Construction method of dwarf syndrome animal model
A technology for constructing methods and animal models, which can be applied in the field of genetic engineering and can solve problems such as greatly limited applications
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] Embodiment 1, the construction of pig GHR gene knockout vector
[0037] (1-1) Exon 6 of the porcine GHR gene (NCBI GenBank Gene ID: 397488) was selected as the target of ABE-mediated exon skipping. The length of the exon is 173bp, and if skipping is successfully realized, it will lead to a frameshift mutation, which will result in the knockout of the pig GHR gene.
[0038] (1-2) Use pig GHR gene-specific upstream primer 5'-TCTGACTGTCAAAGCACCTTG-3' (SEQ ID NO.1) and pig GHR gene-specific downstream primer
[0039] 5'-GTTCACCAGCTGATCTCATG-3' (SEQ ID NO.2) was amplified by PCR on the pig genome template, and the wild-type amplified fragment was 410bp, and its sequence composition was determined by gene sequencing.
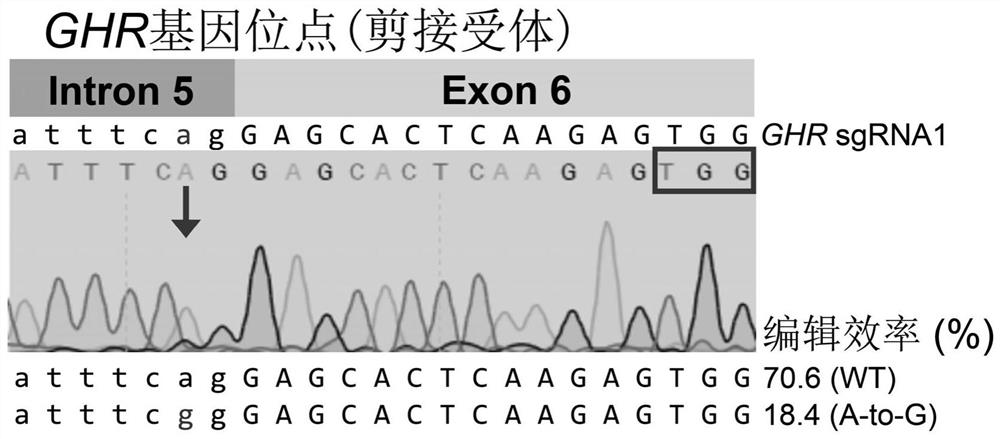
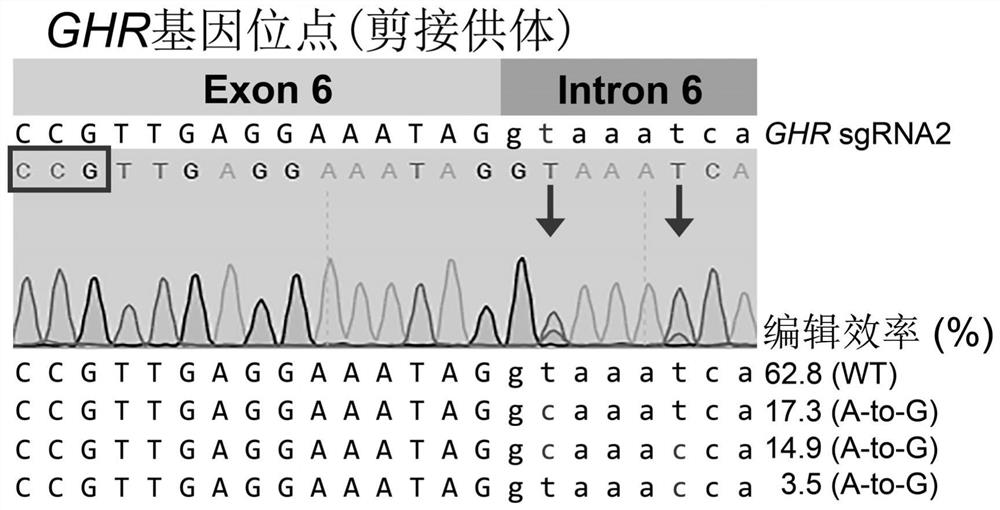
[0040] (1-3) Sequence analysis found that both the porcine GHR gene exon 6 splice acceptor and the porcine GHR gene exon 6 splice donor have an sgRNA target, which can be used for ABE-mediated conservative sequence mutations to achieve penetrance The sub-jump...
