Disposal technology of waste chrome plating bath
A chrome plating tank and process technology, applied in the direction of chromium alum, chromium sulfate, etc., can solve the problems of low recovery rate, low product purity, inorganic acid, alkali and salt discharge, etc., and achieve the effect of high added value and high purity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0019] This embodiment specifically includes the following steps:
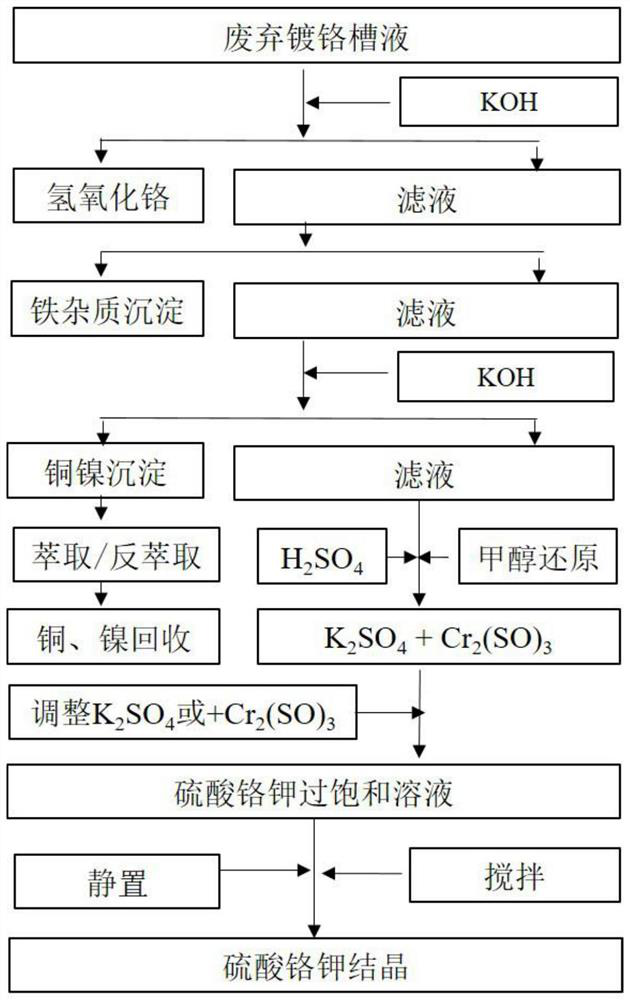
[0020] 1) Metal ion Cr 3+ Separation: slowly add KOH solution to the waste chrome plating bath, pH rises from 2.0 to final 4.0, stirring speed is 10 rev / min, KOH is added slowly and evenly; KOH addition amount and speed are based on the pH rising rate per hour (ΔpH / h) 0.30 is controlled, KOH is added for about 7h to form chromium hydroxide precipitate; filtrate A and chromium hydroxide precipitate are obtained by filtration; chromium hydroxide precipitate is reacted with 50% sulfuric acid in a stoichiometric ratio to obtain chromium sulfate solution B.
[0021] 2) Separation of iron impurities: in the filtrate A obtained in step 1), KOH solution was slowly and uniformly added to pH 4.50, and air was introduced, and the reaction was slowly stirred for 5 hours. The iron ions were converted into precipitation, and filtered to obtain chromic anhydride and Filtrate C of copper and nickel ions;
[0022] 3)Cu 2+ ,...
Embodiment 2
[0060] This embodiment specifically includes the following steps:
[0061] 1) Metal ion Cr 3+ Recycling: slowly add KOH solution to the discarded chrome plating bath, pH rises from 2.0 to final 4.0, stirring speed is 10 rev / min, KOH is added slowly and evenly; KOH addition amount and speed are based on the pH rising rate per hour (ΔpH / h) 0.25 was controlled, KOH was added for 8h to form chromium hydroxide precipitate; filtrate A and chromium hydroxide precipitate were obtained by filtration; chromium hydroxide precipitate was reacted with 50% sulfuric acid in a stoichiometric ratio to obtain chromium sulfate solution B.
[0062] 2) Removal of iron impurities: in the filtrate A obtained in step 1), KOH solution was slowly and uniformly added to pH 4.50, and air was introduced, and the reaction was slowly stirred for 5 hours. The iron ions were converted into precipitation, and filtered to obtain chromic anhydride and Filtrate C of copper and nickel ions;
[0063] 3)Cu 2+ , N...
Embodiment 3
[0071] This embodiment specifically includes the following steps:
[0072] 1) Metal ion Cr 3+ Recycling: slowly add KOH solution to the discarded chrome plating bath, pH rises from 2.0 to final 4.0, stirring speed is 10 rev / min, KOH is added slowly and evenly; KOH addition amount and speed are based on the pH rising rate per hour (ΔpH / h) 0.40 was controlled, KOH was added for 5h to form chromium hydroxide precipitate; filtrate A and chromium hydroxide precipitate were obtained by filtration; chromium hydroxide precipitate was reacted with 50% sulfuric acid in a stoichiometric ratio to obtain chromium sulfate solution B.
[0073] 2) Removal of iron impurities: in the filtrate A obtained in step 1), KOH solution was slowly and uniformly added to pH 4.50, and air was introduced, and the reaction was slowly stirred for 5 hours. The iron ions were converted into precipitation, and filtered to obtain chromic anhydride and Filtrate C of copper and nickel ions;
[0074] 3)Cu 2+ , N...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com