An optimized kraken2 algorithm and its application in next-generation sequencing
A sequencing data and sequence technology, applied in the field of bioinformatics, can solve problems such as sequence error alignment, inaccurate alignment, and short read length, so as to improve accuracy, reduce meaningless detection, and reduce false positive detection Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
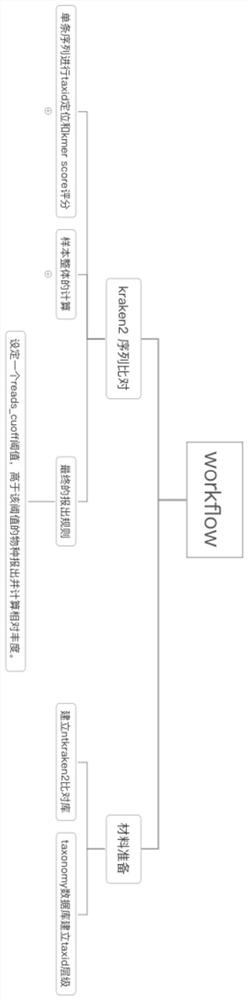
[0107] The design optimization of embodiment 1 method system
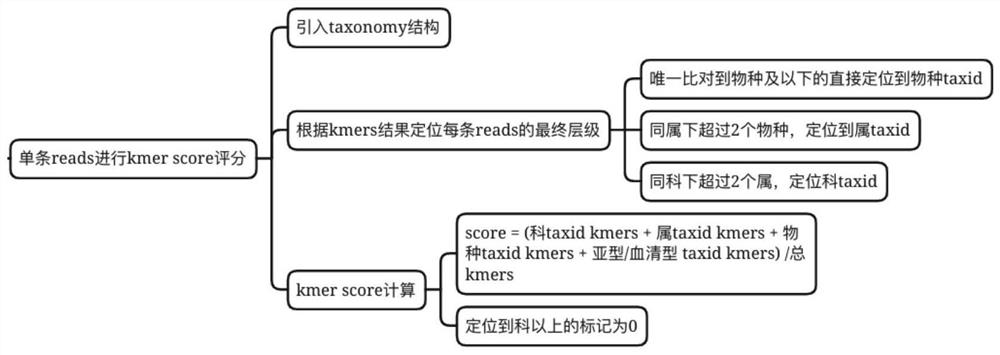
[0108] The problem to be solved in this embodiment is how to ensure the accuracy of the kraken2 comparison results as much as possible through the data analysis method.
[0109] 1. First of all, for this problem, it can be divided into two problems, how to reduce the detection of false positive species to improve specificity, and ensure the detection of real species to obtain higher sensitivity. The two achieve the best balance, that is, get best accuracy. By analyzing how kraken2 produces false positive species results, and the cases where the sensitivity will be reduced.
[0110] a) The redundancy of the database, whether it is refseq, genbank or nt, there is a large amount of reference genome redundancy, which is an important reason for false positive detection, and wrong comparison will also reduce the sensitivity;
[0111] b) Sequence similarity, typically, the sequence degree of Escherichia coli and Shigell...
Embodiment 2
[0177] Comparison of the effects of Example 2 and the traditional kraken2 method
[0178] 1. According to the simulation sample results of the final detection of the optimization method, the false positive and false negative detections are sorted out as follows:
[0179]
[0180] Statistical indicators:
[0181] Sensitivity is 117 / 120 (total number of non-human species)=97.5%;
[0182] Three false positive species were detected.
[0183] 2.2 According to the results of kraken2 confidence 0.5+braken process detection, the false positive detection and false negative detection are sorted out as shown in the following table:
[0184] sample taxi species reads relative abundance result sample 1 340412 Aspergillus novofumigatus 1 0.00011 false positive sample 1 984962 Heterobasidion irregular 1 0.00011 false positive sample 1 145522 Nannochloropsis oceanica 4 0.00044 false positive sample 1 28037 Streptococcus miti...
Embodiment 3
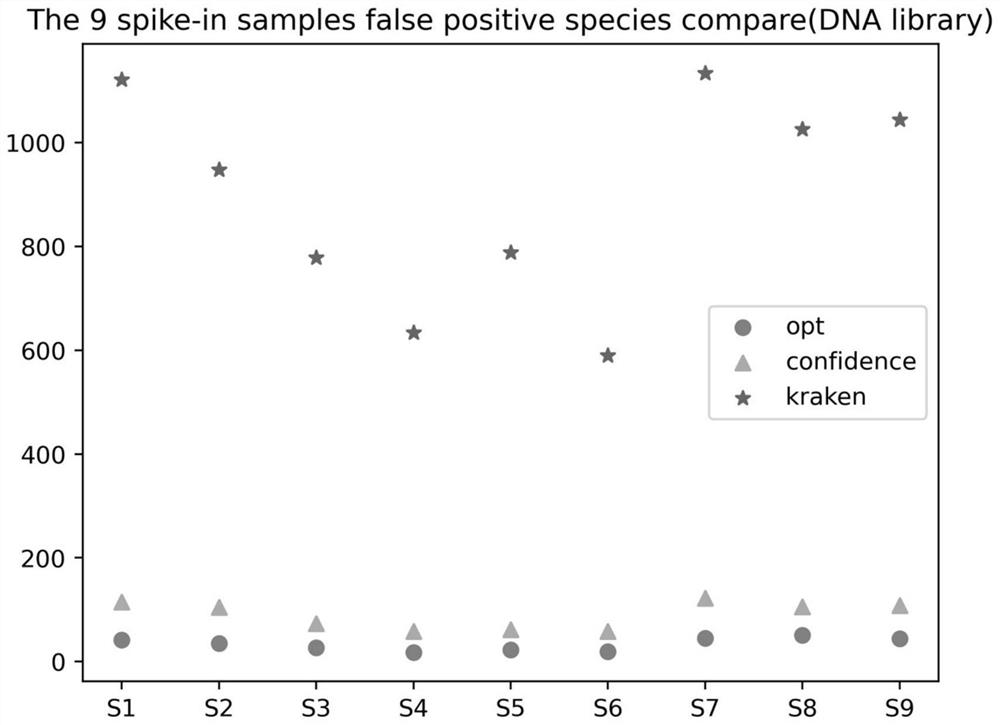
[0190] Embodiment 3 actual sample detection experiment
[0191] Nine spike-in samples were used to establish DNA libraries and RNA libraries for sequencing on the machine. The specific samples and positive species are shown in the table below:
[0192]
[0193]
[0194]
[0195]
[0196]The positive species not detected by the process of the present invention, the positive species not detected by the kraken2 confidence 0.5+bracken process, and the statistics of the positive species not detected by the kraken2+bracken process are shown in the table below (wherein reads_opt, abundance_opt represent the positive species of the process of the present invention Species detection, reads_confidence, abundance_confidence represent positive species detection of kraken2 confidence 0.5+bracken process, reads_kraken, abundance_kraken represent positive detection of kraken2+bracken process):
[0197]
[0198] The total number of positive species is 148, kraken2 confidence 0....
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com