Silicon carbide joint and metal penetration connection method thereof
A technology of metal infiltration and connection method, which is applied in the field of ceramic material connection, can solve the problems of lower connection strength, use of solder under low temperature conditions, and accelerate the decomposition of the MAX phase of the middle layer, so as to achieve lower requirements, lower preparation conditions, and high-strength connection gas. tightness effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
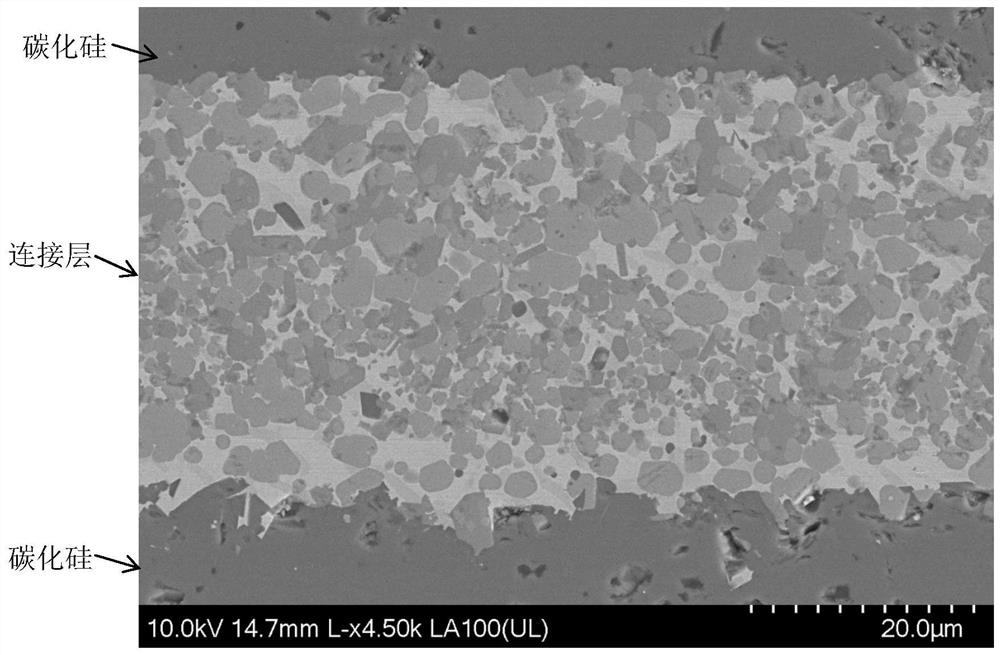
[0053]Metal Ti foil (thickness 10 μm, purity 99.99%) and Si powder (particle size 1 μm, purity 99.999%) were used as raw materials for connecting materials; after the metal Ti foil was polished with sandpaper, Si powder was applied on both sides of the metal Ti foil. On the other hand, the molar ratio of metal Ti foil and Si powder is 2:3; the above metal Ti foil and Si powder are placed between silicon carbide to form a sandwich structure. In the graphite crucible, the above sandwich structure is placed around the iron, cobalt and nickel blocks, and then the graphite crucible is placed in a sintering furnace for sintering connection. During sintering, the temperature was raised to 1500°C at 20°C / min, kept for 1h, the sintering atmosphere was vacuum, and silicon carbide joints were obtained after sintering.
[0054] The electron scanning electron microscope picture of the silicon carbide joint obtained above is as follows figure 1 shown. From figure 1 It can be seen that th...
Embodiment 2
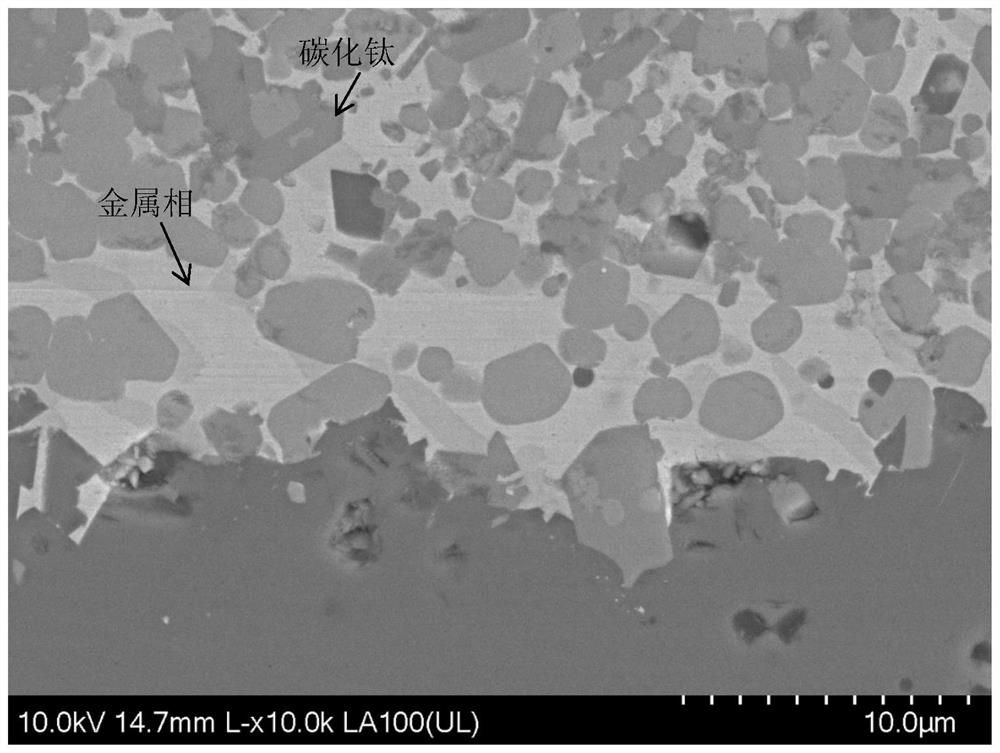
[0057] Metal Mo (thickness 20 μm, purity 99.99%) and Si powder (particle size 5 μm, purity 99.999%) are used as raw materials for connecting materials; the connection of silicon carbide is realized according to the method in Example 1, wherein during sintering, the sintering temperature is 1600 ℃, heat preservation for 2 hours, and the sintering atmosphere is argon, and a silicon carbide joint with a dense connection layer is obtained.
[0058] For the silicon carbide joint prepared above, the thickness of the connecting layer is 60 μm. In the shear strength test, the shear strength is 120MPa at room temperature and 150MPa at a high temperature of 1200°C. SiC joints have a leak rate of 1 x 10 -9 Pa·L / s.
Embodiment 3
[0060] Metal Ta (20 μm in thickness, 99.99% in purity) and Al powder (20 μm in particle size, 99.999% in purity) are used as raw materials for connecting materials; the connection of silicon carbide is realized according to the method in Example 1, wherein during sintering, the sintering temperature is 1700 ℃, heat preservation for 2 hours, and the sintering atmosphere is argon, and a silicon carbide joint with a dense connection layer is obtained.
[0061] For the silicon carbide joint prepared above, the thickness of the connecting layer is 50 μm. In the shear strength test, the shear strength is 150MPa at room temperature and 200MPa at a high temperature of 1200°C. SiC joints have a leak rate of 1 x 10 -8 Pa·L / s.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| shear strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| shear strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com