Method for leaching and separating bismuth from blast furnace gas dust or/and mud
A blast furnace gas ash and leaching technology, which is applied to the field of leaching and separating bismuth from blast furnace gas ash or/and mud, can solve the problems of increasing the difficulty of purification and separation of bismuth compounds, waste of valuable resources, and low recovery rate, etc., to achieve The effect of high bismuth leaching rate, high selection efficiency and simple process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
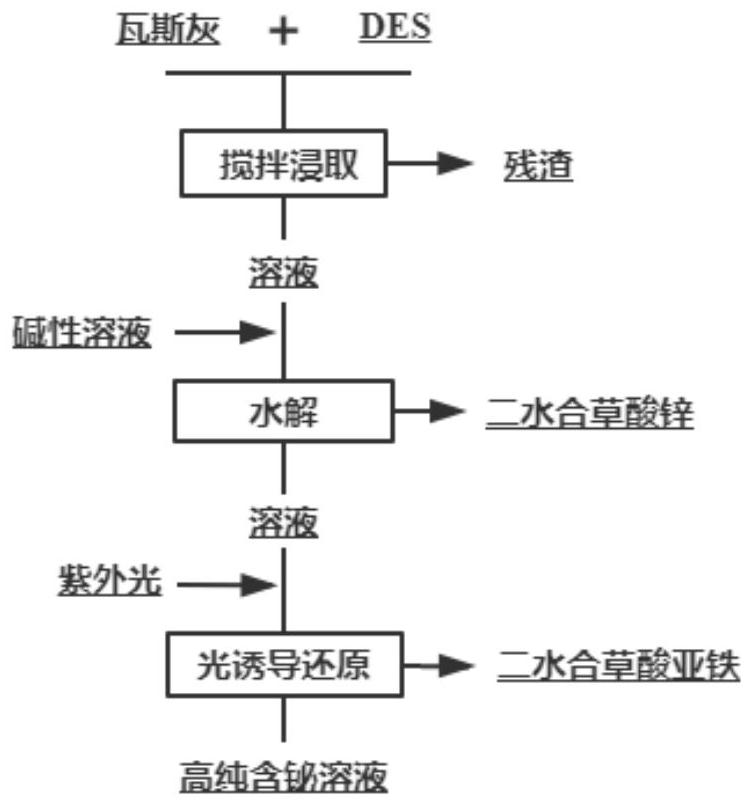
[0027] (1) The quaternary ammonium salt and oxalic acid are formulated into an oxalic acid-based deep eutectic solvent according to a molar ratio of 1:1.
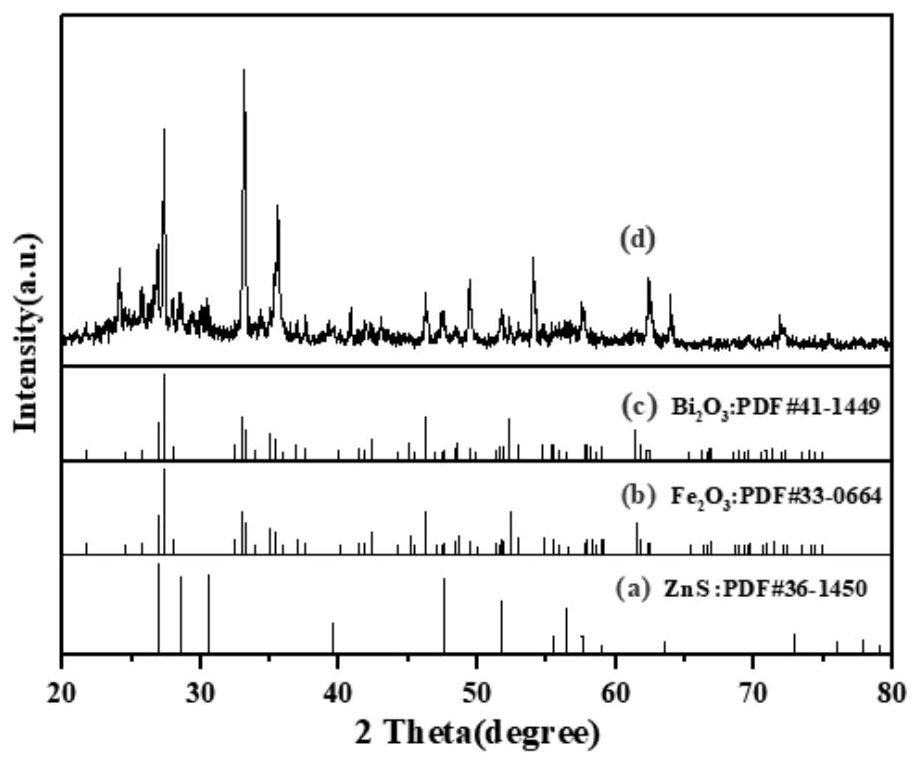
[0028] (2) Add blast furnace gas ash or / and mud (with a bismuth content of 1.56wt%) to the oxalic acid-based deep eutectic solvent prepared in step (1) according to the solid-to-liquid mass ratio of 1:10, at 50°C Stir and leach for 20 hours, and obtain leachate and reaction residue through solid-liquid separation.
