Method for inducing human placental mesenchymal stem cells to differentiate into hepatocytes in vitro and composition containing schisandrin B
A technique for schisandra B and stem cells, which is applied in the field of stem cell biology, can solve the problem that the induction method is not effective, and achieve the effects of clear ingredients, convenient extraction and improved expression level.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
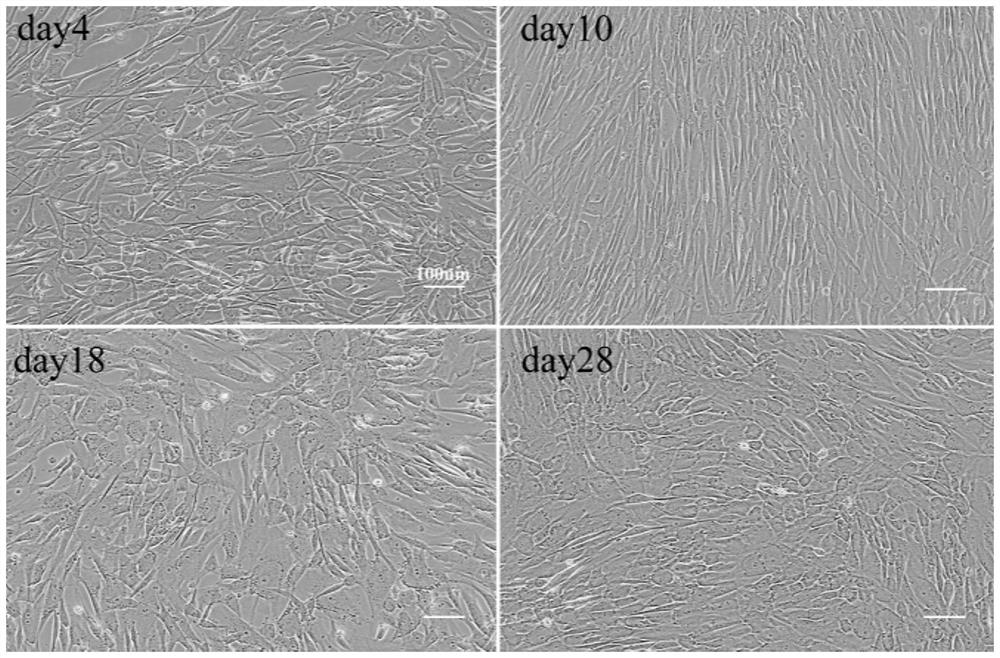
[0038] Example 1: Induction of Human Placental Mesenchymal Stem Cells (PDMSCs) Differentiated into Hepatocytes in Vitro
[0039] A basic method for inducing human placental mesenchymal stem cells to differentiate into hepatocytes in vitro, comprising the following three steps:
[0040] Pretreatment stage: human placental mesenchymal stem cells were induced in human mesenchymal stem cell serum-free medium containing 20ng / ml EGF (epidermal growth factor) and 10ng / ml bFGF (basic fibroblast growth factor) Cultivate for 2-3 days. Specifically:
[0041] 1) The PDMSCs cells of the P3 generation were selected and digested with a mixed liquid containing 0.25% Trypsin and 0.04% EDTA, and 1×10 4 cells / cm 2 The density was seeded in a six-well plate, and human mesenchymal stem cells were cultured in a serum-free environment at 37°C, 5% CO 2 , cultivated in a saturated humidity incubator for 24 hours. The human mesenchymal stem cell serum-free medium is prepared from human mesenchymal...
