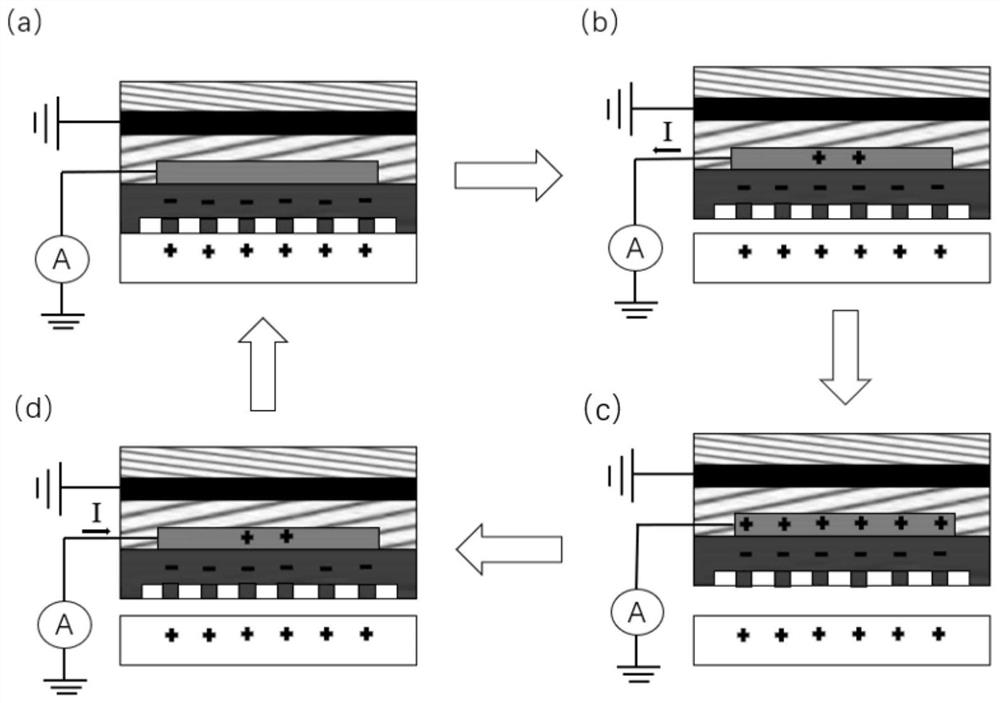
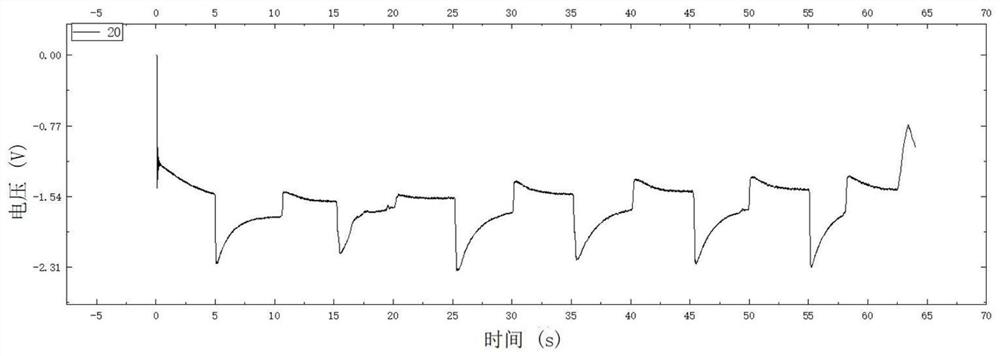
A wearable epidermal sensor for human intention recognition and its application
A sensor and human body technology, applied in the direction of electric/magnetic solid deformation measurement, electromagnetic measurement device, etc., can solve the problems of slow development of mechanical human-machine interface, limited normal activities of human hands, limited wearability, etc., to achieve a good human body. Intent recognition effect, improved wearability, good contact separation effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
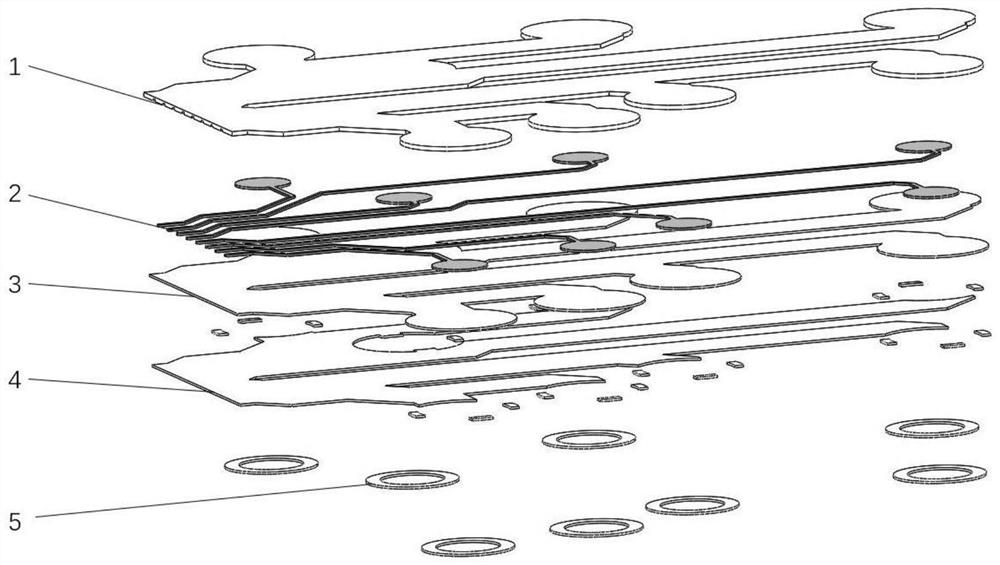
[0046] Select flexor hallucis longus, flexor digitorum profundus, flexor carpi radialis, flexor digitorum superficiale, extensor index finger, extensor hallucis longus, extensor digitorum, extensor carpi radialis brevis, and the encapsulation layer is selected according to The polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) film patterned at the above 8 muscle positions, the electrode layer is sprayed with silver nanowires (AgNWs) to form an electrode film patterned according to the above 8 muscle positions, and the friction layer is selected according to the above 8 muscle positions. The polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) film patterned on the muscle position, the adhesive layer is selected from the adhesive polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) film patterned according to the above 8 muscle positions, and the isolation layer is selected with an inner diameter of 14mm. For a ring-shaped polyethylene terephthalate (PET) film with an outer diameter of 18 mm, the maximum distance between the friction layer PDMS and ...
Embodiment 2