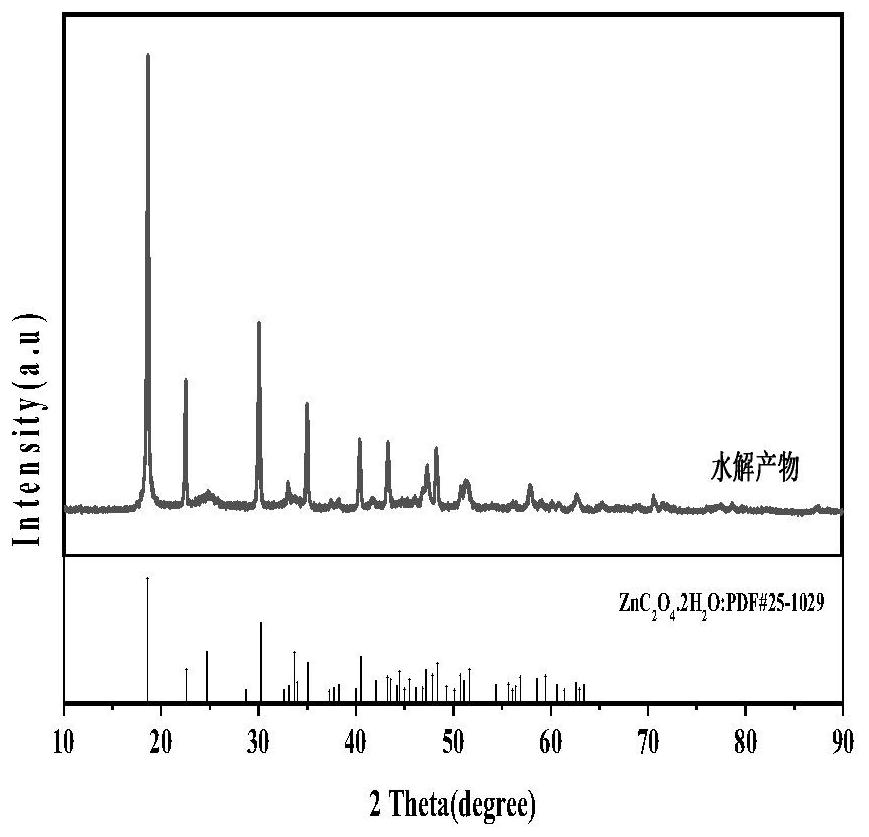
[0029] (3) Add 1mol / l NaOH solution to the leachate obtained in step (2) to adjust the pH of the leachate to 1.50, stir evenly and let stand for 1 hour to obtain a filter residue rich in zinc oxalate and a hydrolyzate through solid-liquid separation.
[0030] (4) The filter residue obtained in step (3) was washed and filtered with magnesium sulfate solution, and dried at 70° C. to obtain a zinc oxalate by-product with a purity of 99.34%.
[0031] (5) The hydrolyzate obtained in step (3) was irradiated with the ...
Embodiment 2
[0033] (1) The quaternary ammonium salt and oxalic acid are formulated into an oxalic acid-based deep eutectic solvent according to a molar ratio of 1:1.
[0034] (2) Add blast furnace gas ash or / and mud (with a bismuth content of 1.36wt%) to the oxalic acid-based deep eutectic solvent prepared in step (1) according to the solid-to-liquid mass ratio of 1:10, at 50°C Stir and leach for 20 hours, and obtain leachate and reaction residue through solid-liquid separation.
[0035] (3) Add 1mol / l NaOH solution to the leachate obtained in step (2) to adjust the pH of the leachate to 1.50, stir evenly and let stand for 1 hour to obtain a filter residue rich in zinc oxalate and a hydrolyzate through solid-liquid separation.
[0036] (4) The filter residue obtained in step (3) was washed and filtered with magnesium sulfate solution, and dried at 70° C. to obtain a zinc oxalate by-product with a purity of 99.66%.
[0037] (5) The hydrolyzate obtained in step (3) was irradiated with the ...
Embodiment 3
[0039] (1) The quaternary ammonium salt and oxalic acid are formulated into an oxalic acid-based deep eutectic solvent according to a molar ratio of 1:1.
[0040] (2) Add blast furnace gas ash or / and mud (with a bismuth content of 1.36wt%) to the oxalic acid-based deep eutectic solvent prepared in step (1) according to the solid-to-liquid mass ratio of 1:5, at 50°C Stir and leach for 20 hours, and obtain leachate and reaction residue through solid-liquid separation.
[0041] (3) Add 1 mol / l NaOH solution to the leachate obtained in step (2) to adjust the pH of the leachate to 1.50, stir evenly and let stand for 1 hour, and obtain a filter residue rich in zinc oxalate and a hydrolyzate through solid-liquid separation.
[0042] (4) Wash and filter the filter residue obtained in step (3) with magnesium sulfate solution, and dry at 70° C. to obtain a zinc oxalate by-product with a purity of 99.09%.
[0043](5) The hydrolyzate obtained in step (3) was irradiated with the ultraviol...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com