Method for redesigning enzyme based on isothermal compression coefficient disturbance, application and mutant screened by method
A technology of isothermal compression and redesign, applied in the field of computational chemistry, can solve the problem of lack of globality in high-fluctuation regions, and achieve the effect of reducing screening workload, saving time and computing resources, and improving stability and activity.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
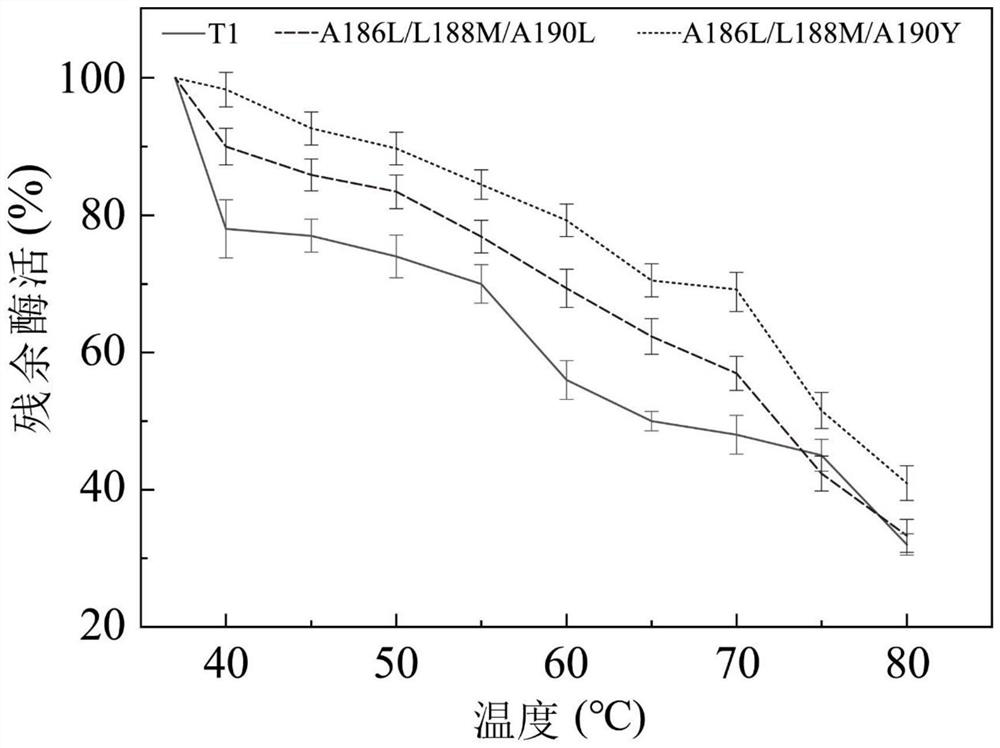
Embodiment 1T1
[0060] Example 1T1 lipase
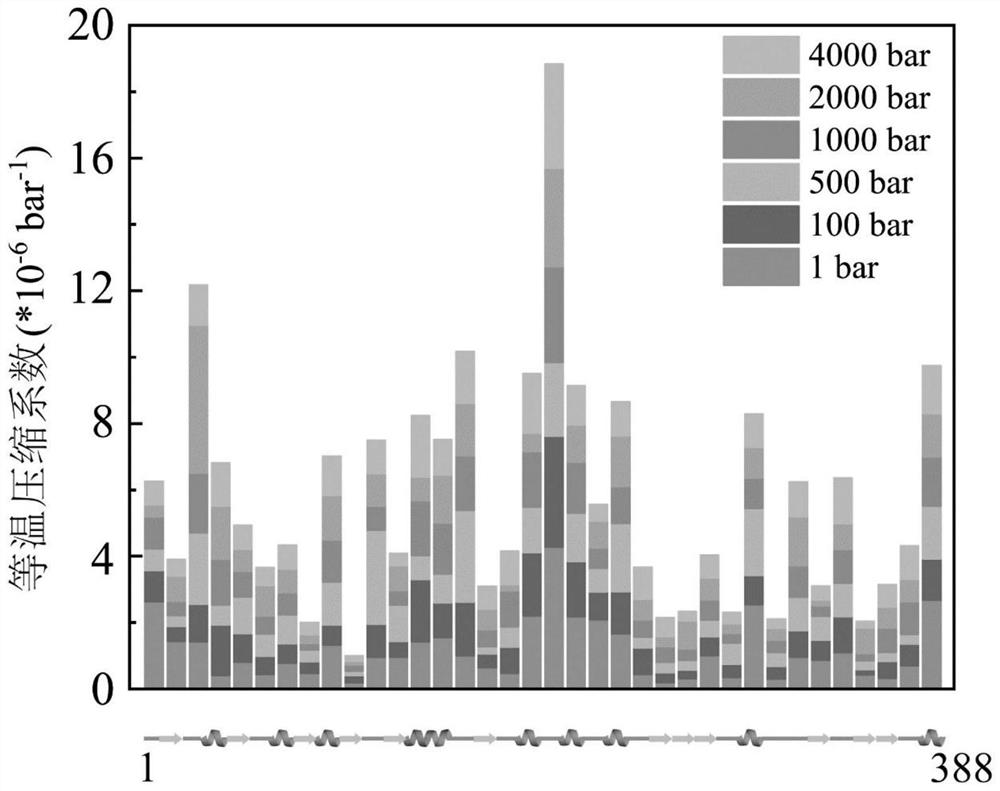
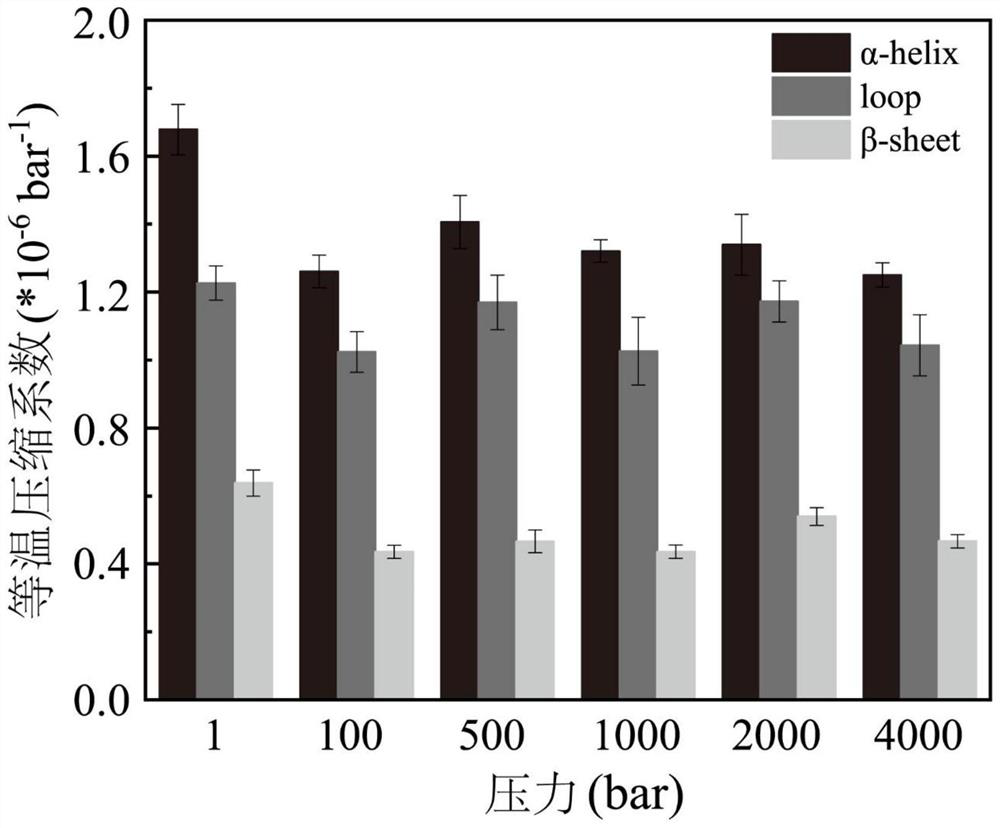
[0061] 1 Screening of high fluctuating area based on isothermal compression coefficient
[0062]The present example is the initial model with the primary model (PDB ID: 2DSN) of the wild-type T1 lipase (T1 lipase from GeoBacillus Zalihae Strain T1, using GromACS (2019.06 version). Molecular kinetic simulation. Applying the AMBER99 force field when simulated, putting the protein into a cube box filled with water, and the protein distance cassette is a shortest 1.0 nm, and the water model is TIP4P, then 5 sodium ions are added to charge balance. The system is used to minimize the system to ensure normal structure, the atomic distance is appropriate, the geometric configuration is reasonable, and then the NVT balance of 400 ps is performed under the cycle boundary conditions, and the Berendsen temperature is coupled to 313K, using Parrinell-Rahman pressure Coupling gradually increases from the atmosphere to the expected high pressure (100 bar, 500 bar, 100...
Embodiment 2
[0087] Example 2 Protein Glutamine Enzyme
[0088] 1 Screening of high fluctuating area based on isothermal compression coefficient