[0049] Select 8 arm muscles, flexor carpi radialis, flexor carpi ulnaris, flexor digitorum superficiale, extensor carpi radialis longus, extensor carpi radialis brevis, extensor carpi ulnaris, and extensor digitorum The encapsulation layer is selected from the aliphatic aromatic random copolyester (Ecoflex) film patterned according to the above 8 muscle positions, and the electrode layer is formed by spin-coating conductive hydrogel to form an electrode film patterned according to the above 8 muscle positions. The aliphatic aromatic random copolyester (Ecoflex) film patterned according to the above 8 muscle positions was selected as the layer, the film formed by spin coating with 3M-VHB tape patterned according to the above 8 muscle positions was selected as the adhesive layer, and the isolation layer was selected from For a ring-shaped polyimide film with an inner diameter of 14mm and an outer diameter of 18mm, the maximum distance between the friction layer Ecoflex and human ...
Embodiment 3
[0052] Human body intention recognition using wearable epidermal sensors includes the following steps:
[0053] S1. Using the wearable epidermis sensor to collect multi-channel signals of gestures and actions corresponding to different intentions of the human body;
[0054] The user wears the wearable skin sensor on the forearm of the human body, and makes each electrode point located at the position of each corresponding muscle, and the offset range between the electrode and the above muscle position is feasible within 10mm. Use a multi-channel acquisition card to collect multi-channel signals of this wearable skin sensor. During the collection, the user keeps the body sitting upright and the forearm horizontal, and makes different gestures, such as Arabic numeral gestures 1, 2, 3, 4, 5. Rehabilitation treatment gestures such as wrist flexion, wrist extension, fist clenching, palm extension, left deviation, right deviation, etc. The duration of the action can be reflected by ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com