Welding method for heat pipe radiator fins based on scanning galvanometer laser welding
A heat pipe radiator, laser welding technology, applied in laser welding equipment, welding equipment, resistance welding equipment and other directions, can solve the problems of incomplete infiltration, high laser welding power and low absorption rate of aluminum alloy fins, and reduce porosity. , avoid insufficient infiltration, improve the effect of absorption rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
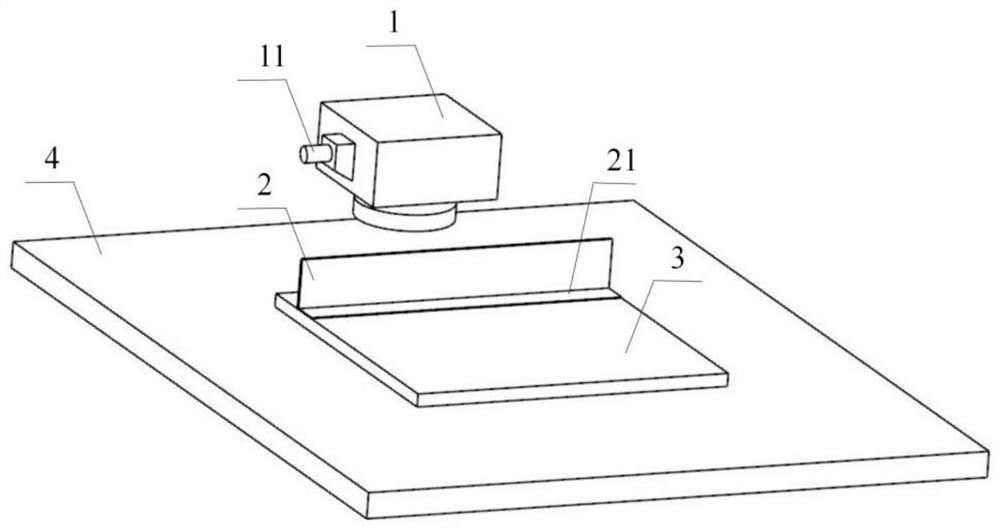
[0049] Such as Figure 4 As shown, the heat conduction substrate 3 of the heat pipe radiator is 120mm long, 90mm wide, and 4mm thick;
[0050] When utilizing the welding method of the present invention, specifically comprise the following steps:
[0051] The first step: the welding surface 21 of the L-shaped fin 2 to be welded is subjected to shot blasting, using irregularly shaped ceramic projectiles with a particle size of 0.05 mm, and the shot peening pressure is 0.1 MPa, and the surface roughness of the obtained fins is at Ra10 - between Ra20;
[0052] Step 2: Place the shot-peened L-shaped fins 2 on the area to be welded on the heat conduction substrate 3 of the heat pipe radiator, adjust the power of the blue laser to 200W, the laser spot diameter to 50μm, and the laser wavelength to 450nm. The beginning and end of the welding surface 21 of the shaped fin 2 are pre-fixed by laser spot welding;
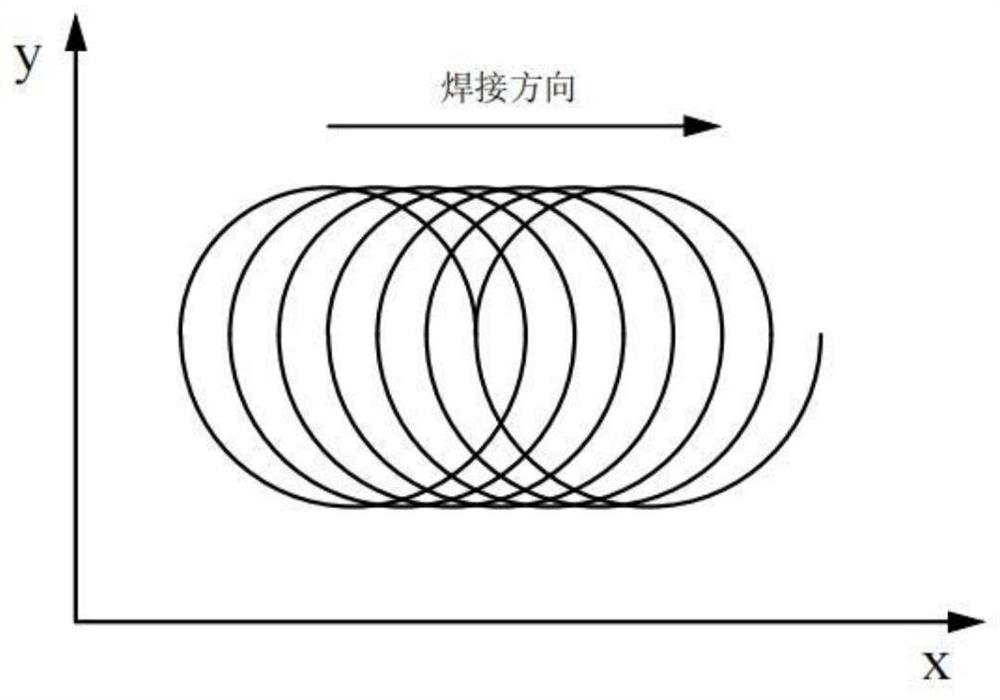
[0053] Step 3: Generate a welding path based on the welding surface 21 of...
