Method for gradient recovery of pyrite minerals from copper separation tailings
A technology for selecting copper tailings and recovering sulfur. It is used in recycling technology, mechanical material recovery, solid separation, etc. It can solve the problems of medium consumption, the inability of heavy medium to reduce medium consumption, and the high medium consumption.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
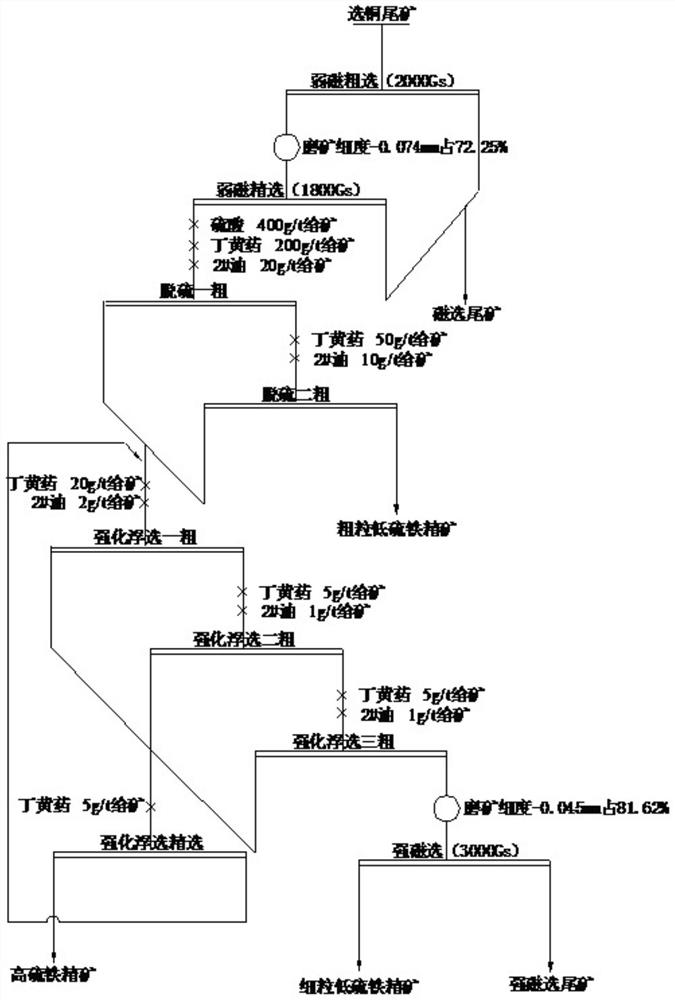
[0024] Example 1, the copper beneficiation tailings used were taken from a copper ore dressing plant in Anhui. The results of sulfur phase analysis of the copper beneficiation tailings are shown in Table 1, and the results of iron phase analysis are shown in Table 2.
[0025] Table 1 Sulfur phase analysis results of copper beneficiation tailings
[0026] Sulfur phase magnetic sulfide sulfur non-magnetic sulfide sulfur total Sulfur content / % 1.19 0.11 1.30 Occupancy / % 91.54 8.46 100.00
[0027] Table 2 Analysis results of iron phase of copper beneficiation tailings
[0028]
[0029]
[0030] It can be seen from the pyrite phase analysis of the copper dressing tailings that the copper dressing tailings contain some magnetic pyrite minerals, the sulfur content of the magnetic sulfide is 1.19%, the sulfur content of the non-magnetic sulfide is 0.11%; the TFe content is 32.42%.
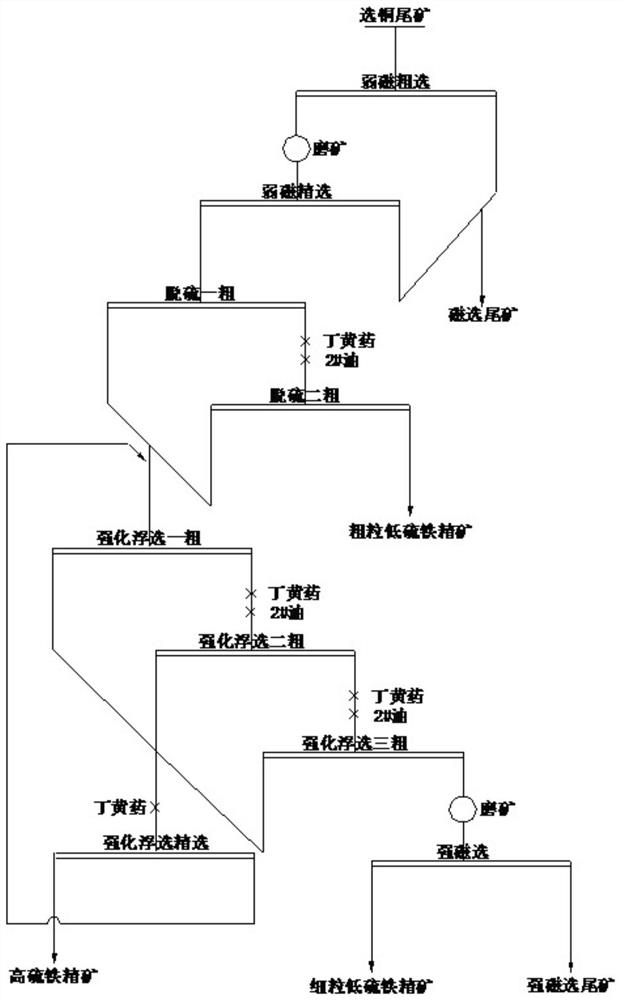
[0031] A method for gradient recovery of pyrite minerals fr...
Embodiment 2
[0048] Example 2, compared with Example 1, the difference is that the magnetic field strength of weak magnetic roughing in S1 is 2200Gs, the magnetic field strength of weak magnetic separation is 2000Gs, and the grinding fineness is controlled at -0.074mm, accounting for 75%; S4 The strength of the medium magnetic field is 3000Gs, and the fineness of regrinding should be controlled at -0.045mm, accounting for 85%. The fine-grained low-sulfur iron concentrate obtained in Example 2 is used as a dense medium in coal preparation and coal washing, and its contained Ti 4+ ,Mg 2+ ,Mn 2+ The grade is relatively lower and the dielectric loss is also lower.
[0049] Table 5 embodiment 2 test scheme iron sulfur resource data are as follows:
[0050]
[0051] Table 6 embodiment 2 test scheme is easy to replace the ion data of iron ion as follows:
[0052]
Embodiment 3
[0053] Embodiment 3, compared with embodiment 1, its difference is that in S3, once rough selection butyl xanthate consumption is 30g / t, 2# oil consumption 4g / t; Secondary and three times rough selection butyl xanthate consumption is 10g / t , the dosage of 2# oil is 2g / t; the dosage of selected Dinghuang is 10g / t. The fine-grained low-sulfur iron concentrate obtained in Example 3 has lower sulfur grade and lower dielectric loss in coal washing.
[0054] Table 5 embodiment 3 test scheme iron sulfur resource data are as follows:
[0055]
[0056] Table 6 embodiment 3 test scheme is easy to replace the ion data of iron ion as follows:
[0057]
[0058] The present invention proposes a method for gradient recovery of pyrite minerals from copper beneficiation tailings. In the method, coarse-grained low-sulfur iron concentrates are first obtained from copper beneficiation tailings through weak magnetic separation and flotation desulfurization, and then the desulfurization foam...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Magnetic field strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Magnetic field strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com