Application of extracellular vesicles in preparation of preparation for treating or preventing metabolic inflammatory syndrome diseases
A technology of vesicles and preparations, applied in the biological field, can solve problems such as time-consuming, high equipment requirements, and restrictions on the clinical transformation and application of exosome therapy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
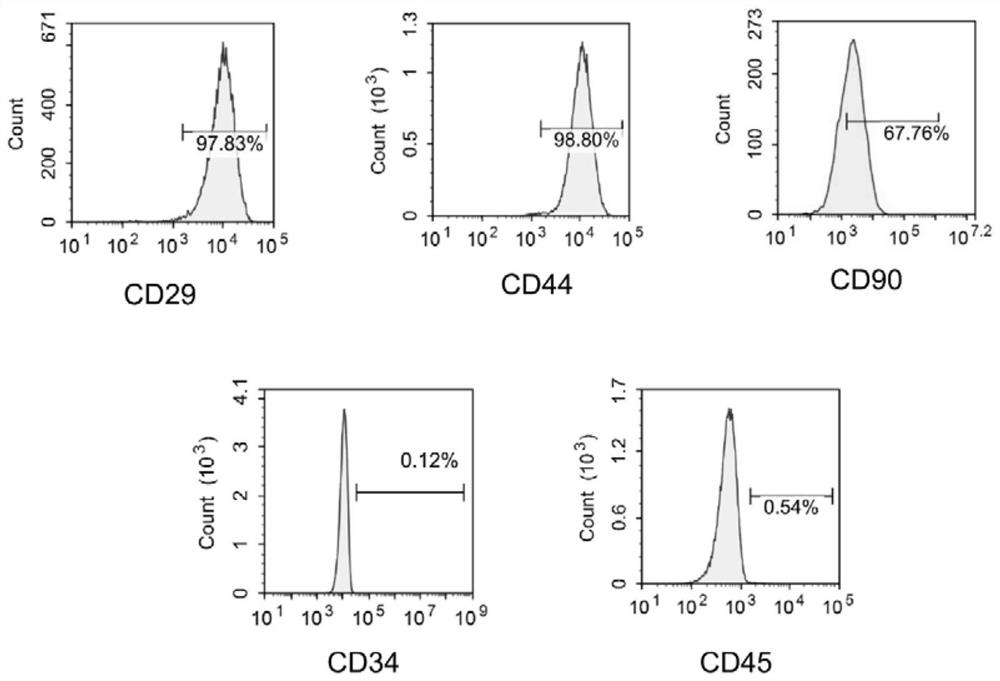
[0091] Example 1 Isolation and culture of BMMSCs
[0092] Excess CO was used according to the guidelines of the Animal Ethics Committee 2 Sacrifice the mice, remove the tibia and femur under aseptic conditions, peel off the muscles and connective tissue attached to them, further separate the metaphysis, expose the bone marrow cavity, and extract the volume fraction of 10% with a 10mL sterile syringe. The bone marrow cavity was washed repeatedly with PBS of fetal bovine serum, filtered through a cell strainer with a pore size of 70 μm, centrifuged at 500 g for 5 min, the supernatant was removed, and the cell pellet at the bottom was collected, resuspended in PBS, centrifuged at 500 g for 5 min again, and the final cell pellet was collected. Then, the cells were sorted by flow cytometry, and bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMMSCs) were sorted out by using CD34- and CD90+ as sorting criteria. Finally, the cells were resuspended in Dex(-) medium and inoculated in a 10cm diame...
Embodiment 2
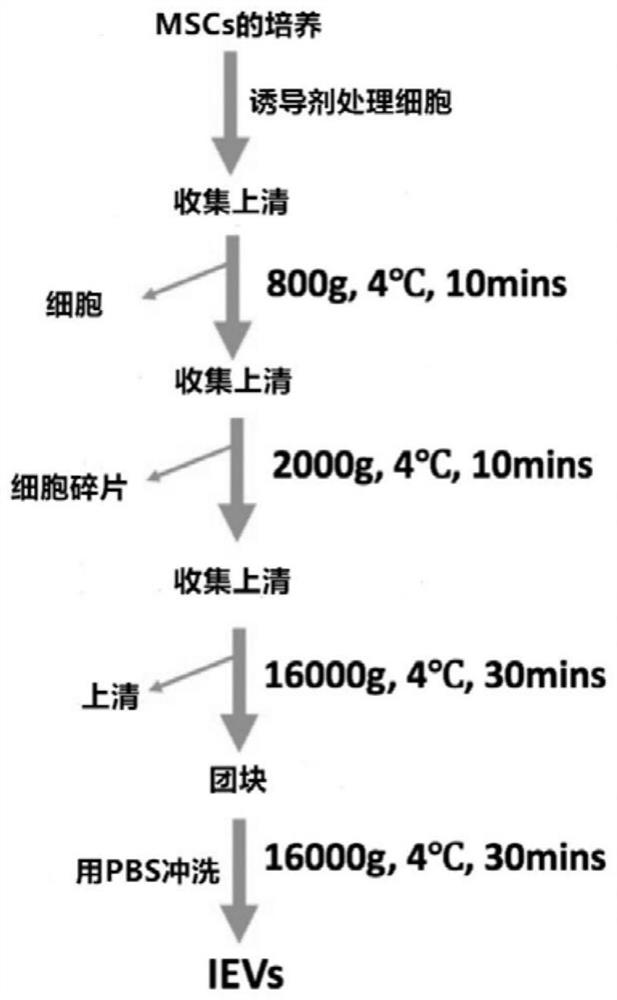
[0099] The acquisition of the IEVs of embodiment 2 BMMSC source
[0100] The MSCs (MSCs derived from bone marrow) cultured to the second generation in Example 1 were continued to be cultured with the medium (Dex(+) culture fluid) in Example 1 until the cells were confluent 80%-90%, washed with PBS for 2 Add serum-free medium containing 500nM STS (the medium is the medium in Example 1 with 500nM STS added), incubate at 37°C for 16-24h, collect the cell supernatant, and centrifuge at 800g for 10 hours at 4°C Minutes, the supernatant was collected and centrifuged at 2000g at 4°C for 10 minutes, and the supernatant was collected again and centrifuged at 16000g at 4°C for 30 minutes, and the obtained precipitate was IEVs. The pellet was resuspended in 500 μl of PBS, centrifuged again at 16,000 g for 30 minutes at 4°C, and the washed IEVs were obtained.
