Method for removing cell components and/or nucleic acid substances of homogeneous or heterogeneous biological materials
A biomaterial and cell component technology, applied in medical science, prosthesis, etc., can solve the problems of three-dimensional structure damage of extracellular matrix, long processing time, influence of mechanical properties of acellular tissue, etc., and achieve low residual immunogenicity, The effect of short processing time and low damage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
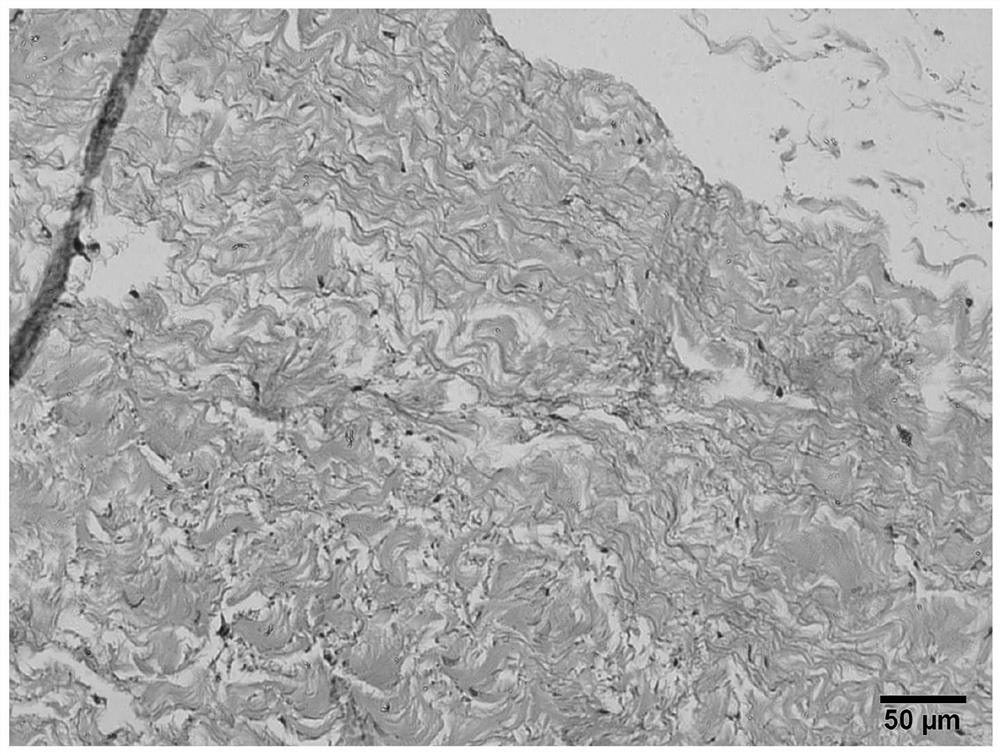
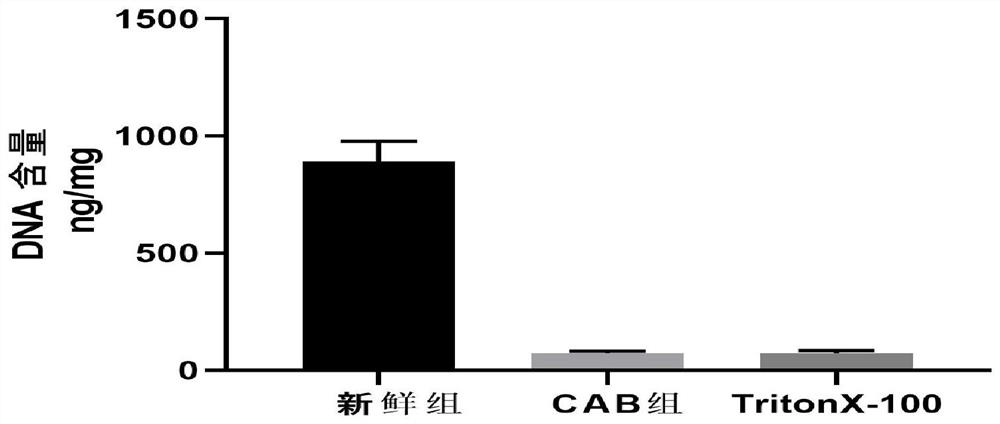
[0048] In the preparation method, the key point is the combination of detergent and enzyme. After the initial action of the detergent, the cell membrane ruptures, the cells are basically broken, and most of the cell components are also washed away, but there are still chromosomes of the nucleus, Small substances such as DNA, RNA, and broken phospholipids stay in the biological material, and further DNase-I and RNase-A actions are required to remove most of the nucleic acid substances; finally, the residuals are removed by repeated rinsing with sterile PBS solution Base fragments to achieve satisfactory immunogenicity removal effect.
[0049] In the described preparation method, the key point is soaking with bromogeramine. In the present invention, the soaking of bromogeramine can have better bactericidal effect and prevent bacterial pollution in the subsequent treatment and preservation process.
[0050] In the preparation method, the key points are the concentration and acti...
Embodiment 1
[0054] Embodiment 1 Early stage treatment
[0055] The bovine pericardium was provided by the local slaughterhouse, and the specimens were collected in the slaughterhouse. After the samples were taken out, they were stored in pre-cooled PBS solution and delivered to the laboratory within 4 hours. Wash with sterile PBS solution containing antibiotics (penicillin and streptomycin, the concentrations are 100U / ml, 100ug / ml respectively), immerse in 0.1% bromogeramine for 30min, wash pericardium with sterile PBS containing antibiotics for 10min×3 times, store at 4°C .
Embodiment 2
[0056] Embodiment 2 sample pruning
[0057] Use a magnifying glass to observe whether there are obvious knife wounds, cut off all areas that do not meet the requirements, carefully remove the fatty tissue on the material matrix with scissors and tweezers, and hold the tweezers parallel to the material to avoid damage to the material. This process should be as gentle as possible. To maximize the protection of tissue fibers from being damaged, so as not to affect its mechanical properties.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com