mix well, then add enough ethanol to precipitate, and after suction filtration, the precipitate is dissolved in deionized water, repeat the steps of ethanol precipitation, suction filtration, and dissolution 3 times, Vacuum-dried at 50°C to obtain oxidized sodium alginate; 13 g...
Embodiment 2
[0065] This example provides another airgel-immobilized microbial preservation method. In the process of preparing sodium alginate derivatives, no oxidized sodium alginate is added, and only sodium alginate is used for modification to obtain sodium alginate derivatives. thing; All the other steps are the same as in Example 1.
Embodiment 3
[0067] This example provides another airgel-immobilized microorganism preservation method. In the process of preparing sodium alginate derivatives, no sodium alginate is added, and only oxidized sodium alginate is used for modification to obtain sodium alginate derivatives. thing; All the other steps are the same as in Example 1.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com