[0089] This example is the initial model with the crystal structure (PDB ID: 2ZK9) of wild-type protein glutamine (Pgase) (PDB ID: 2ZK9), using GromACS (2019.06 version). Molecular kinetic simulation. Applying the AMBER99 force field when simulated, putting the protein into a cube box filled with water, and the edge of the protein distance is 1.0 nm, the water model is TIP4P, and 3 chloride ions are added to charge balance. Using the 50000 step to minimize the system, under cycle boundary conditions, the NVT balance of 400 ps is performed, and the Berendsen temperature is coupled to 318K, and the Parrinell-Rahman pressure coupling gradually increases from the atmosphere to the expected high pressure (100 bar, 500 bar, 1000 bar, 2000Bar, 4000Bar). The balance removal limit of the system is applied to the finished product simulation. During the entire...
Embodiment 3
[0112] Example 3 xylanase
[0113] 1 Screening of high fluctuating area based on isothermal compression coefficient
[0114] The present example is the initial model of the crystal structure (PDB ID: 2DFC) of the wild-type xylase (PDB ID: 2DFC), the Monte Carlo sample algorithm based on the random generated variable, using the sampling mean of the function to approximate the estimation target The expectation of functions. Put the initial constructure into the system, the initial structure is randomly disturbed by RotAmertrialMover (), and the Monte Carlo sample algorithm uses a random number that meets uniform distribution within the interval [0, 1]. The algorithm obtains a series of predictive conformations, and the energy average of these conformations serves as an estimate of the average energy of the protein, and all simulations are repeated five times.
[0115] The secondary structure of the protein in this example is calculated by DSSP, and the structural analysis and visual...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com