Transmitting end and receiving end of quantum communication system for time phase coding
A quantum communication and time phase technology, applied in the field of quantum communication, can solve the problems of reducing the coding rate of the quantum communication system and the low counting efficiency of single photon detectors, so as to increase the practicality, improve the coding rate and reduce the start-up time Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
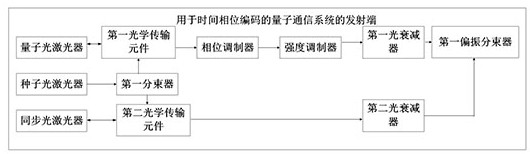
[0041] Such as figure 1 As shown, the transmitting end of the quantum communication system for time-phase encoding provided by the embodiment of the present invention includes a seed optical laser, a first beam splitter, a quantum optical laser, a synchronous optical laser, a phase modulator, an intensity modulator, a first Polarizing beam splitter, first optical attenuator, second optical attenuator, wherein:
[0042] The seed light laser is used to prepare the seed light.
[0043] The first beam splitter is used to split the seed light and input the two split beams into the quantum laser and the synchronous laser respectively in an injection-locked manner.
[0044] In this way, the synchronous optical laser and the quantum optical laser can work in an injection-locked mode based on the seed light output by the main laser, so that the synchronous optical laser and the quantum optical laser have the same wavelength characteristics, so that the synchronous optical laser and th...
Embodiment 2
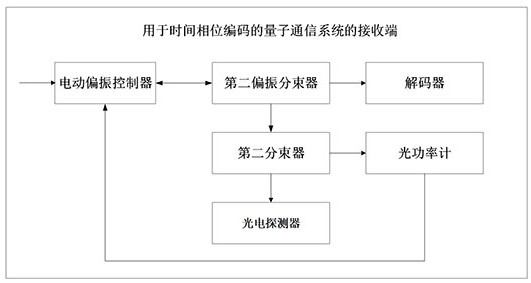
[0065] Such as figure 2 As shown, the receiving end of the quantum communication system for time-phase encoding provided by the embodiment of the present invention includes a motorized polarization controller, a second polarization beam splitter, a decoder, and a second beam splitter, wherein:
[0066] The motorized polarization controller is used to receive the beam-combined quantum light and synchronous light sent by the transmitting end and input the quantum light and synchronous light into the second polarization beam splitter;
[0067] The second polarization beam splitter is used to split the quantum light and the synchronous light and input the split quantum light to the decoder, and input the split synchronous light to the second beam splitter.
[0068] The decoder is used to decode the information to be transmitted from the quantum light.
[0069] Specifically, the decoder includes a single-photon detector, and the single-photon detector is in a gating mode, and qua...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com