Low-shrinkage 3D printing concrete co-doped with lignin fibers and preparation method of low-shrinkage 3D printing concrete
A lignin fiber, 3D printing technology, used in sustainable waste treatment, solid waste management, climate sustainability, etc., can solve problems such as deficiencies, severe shrinkage cracking, and inability to 3D print the improvement of interlayer bonding properties of concrete. Achieve the effect of optimizing printability, improving interlayer adhesion, and improving early crack resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0036] The present invention also provides a method for preparing low-shrinkage 3D printed concrete compounded with lignin fibers (method for short), characterized in that the method comprises the following steps:
[0037] (1) Mix the dry materials of high belite sulfoaluminate cement, ordinary portland cement, lignin fiber, UEA expansion agent, silica fume and quartz sand to obtain a composite cement-based material;
[0038] Add the thickener and the polycarboxylate water reducer into the water, and stir evenly to obtain a mixed aqueous solution;
[0039] (2) Mix the composite cement-based material with the mixed aqueous solution to obtain low-shrinkage 3D printed concrete compounded with lignin fibers.
[0040] Preferably, in step (1), the mixing equipment of high belite sulfoaluminate cement, ordinary Portland cement, lignin fiber, UEA expansion agent, silica fume and quartz sand is a concrete mixer, and the mixing time is 3- 5min; the mixing time of thickener, polycarboxyla...
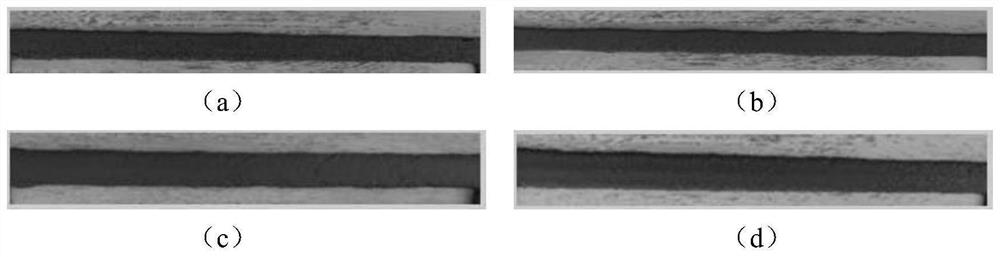
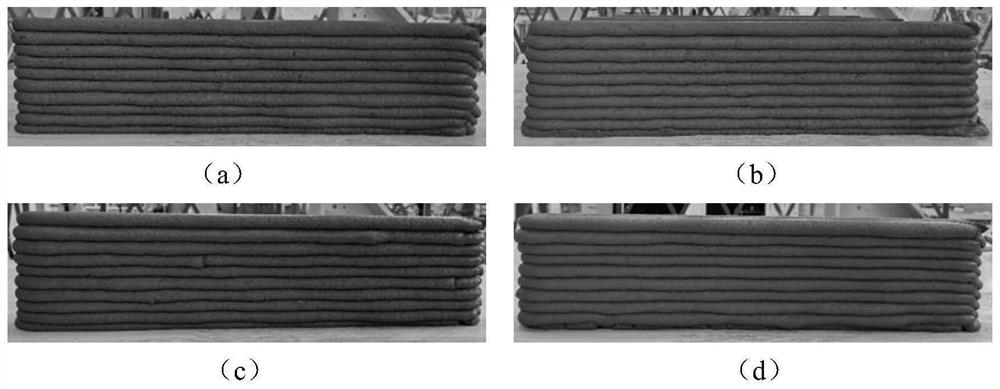
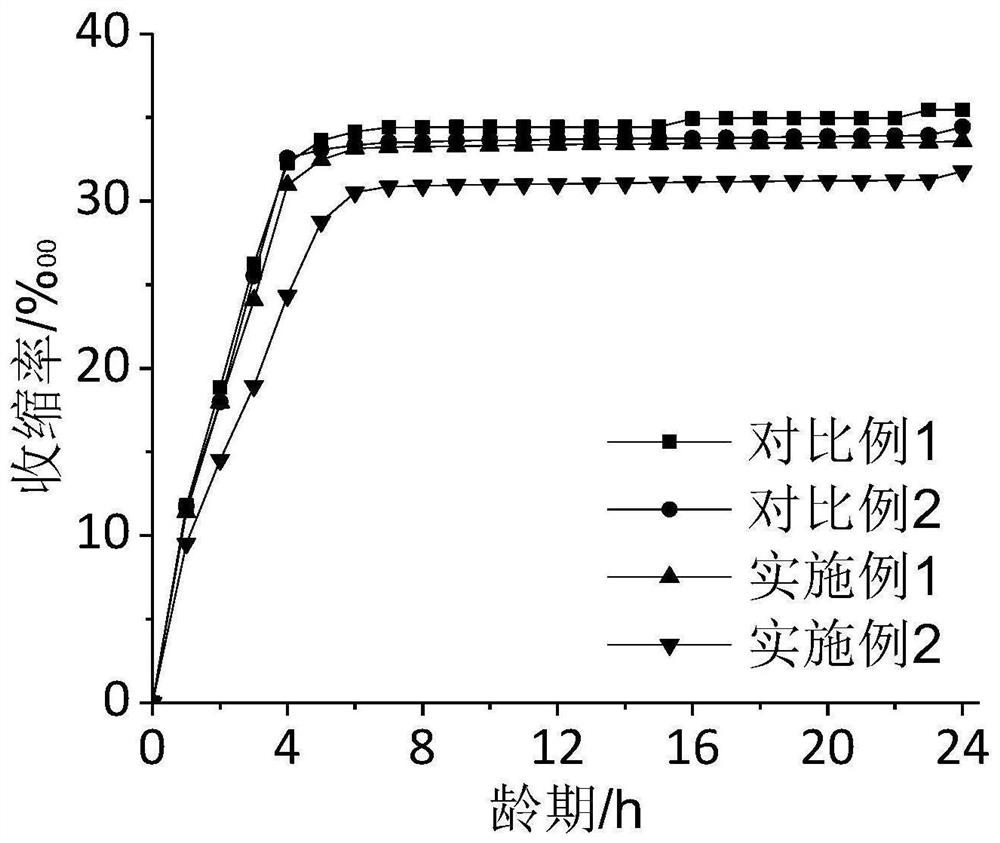
Embodiment 1
[0052] In Example 1, the low-shrinkage 3D printed concrete compounded with lignin fibers includes the following components in parts by weight: 0.05 parts of high belite sulfoaluminate cement, 0.9 parts of ordinary portland cement, and 0.02 parts of lignin fibers 0.05 parts of UEA expansion agent, 0.12 parts of silica fume, 1.2 parts of quartz sand, 0.4 parts of water, 0.001 parts of thickener and 0.002 parts of polycarboxylate water reducer.
