Method for extracting valuable metals from low-nickel matte converter slag
A valuable metal and converter slag technology, applied in the field of metallurgy, can solve the problems of complex method parameters, waste of resources, repeated consumption, etc., and achieve the effects of ensuring the reaction rate, saving the amount of use, and reducing the loss.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
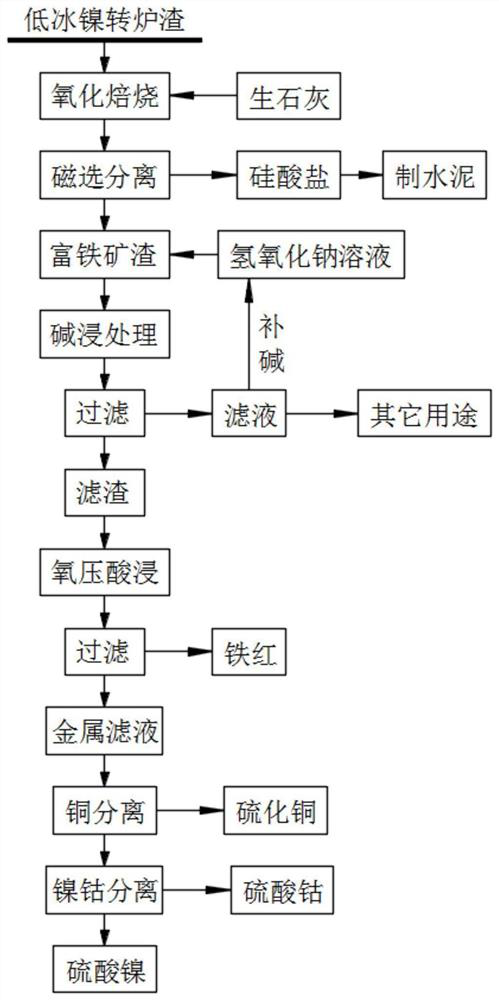
[0035] A method for extracting valuable metals from low nickel matte converter slag, the main components of low nickel matte converter slag: nickel 1.38%, cobalt 0.65%, copper 0.78%, iron 51.29%, silicon 27.88%, refer to figure 1 , extract and separate valuable metals through the following steps:
[0036] (1) Oxidation roasting: the converter slag produced by blowing high nickel matte with low nickel matte is mixed with quicklime and roasted in air, the mass ratio of quicklime and converter slag is controlled to be 0.3:1, the roasting temperature is 1350°C, and the roasting time is 0.5h;
[0037] (2) Magnetic separation: Grind the calcined material obtained in step (1) to a particle size of ≤100 μm, then use a magnetic field strength of 500GS for magnetic separation to obtain silicate and iron-rich slag, and the separated silicate can be used for making cement;
[0038] (3) Alkali leaching treatment: adding a concentration of 0.1mol / L sodium hydroxide solution to the iron-ric...
Embodiment 2
[0046] A method for extracting valuable metals from low nickel matte converter slag, the main components of low nickel matte converter slag: nickel 1.13%, cobalt 0.58%, copper 0.43%, iron 49.38%, silicon 25.82%, extracted and separated by the following steps Valuable metals:
[0047] (1) Oxidation roasting: the converter slag produced by blowing high nickel matte with low nickel matte is mixed with quicklime and then roasted in air, the mass ratio of quicklime and converter slag is controlled to be 0.2:1, the roasting temperature is 1100°C, and the roasting time is 1.0h;
[0048] (2) Magnetic separation: Grind the calcined material obtained in step (1) to a particle size of ≤100 μm, then use a magnetic field strength of 1000 GS for magnetic separation to obtain silicate and iron-rich slag, and the separated silicate can be used for making cement;
[0049] (3) Alkali leaching treatment: adding a concentration of 2.0mol / L sodium hydroxide solution to the iron-rich slag obtained...
Embodiment 3
[0057] A method for extracting valuable metals from low nickel matte converter slag. The main components of low nickel matte converter slag are: 0.93% nickel, 0.71% cobalt, 0.38% copper, 52.64% iron, and 22.13% silicon, which are extracted and separated by the following steps Valuable metals:
[0058] (1) Oxidation roasting: the converter slag produced by blowing high nickel matte with low nickel matte is mixed with quicklime and then roasted in air, the mass ratio of quicklime and converter slag is controlled to be 0.1:1, the roasting temperature is 800°C, and the roasting time is 2.0h;
[0059] (2) Magnetic separation: Grind the calcined material obtained in step (1) to a particle size of ≤100 μm, then use a magnetic field strength of 1500 GS for magnetic separation to obtain silicate and iron-rich slag, and the separated silicate can be used for making cement;
[0060] (3) Alkali leaching treatment: adding a concentration of 4.0mol / L sodium hydroxide solution to the iron-r...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com