[0101] Preparation routes such as figure 2 shown.
Embodiment 3
[0105] The analysis of embodiment 3 IEVs
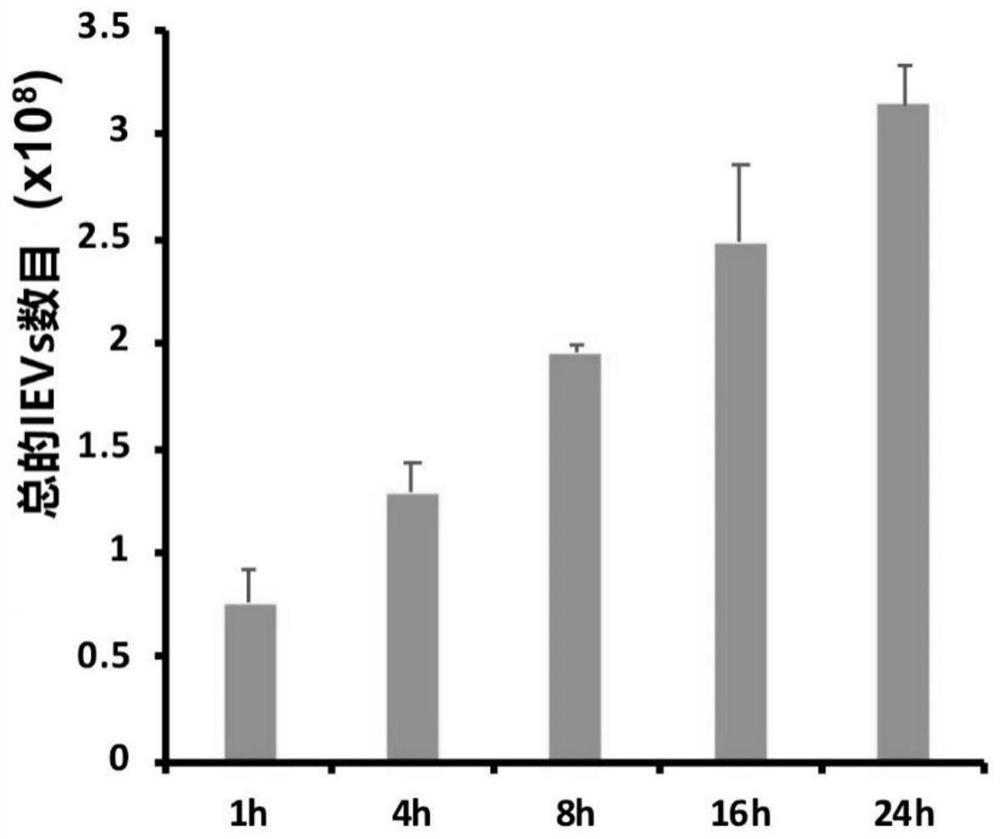
[0106] (1) Quantification of IEVs and analysis of membrane proteins
[0107] The IEVs obtained in Example 2 were quantitatively analyzed by flow cytometry, and the measurement time points were 1h, 4h, 8h, 16h and 24h, and the results showed that 106 MSCs were induced to 1h, 4h, 24h After 8h, 16h and 24h, 0.76×10 8 pcs, 1.29×10 8 pcs, 1.95×10 8 pcs, 2.48×10 8 pcs, 3.14×10 8 IEVs, it can be seen that after induction to 24h, a single MSC can produce 300 IEVs ( image 3 ).
[0108] The scattered light intensity of IEVs was analyzed by the standardized small particle microspheres (0.2 μm, 0.5 μm, 1 μm) produced by Bangs Laboratories, and the results showed that the particle diameters of IEVs were all below 0.2 μm ( Figure 4A ).
[0109] The results observed by transmission electron microscopy (TEM) are similar to those of flow cytometry, most of the vesicles have a diameter of 200nm or less ( Figure 4B ).
[0110] The results o...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com