Embodiment 2
[0053] Example 2: Optimization of conditions for inducing human placental mesenchymal stem cells to differentiate into hepatocytes in vitro
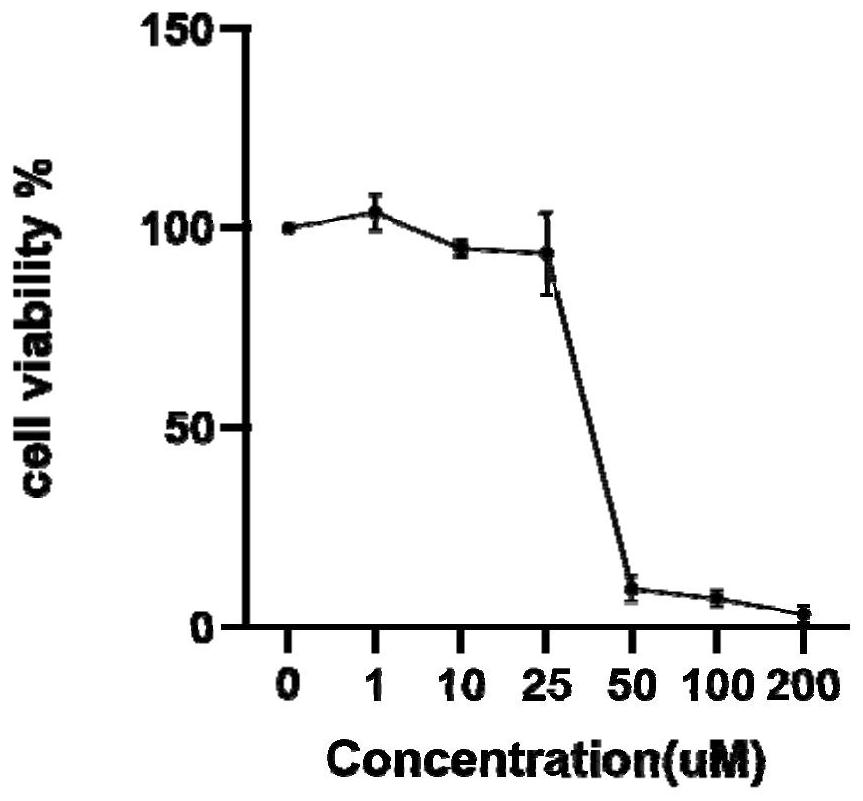
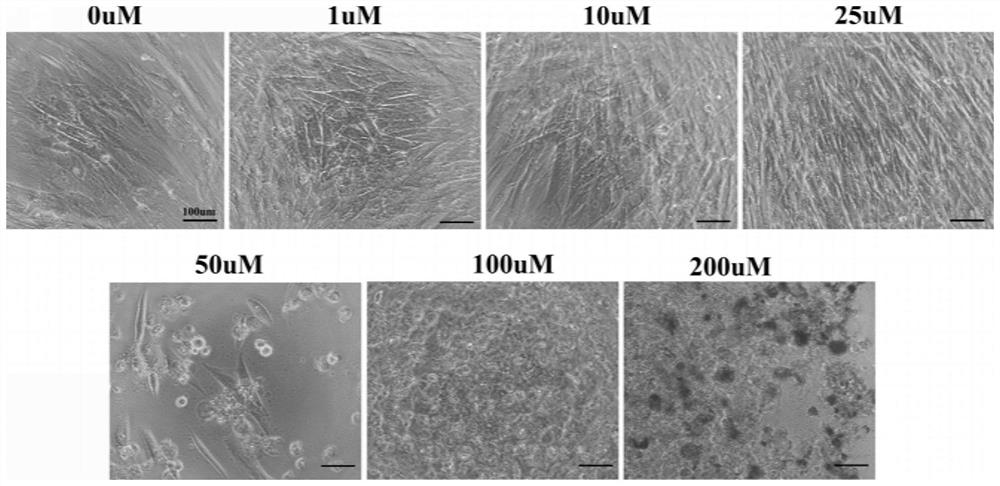
[0054] In order to determine that Schisandrin B (Schisandrin B) can promote the differentiation of PDMSCs to hepatocytes, promote the expression of cytochrome enzymes, and improve the drug metabolism function of hepatocytes, the addition of Schisandrin B to the culture medium at different induction stages was designed for comparison, and the final addition was determined. Timing and dosage of Schisandrin B.
[0055] The cytotoxicity of Schisandrin B was determined by CCK-8, specifically:
[0056] 1) The cells were treated with Schisandrin B at concentrations of 0, 1, 10, 25, 50, 100, and 200 μM, cultured at 37° C. in a 5% CO2 incubator for 3 days, and the cell morphology was observed under a microscope.
[0057] 2) Remove the culture medium, add the culture medium containing 10% CCK-8 reagent under the condition of avoiding light, incub...
Embodiment 3
[0079] Example 3: Identification of Induced Differentiation Hepatocytes
[0080] According to the experimental results of Example 1 and Example 2, the optimized induction scheme was obtained, and the induced hepatocytes were further identified, and the expression of liver cell markers was identified by fluorescent quantitative PCR and cellular immunofluorescence methods, and glycogen staining, albumin Secretion test, urea synthesis test, etc. to identify liver cell function.
[0081] 1. Optimized induction program
[0082]
[0083] 2. Experimental grouping
[0084] Blank control group (MSC group): use uninduced PDMSC as blank control
[0085] Control group (HLC-A): no addition of Schisandrin B to induce PDMSC differentiation into hepatocytes was used as the control group
[0086]Experimental group (HLC-B): Add 10 μM Schisandrin B at the beginning of hepatocyte differentiation stage to induce PDMSC to differentiate into hepatocytes as the experimental group
[0087] 3. F...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com