Amphiphilic block polymer nanoparticles with different morphologies as well as preparation method and application of amphiphilic block polymer nanoparticles
An amphiphilic block and nanoparticle technology, applied in the field of polymers, can solve problems such as complex processes, and achieve the effects of simple process, short polymerization reaction time, and suitability for industrial production.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0036] The invention provides a method for preparing amphiphilic block polymer nanoparticles with different morphologies, comprising the following steps:
[0037] Stable segment monomers, nucleating segment monomers, Lewis acids, Lewis bases and aromatic solvents are mixed, and the resulting mixed reaction solution is polymerized to obtain amphiphilic block polymer nanoparticles with different morphologies.
[0038] In the present invention, unless otherwise specified, all raw material components are commercially available products well known to those skilled in the art.
[0039] In the present invention, the stable segment monomer is an acrylate monomer, preferably including dimethylaminoethyl acrylate (DMAEA), diethylaminoethyl acrylate (DEAEA), methyl acrylate (MA) ethyl acrylate (EA), butyl acrylate (BA), 2-methoxyethyl acrylate (MEA) or 2-ethylhexyl acrylate (2-EHA). In the present invention, the nucleating segment monomers include trifluoroethyl methacrylate (TFEMA), 2,...
Embodiment 1
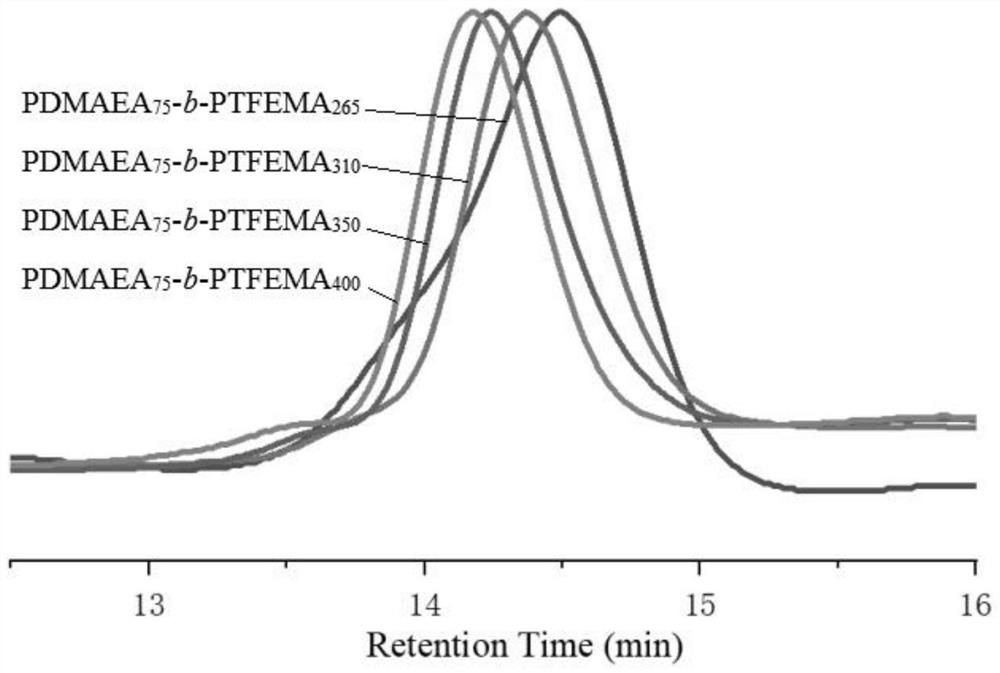
[0049] At room temperature, DMAEA and TFEMA were added to toluene at the same time, Lewis acid was added for pre-mixing for 2 minutes, and then Lewis base was added, and the resulting mixed reaction solution was polymerized for 18 minutes to obtain a solution of amphiphilic block polymer nanoparticles. After the morphology of the amphiphilic block polymer nanoparticles in the solution, add n-hexane to the solution of the amphiphilic block polymer nanoparticles to quench and filter, and use n-hexane to wash the resulting solid product 3 times and then drain it , to obtain amphiphilic block polymer nanoparticles (denoted as PDMAEA 75 -b-PTFEMA 265 , wherein, 75 and 265 represent the degree of polymerization), and then carry out subsequent characterization and testing.
[0050] Among them, the Lewis base is Lewis acid as BHTAl i Bu 2 The solid content of the mixed reaction solution is 15%; the molar ratio of Lewis base: Lewis acid: DMAEA: TFEMA = 1:2:75:265.
Embodiment 2~7
[0052] Prepare amphiphilic block polymer nanoparticles according to the method of Example 1, and the preparation conditions are as shown in Table 1:
[0053] Table 1 Preparation conditions of Examples 1-7
[0054]
[0055]
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| degree of polymerization | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| degree of polymerization | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com