Method for extracting isotope labeled extracellular polymeric substance
An extracellular polymer and isotope labeling technology, which is applied in the field of high-efficiency isotope-labeled chlorella soluble extracellular polymer extraction, can solve problems such as difficulty in obtaining a preset concentration of extracellular polymer, and achieve efficient and rapid labeling, applicable Wide-ranging, fast-concentrating effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
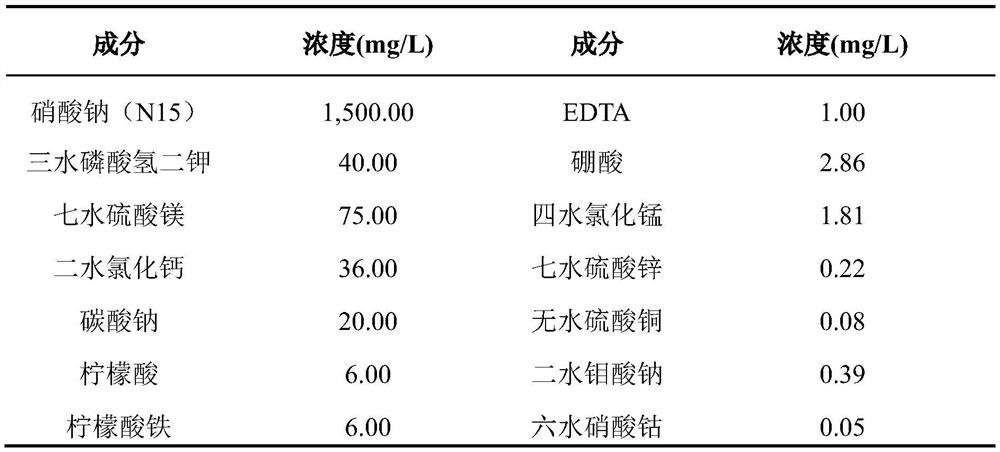
[0034] Chlorella culture: Chlorella algae species (FACHB-8) are added to the sterilized medium containing isotopes and cultivated in a light incubator with a culture temperature of 25°C and a light intensity of 30 μmolm -2 the s -1 , Illumination: the dark time ratio is 12h:12h, and the algae growth standard curve prepared by the ultraviolet spectrophotometer at 689nm absorbance value is used to calculate the growth amount of algae.
[0035]
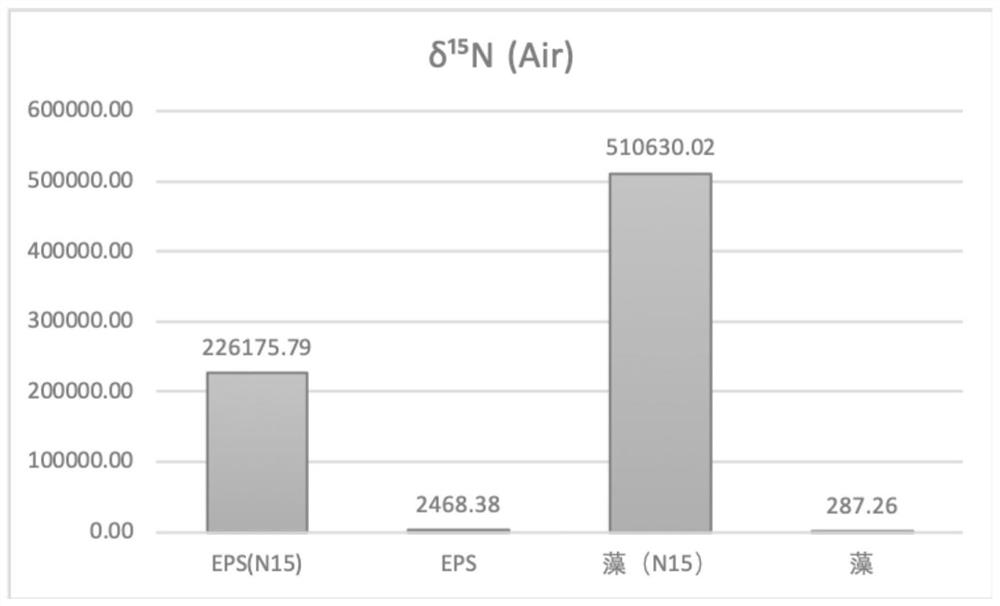
[0036] Extraction of isotope-labeled extracellular polymers by centrifugation: centrifuge the collected algae cells at 4°C and 4200rpm for 15 minutes, remove the supernatant and pass through a 0.45 micron filter membrane, and the filtrate is crude isotope-labeled extracellular polymers.
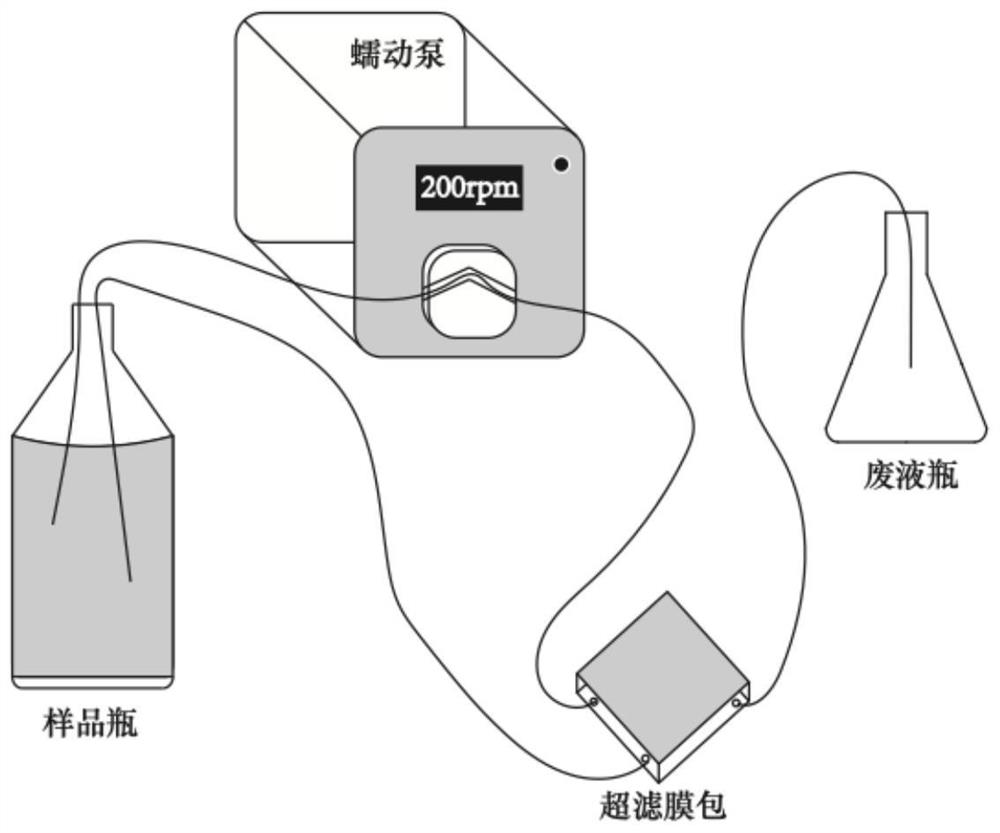
[0037] Purification and concentration of extracellular polymers: using tangential flow ultrafiltration devices such as figure 2 As shown, the crudely extracted extracellular polymer is quantitatively placed in a sample bottle, and it is concentrate...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com