Method for enhancing antibiotic antibacterial sensitivity by NO and application
An antibiotic and sensitivity technology, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve the problems of difficult pathogenic bacteria and complex drug resistance mechanism, and achieve the effects of enhancing sensitivity, avoiding the generation of drug resistance, and reducing the amount of use
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
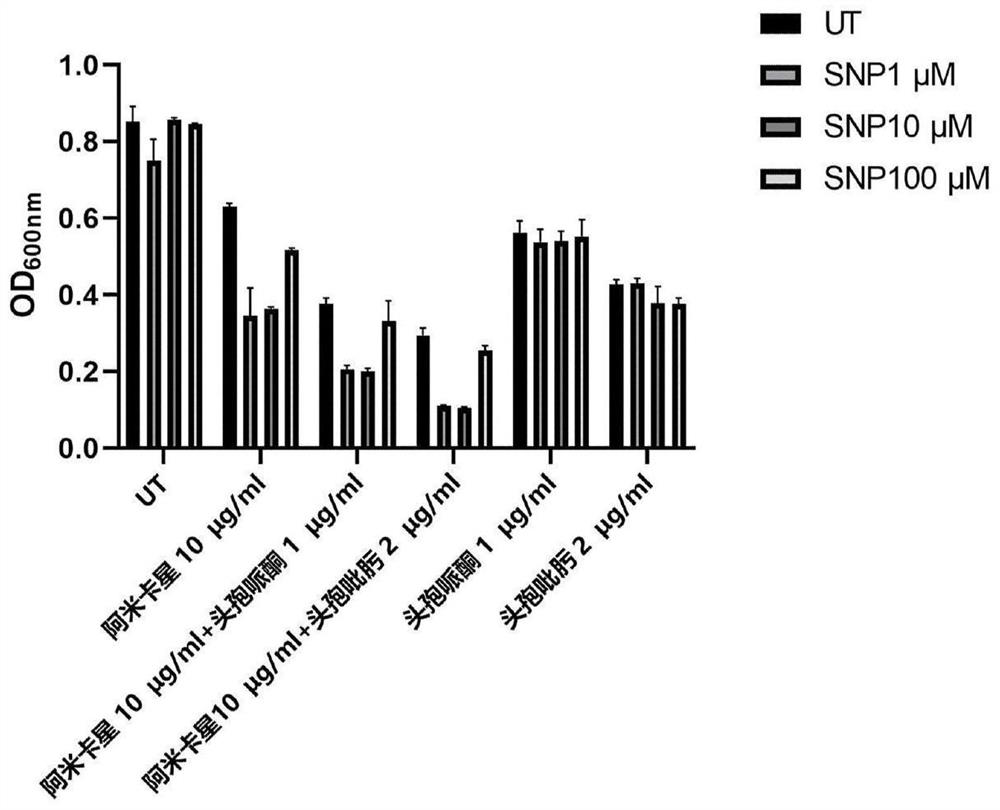
[0040] The effect test of exogenous NO donor SNP combined with aminoglycoside and β-lactam antibiotics on the growth characteristics of Pseudomonas aeruginosa adherent bacteria (Sessilebacteria, that is, bacteria adhered to the surface of the medium) is as follows:
[0041] (1) Antibiotic susceptibility test of PA bacteria of adhesion type
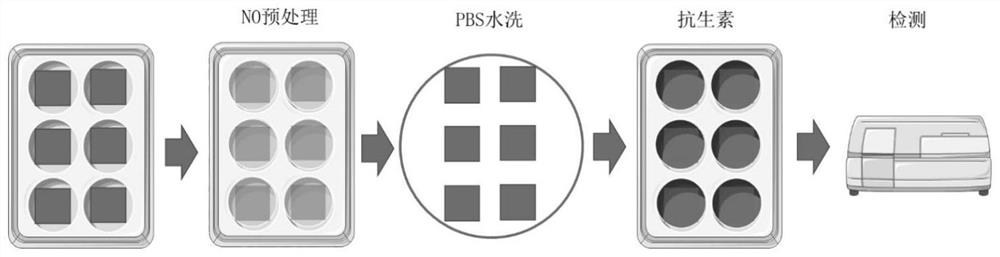
[0042] The preserved strain PAO1 was inoculated in M9 medium and cultured at 37°C until OD 600nm is 0.5. This is PAO1 liquid seed solution. Add slides to the 6-well plate, add M9 medium to the wells, and then add seed solution to each well at an inoculation amount of 0.5%. The bacterial solution in the wells was pretreated by adding NO donors with different concentrations of 1-100 μM SNP at 37°C for 24 hours, and the blank was set as the control well. The slides were taken out, and the slides were gently washed with PBS 3 times to remove planktonic bacteria. Put the cleaned slides back into a new 6-well plate and add M9 medium and antib...