Embodiment 2
[0056] Such as Figure 5 As shown, the heat-conducting substrate 3 of the heat pipe radiator is 90mm long, 100mm wide, and 4mm thick;
[0057] When utilizing the welding method of the present invention, specifically comprise the following steps:
[0058] The first step: the welding surface 21 of the L-shaped fin 2 to be welded is subjected to shot peening treatment, and irregular-shaped cast steel projectiles with a particle size of 0.1 mm are used, and the shot peening pressure is 0.15 MPa. The surface roughness of the obtained fin is at Between Ra10-Ra20;
[0059] Step 2: Place the shot-peened L-shaped fins 2 on the area to be welded on the heat conduction substrate 3 of the heat pipe radiator, adjust the power of the blue laser to 150W, the laser spot diameter to 40μm, and the laser wavelength to 430nm. The beginning and end of the welding surface 21 of the shaped fin 2 are pre-fixed by laser spot welding;
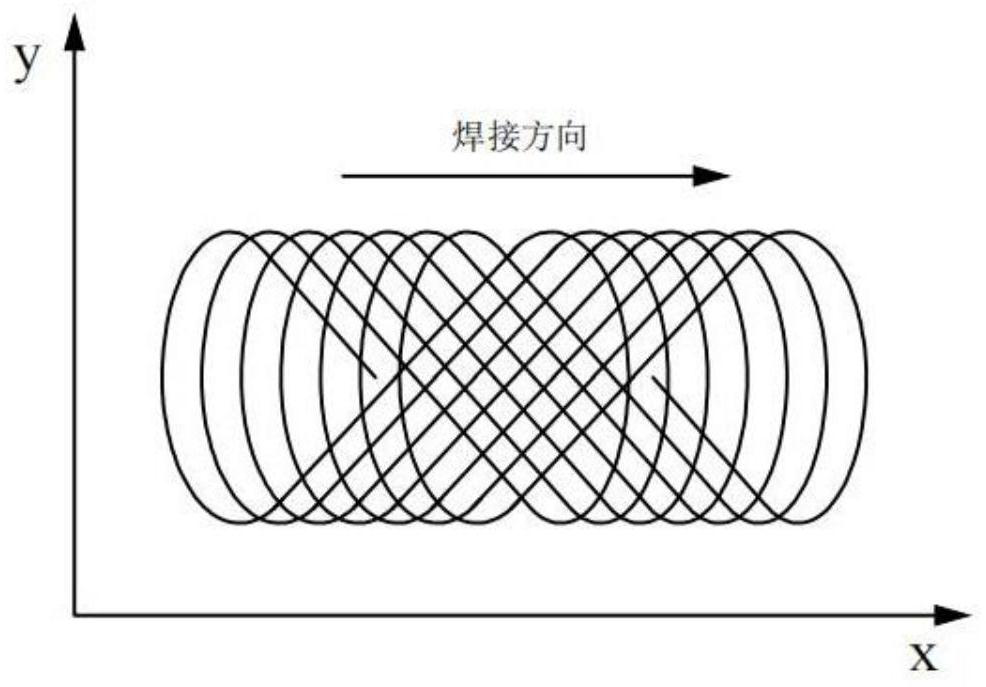
[0060] Step 3: Generate a welding path based on the welding sur...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Laser power | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Laser wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com