[0053] The strength grade of the high belite sulfoaluminate cement is 42.5, the particle size is 0.1-632.5 μm, the initial setting time is ≥ 30 minutes, and the final setting time is ≤ 90 minutes. The strength grade of the ordinary Portland cement is 42.5, the particle size is 0.2-355.7 μm, the initial setting time is ≥ 50 minutes, and the final setting time is ≤ 560 minutes. The density of the lignin fiber is 0.8g / cm 3 , The saturated water absorption rate is 200%. The 14-day water curing limit swelling rate of the UEA swelling agent ...
Embodiment 2
[0060] In Example 2, the low-shrinkage 3D printed concrete compounded with lignin fibers includes the following components in parts by weight: 0.05 parts of high belite sulfoaluminate cement, 0.9 parts of ordinary portland cement, and 0.04 parts of lignin fibers 0.05 parts of UEA expansion agent, 0.12 parts of silica fume, 1.2 parts of quartz sand, 0.4 parts of water, 0.001 parts of thickener and 0.002 parts of polycarboxylate water reducer.
[0061] The strength grade of the high belite sulfoaluminate cement is 42.5, the particle size is 0.1-632.5 μm, the initial setting time is ≥ 30 minutes, and the final setting time is ≤ 90 minutes. The strength grade of the ordinary Portland cement is 42.5, the particle size is 0.2-355.7 μm, the initial setting time is ≥ 50 minutes, and the final setting time is ≤ 560 minutes. The density of the lignin fiber is 0.8g / cm 3 , The saturated water absorption rate is 200%. The 14-day water curing limit swelling rate of the UEA swelling agent ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| compressive strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| flexural strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com