Embodiment 2
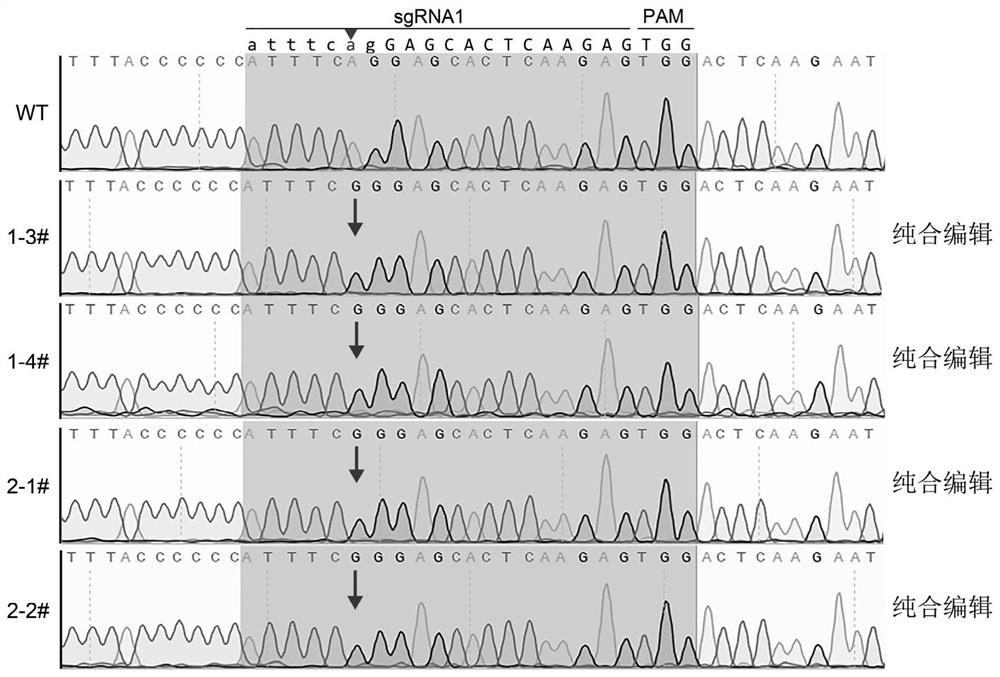
[0057] Example 2, Preparation of Gene Knockout Cells
[0058] (2-1) ABE plasmid PX-ABEmaxAW is linearized with BbsI restriction endonuclease (the nucleotide sequence after linearization is shown in SEQ ID NO.9), the gene fragment is split by agarose gel electrophoresis, and the gel is cut After recovery, mixed with the primer-dimer formed by high-temperature annealing of sgRNA1-F and sgRNA1-R, it was reacted overnight at 4°C with DNA ligase to obtain a ligation product.
[0059] (2-2) Culture low-passage Bamaxiang pig fibroblasts, and use Lipofectamine 3000 reagent for cell transfection.
[0060] (2-3) After 24 hours of transfection, the cells were subcultured at a density of 10,000 / 35 mm culture dish.
[0061] (2-4) After subculture of cells for 2 days, add 1 μg / mL puromycin and culture for 7-10 days until single-cell colonies grow, pick out single-cell colonies and culture them in 4-well dishes, and inoculate each single-cell colony in 1 well , spread to 35mm petri dish to...
Embodiment 3
[0068] Example 3, Construction of Gene Knockout Pig Model
[0069](3-1) To produce the GHR gene knockout pig model by somatic cell nuclear transfer technology, collect fresh pig ovaries from the slaughterhouse, wash them with 39°C normal saline several times, and draw out 3-6mm ovaries with a 10ml syringe with a 1.2mm diameter needle. The follicular fluid in the follicles with a diameter of 39°C was mixed with PBS preheated at 39°C, and then the cumulus cell-egg cell complex with compact multi-layered cumulus cells was selected under a stereo microscope, and then washed with oocyte maturation liquid at 38.5 Cultivate in an incubator at ℃, saturated humidity, and 5% CO2 for 38 to 40 hours, remove cumulus cells with 0.1% hyaluronidase, and select under a stereoscope with normal morphology, complete plasma membrane, uniform cytoplasm and discharge of the first polar body The MII stage oocytes used as nuclear transfer recipients were put back into the maturation medium and placed ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com