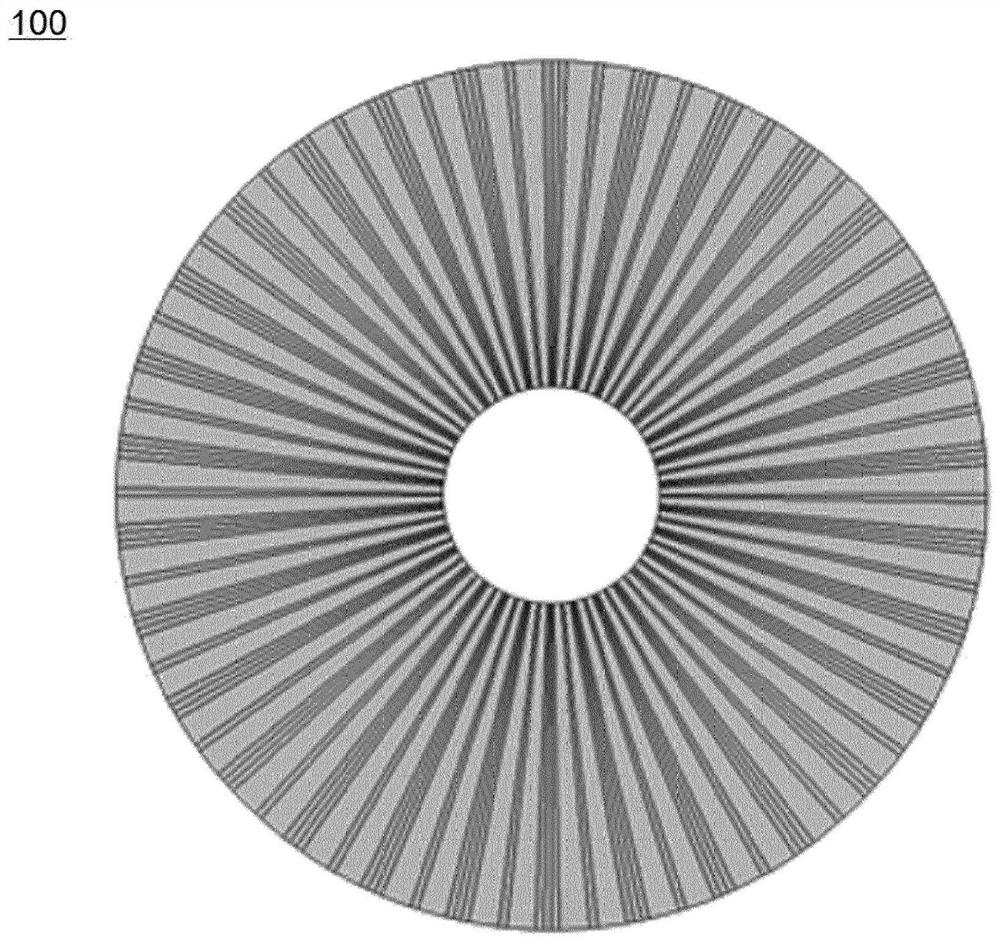
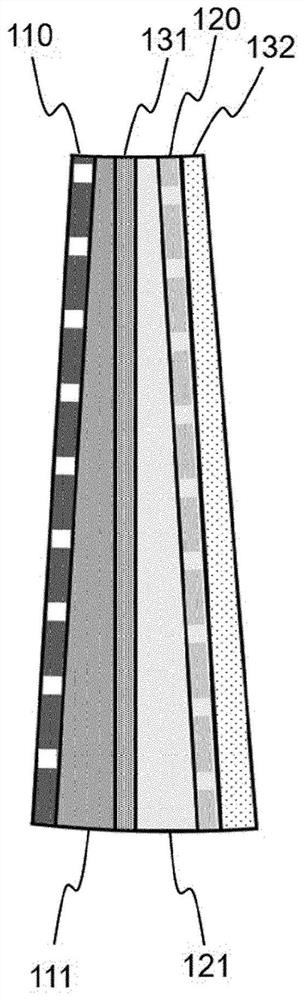
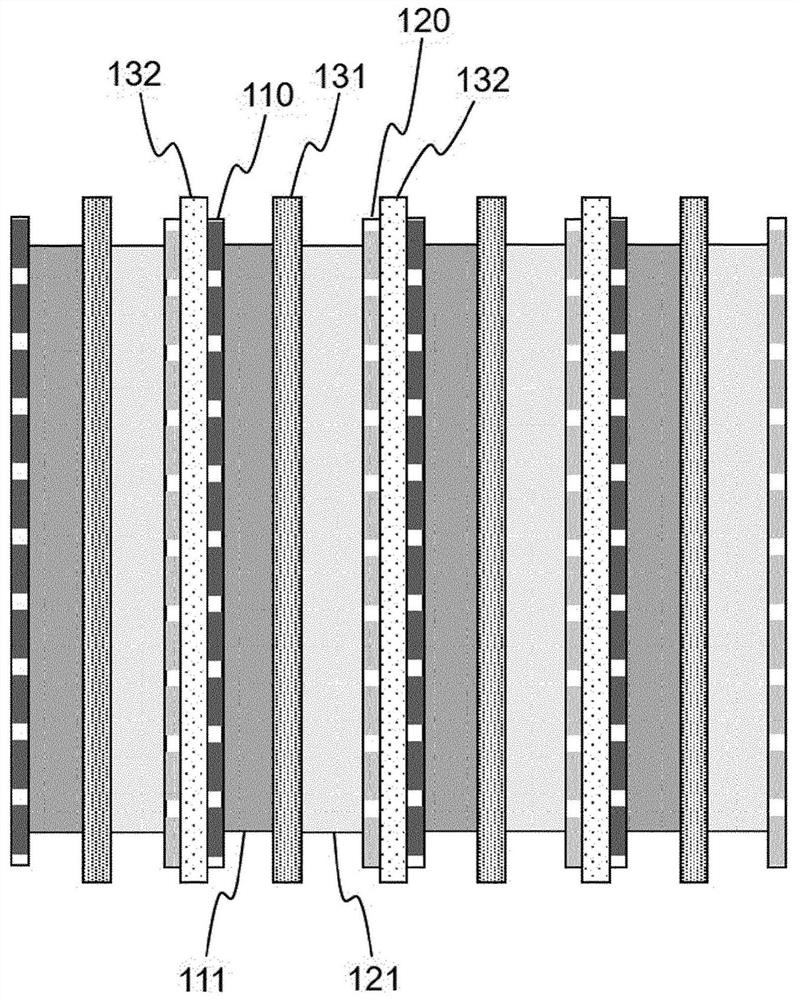
Secondary battery having structure in which unit cells which become thinner in one direction are radially assembled, and device comprising same
A secondary battery and cell technology, which is applied in secondary batteries, secondary battery manufacturing, battery electrodes, etc., can solve problems such as the reduction of ion conductivity, achieve the effect of improving battery performance and reducing concentration changes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0053] With 100 parts by weight of NCM (LiNi 0.8 co 0.1 mn 0.1 o 2 ), 1.5 parts by weight of carbon black (FX35, Denka) as a conductive material and 2.3 parts by weight of polyvinylidene fluoride (KF9700, Kureha) as a binder polymer were added to NMP (N-methyl-2- pyrrolidone), thereby preparing the positive electrode mixture layer slurry. The positive electrode mixture layer slurry is 640mg / 25cm 2 The loading amount of was coated on the aluminum current collector having through-holes in the thickness direction, and then vacuum-dried to obtain a positive electrode. In the aluminum current collector, the formation area ratio of through holes is about 40%, and about 50 holes are formed per unit area of 10 cm×10 cm. In addition, the positive electrode mixture layer was pressed to gradually decrease to a thickness of about 40% in one direction.
[0054] 100 parts by weight of artificial graphite (GT, Zichen (China)) as the negative electrode active material, 1.1 parts by we...
Embodiment 2
[0062] A secondary battery was fabricated in the same manner as in Example 1 except that current collectors having a grid structure were used for the aluminum and copper current collectors, respectively.
experiment example 1
[0067] Experimental example 1: Evaluation of the properties of the secondary battery
[0068] The physical properties of each of the secondary batteries prepared in Example 1 and Comparative Example 1 were evaluated. Specifically, each secondary battery was charged and discharged, and voltage and temperature changes during charging and discharging were measured, respectively. Charging and discharging of the secondary battery were performed at 20°C and 1C.
[0069] Figure 4 The evaluation results of the voltage change during charging and discharging of the secondary battery are shown in , Figure 5 The evaluation results of temperature changes during charge and discharge of the secondary battery are shown in .
[0070] First, see Figure 4 , it can be seen that the secondary battery of Example 1 has a high discharge voltage and a low charge voltage compared with Comparative Example 1. From this, it can be seen that the secondary battery of Example 1 provides higher power ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com