Embodiment 2
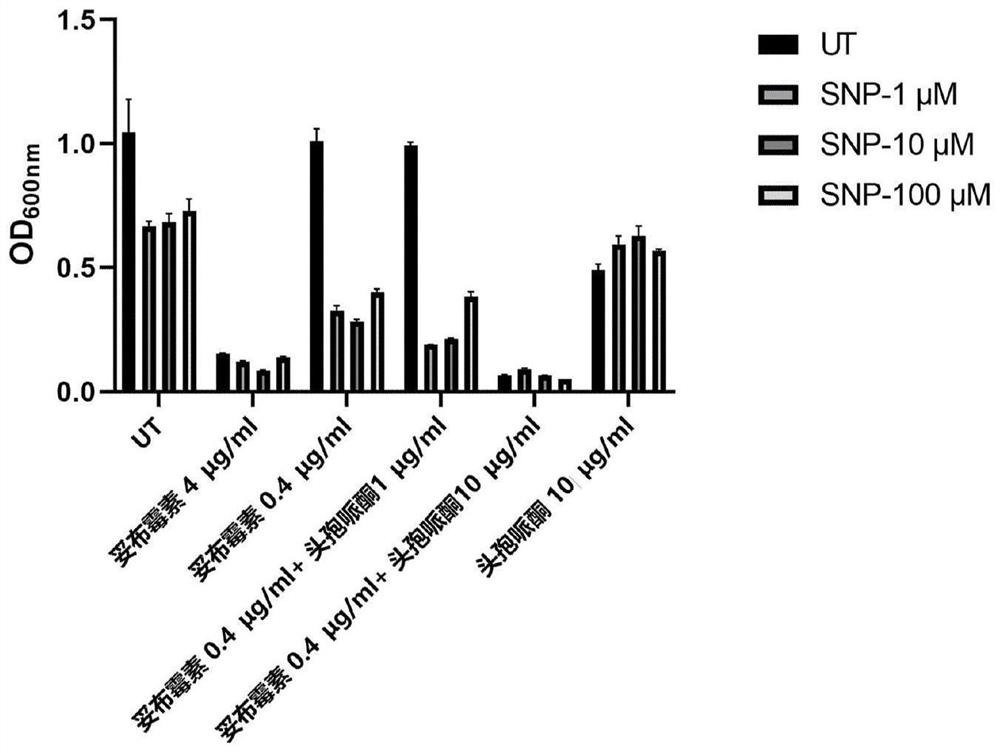
[0049] Exogenous NO donor SNP enhances the susceptibility test of planktonic and sessile bacteria to aminoglycosides and β-lactam antibiotics of Pseudomonas aeruginosa as follows:
[0050] (1) Test method
[0051] After cultured with SNP pretreatment on the round cell culture dish for 24 hours, a group without SNP pretreatment was cultured at the same time as a control. For the specific process, see the attached Figure 6 As indicated, antimicrobial susceptibility of planktonic and adherent cells (settle cells) was analyzed by two methods.
[0052] Antibiotic susceptibility analysis of planktonic bacteria: the supernatant on the circular cell culture dish was diluted 10 times into the M9 medium containing 5 μg / ml tobramycin, and then cultured at 37°C for 72 hours. Measure OD every 2h 600nm To assess the effect of NO on the susceptibility of bacterioplankton.
[0053] Antibiotic susceptibility analysis of sessile bacteria: Treat the adherent PA cells on the glass slide at th...
Embodiment 3
[0061] The effect of endogenous NO on alginate synthesis in Pseudomonas aeruginosa was tested as follows:
[0062] In this experiment, PAO1 is the PA model strain, Δnor is the nitric oxide reductase deletion strain, and Δnor+ is the nitric oxide reductase replenishment strain.
[0063] The function of NO reductase Nor is to convert intracellular NO into N 2 O, to avoid excessive accumulation of intracellular NO. Therefore, the Δnor mutant will continue to accumulate endogenous NO to produce some biological effects. In this experiment, the influence of endogenous NO on PA sensitivity was determined by culturing Δnor mutant strains and nitric oxide reductase replenishing strains, and comparing alginate levels in PAO1, Δnor and Δnor+ strains.
[0064] Determination of alginate levels in PAO1, Δnor and Δnor+ strains, see attached Figure 12 . attached by Figure 12 The data shows that, compared with the PAO1 strain, the alginate levels in the Δnor strain and the Δnor+ strain ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com