Method for carrying out in-situ rapid detection pretreatment on pesticide residues in vegetables and fruits
A pesticide residue and in-situ technology, applied in the preparation of test samples, measuring devices, sampling, etc., can solve the problems of limited application of centrifuges, and achieve significant technological progress, less consumables, and fast processing speed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] The present invention is a method for in-situ rapid detection and pretreatment of pesticide residues in fruits and vegetables, comprising the following steps:
[0029] 1. Sample preparation
[0030] Chop the vegetable or fruit sample, put it directly into the tissue masher and mash it into a homogenous slurry. (You can also remove the root and chop it, or peel it and chop the skin.)
[0031] Furthermore, the sampling volume of vegetables and fruits shall be carried out in accordance with the provisions of GB / T8855. The sampling location of the sample shall be carried out in accordance with the provisions of GB2763. For small individual samples, all samples are processed after sampling; for large individual basically uniform samples, they can be divided or cut into small pieces on the axis of symmetry or symmetry plane and then processed; for elongated, flat or component content in each part For samples with differences, small pieces can be cut from different parts or...
Embodiment 2
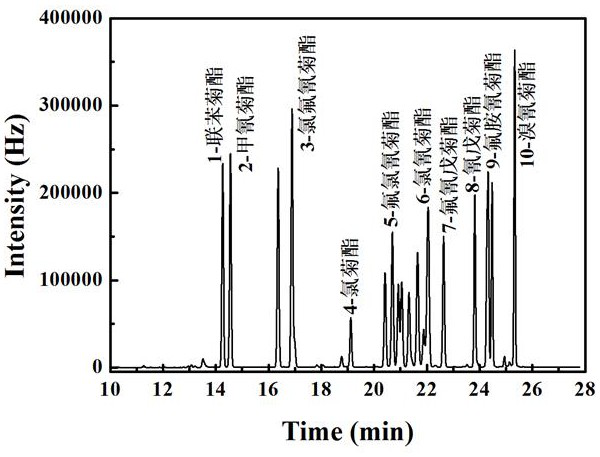
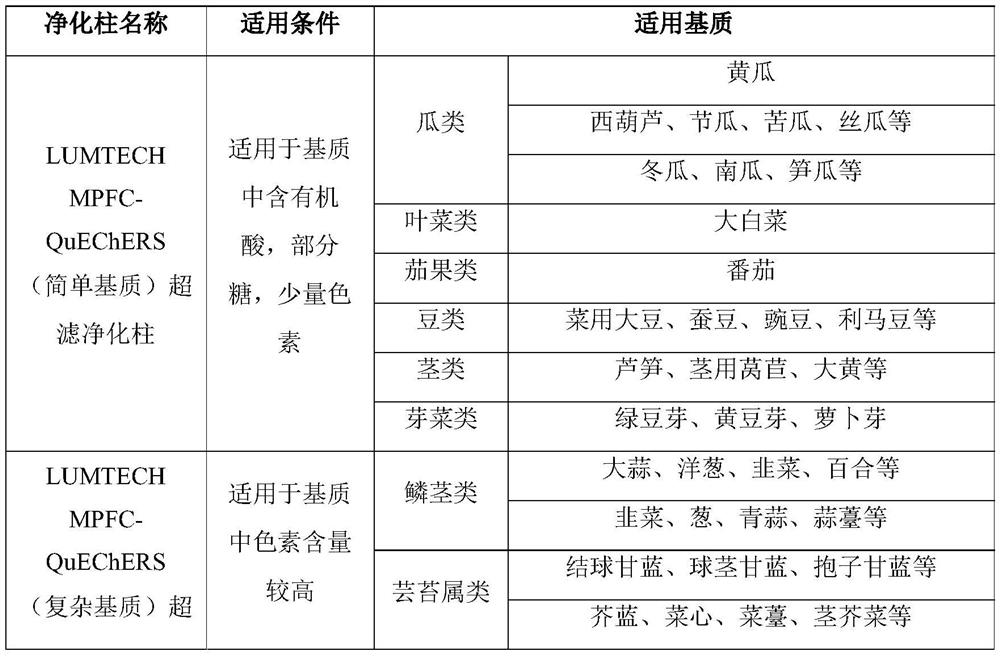
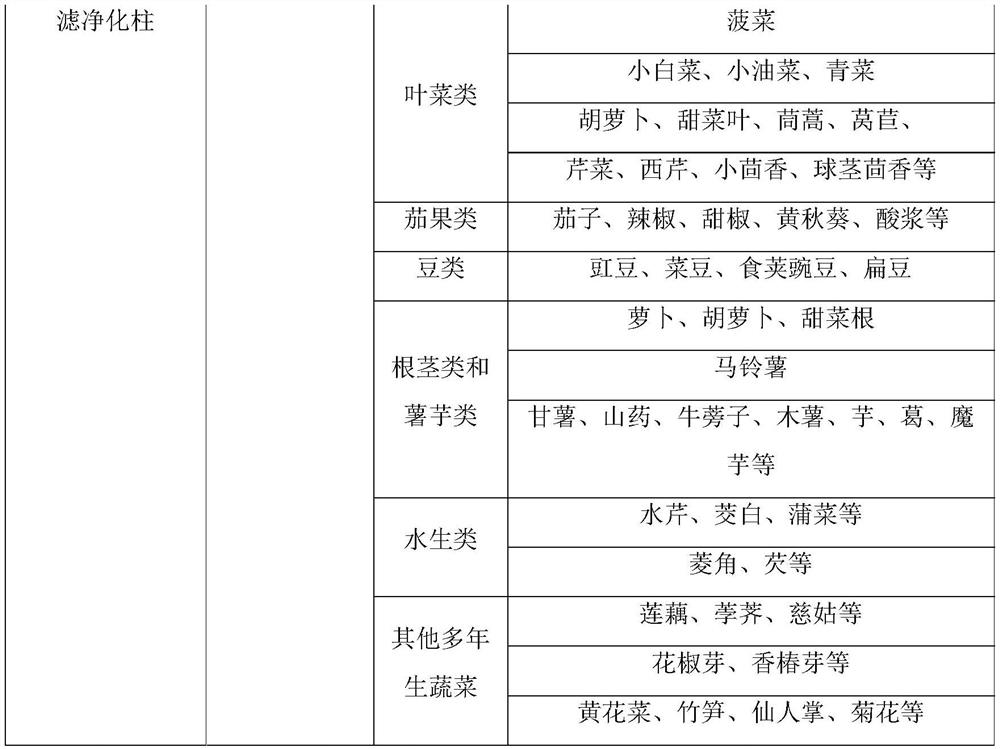
[0046] After the fresh cucumber samples were chopped, they were directly put into a tissue masher to be mashed into a homogenous slurry, and then put into polyethylene bottles. Weigh 10g of sample into a 50mL plastic centrifuge tube, add 20mL of acetonitrile, shake for 2min, filter with filter paper, collect the filtrate, add extraction salt bag and 1 ceramic homogenate to the filtrate, shake vigorously for 1min, and let stand at room temperature for 1 -3min, wait for the solution to separate into layers. Take 1.5mL of supernatant and pass through m-PFC purification column (simple) for one purification, then pass through 0.22μm microporous membrane for gas chromatography determination.
Embodiment 3
[0048] Fresh cucumber samples were peeled, chopped and placed directly into polyethylene bottles. Weigh 10g of cucumber peel into a 50mL plastic centrifuge tube, add 20mL of acetonitrile, shake for 2 minutes, add extraction salt bag and 1 ceramic homogenate, shake vigorously for 1 minute, and let stand at room temperature for 1-3 minutes until the solution is separated. Take 1.5mL of supernatant and pass through m-PFC purification column (simple) for one purification, then pass through 0.22μm microporous membrane for gas chromatography determination.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com